Improving AI Hallucinations
This article explores Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), a cutting-edge AI technique that boosts response accuracy by merging retrieval and generation capabilities. RAG enhances AI's ability to provide reliable, contextually relevant answers by first retrieving pertinent, current information from a knowledge base before generating a response. The discussion covers the RAG workflow in detail, including the use of vector databases for efficient data retrieval, the importance of distance metrics for similarity matching, and how RAG mitigates common AI pitfalls like hallucinations and confabulations. Practical steps for setting up and implementing RAG are also provided, making this a comprehensive guide for anyone aiming to improve AI-based knowledge retrieval.
Key Learning Objectives
- Grasp the fundamental principles and architecture of RAG systems.
- Understand how RAG reduces AI hallucinations by grounding responses in real-time data, thus improving factual accuracy and relevance.
- Explore the role of vector databases and distance metrics in RAG's data retrieval process.
- Identify strategies to minimize AI hallucinations and enhance factual consistency in RAG outputs.
- Gain practical knowledge on setting up and implementing RAG for superior knowledge retrieval.
*This article is part of the***Data Science Blogathon.
Table of Contents
- What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation?
- Deconstructing RAG Architecture
- RAG vs. Traditional AI
- Understanding Vector Databases
- Vector Databases: OLAP, OLTP Comparison
- Distance Metrics in RAG
- Addressing Hallucinations and Confabulations
- The RAG Workflow
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation?
RAG is an AI method that improves answer accuracy by retrieving relevant information before generating a response. Unlike traditional AI, which relies solely on training data, RAG searches a database or knowledge source for up-to-date or specific information. This information then informs the generation of a more accurate and reliable answer. The RAG approach combines retrieval and generation models to enhance the quality and accuracy of generated content, especially in NLP tasks.
Further Reading: Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks
Deconstructing RAG Architecture
The RAG workflow consists of two primary stages: retrieval and generation. The step-by-step process is outlined below.
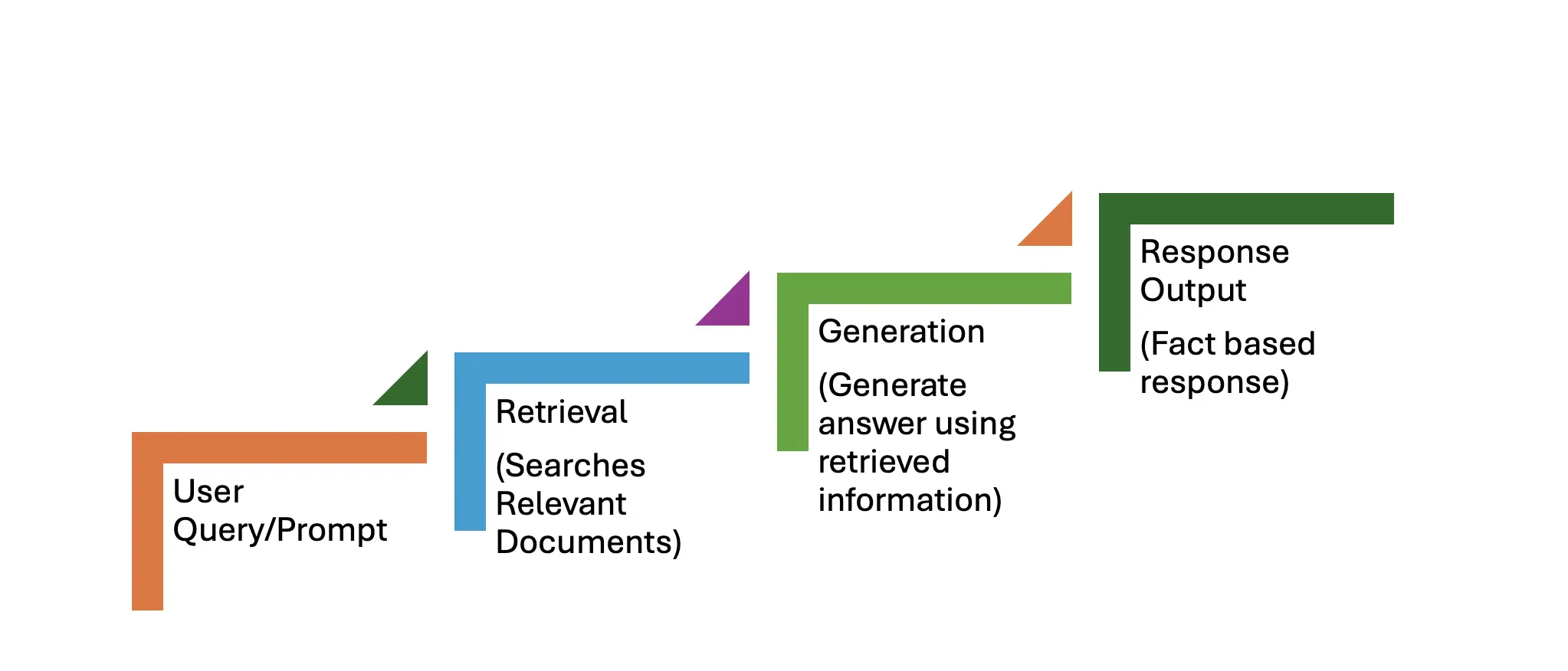
User Query/Prompt
A user query, such as: "What are the latest advancements in quantum computing?" serves as the prompt.
Retrieval Phase
This phase involves three steps:
- Input: The user's query/prompt.
- Search: The system searches a knowledge base, database, or document collection (often stored as vectors in a vector database) for relevant information.
- Retrieval: The system retrieves the top n (e.g., top 5 or 10) most relevant documents or information chunks.
Generation Phase
This phase also involves three steps:
- Integration: The retrieved documents are combined with the input query for added context.
- Answer Generation: A generative model (like GPT or a transformer-based model) generates a response using both the input query and the retrieved data.
- Output: The model produces a final, contextually relevant response, grounded in the retrieved information for improved accuracy.
Response Output
The system returns a factually accurate and up-to-date response, superior to what a purely generative model could produce.
RAG vs. Traditional AI
Comparing AI with and without RAG highlights the transformative power of RAG. Traditional models rely solely on pre-trained data, while RAG enhances responses with real-time information retrieval, bridging the gap between static and dynamic, contextually aware outputs.
| With RAG | Without RAG |
|---|---|
| Retrieves current information from external sources. | Relies solely on pre-trained (potentially outdated) knowledge. |
| Provides specific solutions (e.g., patch versions, configuration changes). | Generates vague, generalized responses lacking actionable details. |
| Minimizes hallucination risk by grounding responses in real documents. | Higher risk of hallucination or inaccuracies, especially for recent information. |
| Includes the latest vendor advisories or security patches. | May be unaware of recent advisories or updates. |
| Combines internal (organization-specific) and external (public database) information. | Cannot retrieve new or organization-specific information. |
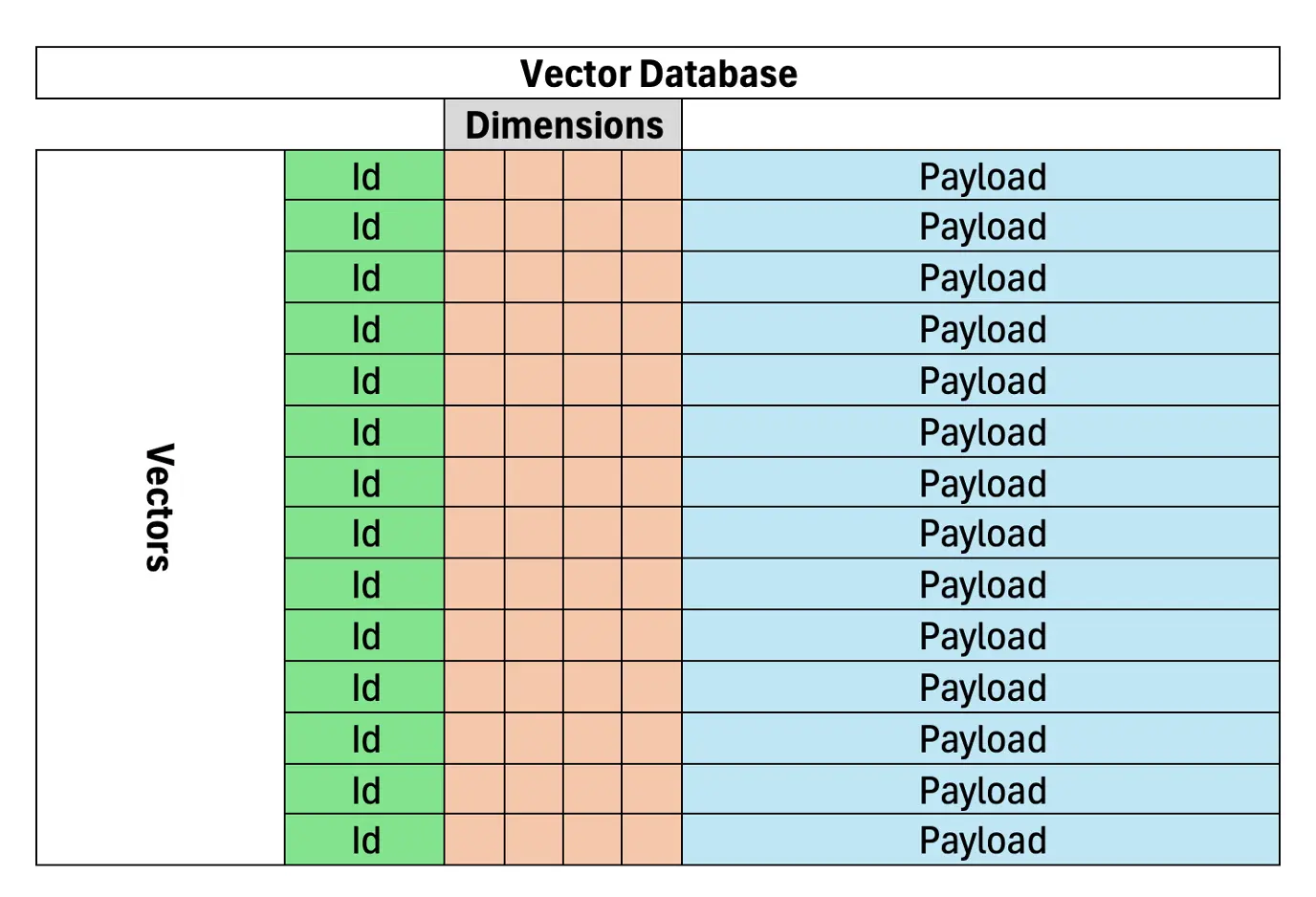
Understanding Vector Databases
Vector databases are crucial for efficient and accurate document or data retrieval in RAG, based on semantic similarity. Unlike keyword-based search, which relies on exact term matching, vector databases represent text as vectors in a high-dimensional space, clustering similar meanings together. This makes them highly suitable for RAG systems. A vector database stores vectorized documents, enabling more precise information retrieval for AI models.
(The remaining sections would follow a similar pattern of rephrasing and restructuring, maintaining the original information and image placement.)
The above is the detailed content of Improving AI Hallucinations. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
The article reviews top AI art generators, discussing their features, suitability for creative projects, and value. It highlights Midjourney as the best value for professionals and recommends DALL-E 2 for high-quality, customizable art.
 Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Meta's Llama 3.2: A Leap Forward in Multimodal and Mobile AI Meta recently unveiled Llama 3.2, a significant advancement in AI featuring powerful vision capabilities and lightweight text models optimized for mobile devices. Building on the success o
 Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
The article compares top AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude, focusing on their unique features, customization options, and performance in natural language processing and reliability.
 Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
The article discusses top AI writing assistants like Grammarly, Jasper, Copy.ai, Writesonic, and Rytr, focusing on their unique features for content creation. It argues that Jasper excels in SEO optimization, while AI tools help maintain tone consist
 AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
This week's AI landscape: A whirlwind of advancements, ethical considerations, and regulatory debates. Major players like OpenAI, Google, Meta, and Microsoft have unleashed a torrent of updates, from groundbreaking new models to crucial shifts in le
 Top 7 Agentic RAG System to Build AI Agents
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:25 PM
Top 7 Agentic RAG System to Build AI Agents
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:25 PM
2024 witnessed a shift from simply using LLMs for content generation to understanding their inner workings. This exploration led to the discovery of AI Agents – autonomous systems handling tasks and decisions with minimal human intervention. Buildin
 Selling AI Strategy To Employees: Shopify CEO's Manifesto
Apr 10, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Selling AI Strategy To Employees: Shopify CEO's Manifesto
Apr 10, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Shopify CEO Tobi Lütke's recent memo boldly declares AI proficiency a fundamental expectation for every employee, marking a significant cultural shift within the company. This isn't a fleeting trend; it's a new operational paradigm integrated into p
 Choosing the Best AI Voice Generator: Top Options Reviewed
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
Choosing the Best AI Voice Generator: Top Options Reviewed
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
The article reviews top AI voice generators like Google Cloud, Amazon Polly, Microsoft Azure, IBM Watson, and Descript, focusing on their features, voice quality, and suitability for different needs.






