Excel GROUPBY function to group rows and aggregate values
Unlock the Power of Excel's GROUPBY Function for Enhanced Data Analysis! This function simplifies data grouping, summarization, sorting, and filtering, all within a single formula. Say goodbye to complex outlines, subtotals, and pivot tables – GROUPBY streamlines your workflow.
Excel's data analysis capabilities just got a significant boost. While features like outlines and pivot tables have long been staples for organizing and interpreting data, the new GROUPBY function offers a more streamlined approach, all within the convenience of your formula bar.
- Understanding the Excel GROUPBY Function: Syntax and Basic Applications
- GROUPBY Function Availability and Compatibility
- Constructing a Basic GROUPBY Formula
- Mastering GROUPBY: Advanced Formula Examples
- Selecting the Right Aggregation Function
- Displaying Headers Effectively
- Grouping Rows Using Multiple Columns
- Grouping with Non-Adjacent Columns
- Controlling the Display of Totals and Subtotals
- Sorting Grouped Data
- Filtering Results
- Aggregating Multiple Columns (Adjacent and Non-Adjacent)
- Multiple Aggregations on a Single Dataset
- Handling Comma-Separated Text Strings
- Auto-Formatting GROUPBY Results with Conditional Formatting
- Troubleshooting GROUPBY Function Issues
The Excel GROUPBY Function
The GROUPBY function efficiently groups and aggregates data rows based on values in one or more columns. It also supports sorting and filtering of grouped data. As a dynamic array function, it returns multiple results, spilling into adjacent cells. The output resembles a pivot table without the formatting; the spill range dynamically recalculates with data changes. This is particularly beneficial for large datasets requiring summarized data through functions like SUM, AVERAGE, or COUNT.

Note: GROUPBY is similar to PIVOTBY, but GROUPBY exclusively groups data in rows.
Function Syntax
GROUPBY(row_fields, values, function, [field_headers], [total_depth], [sort_order], [filter_array])
Seven arguments are available, but only the first three are mandatory:
-
row_fields(required): The range of values to group by. -
values(required): The values to aggregate. -
function(required): The aggregation function (e.g.,SUM,AVERAGE,COUNT,MIN,MAX). -
field_headers(optional): Controls header display (0: No headers, 1: Yes, but don't show, 2: No headers, but generate, 3: Yes, and show). -
total_depth(optional): Controls total/subtotal display (0: No totals, 1: Grand total at bottom, 2: Grand and subtotals at bottom, -1: Grand total at top, -2: Grand and subtotals at top). -
sort_order(optional): Sorts by column index (positive for ascending, negative for descending). Arrays allow multi-column sorting. -
filter_array(optional): Filters rows using a Boolean array.
Usage Tips
- Dynamic Updates: The formula dynamically adjusts to dataset changes within its range. Adding new rows requires including them in the argument ranges or using an Excel table for automatic expansion.
-
Header Detection: If
field_headersis omitted, Excel infers headers based on thevaluesargument (text followed by a number suggests headers). -
Range Consistency:
row_fieldsandvaluesmust have equal lengths to avoid#VALUE!errors. - Conditional Formatting: Enhance readability by using conditional formatting to highlight totals and subtotals.
Note: GROUPBY is under development; thorough testing is recommended.
GROUPBY Function Availability
Currently available in Excel for Microsoft 365 (Insider Beta Channel).
Basic GROUPBY Formula
Let's assume a dataset with project names (Column A), types (Column B), and revenues (Column C). To summarize revenues by project type:
=GROUPBY(B2:B32, C2:C32, SUM)
This yields a list of unique project types with their revenue sums. Defaults are used for optional arguments (no headers, ascending sort, grand total at bottom).

Advanced GROUPBY Formula Examples
This section expands on the basic example, demonstrating the function's versatility.
Choosing the Aggregation Function
GROUPBY supports 16 aggregation functions, including standard functions (SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT, etc.) and specialized ones (PERCENTOF, ARRAYTOTEXT). These are eta-reduced lambdas, simplifying usage. Custom lambda functions are also supported. Multiple aggregations are possible using vectors (vertical for column stacking, horizontal for row stacking).
Displaying Headers
Use the field_headers argument (set to 3) to include headers in the output.
=GROUPBY(B2:B32, C2:C32, SUM, 3)

Grouping by Multiple Columns
Include a multi-column range in row_fields to group by multiple columns. For example, grouping by project type and status:
=GROUPBY(B2:C32, D2:D32, COUNT)

Grouping by Non-Adjacent Columns
Use CHOOSECOLS to select non-adjacent columns for grouping:
=GROUPBY(CHOOSECOLS(A2:D32, 2, 4), C2:C32, COUNT)

Controlling Totals and Subtotals
Use total_depth to control total/subtotal display. Setting it to 2 shows both grand and subtotals.
=GROUPBY(B2:C32, D2:D32, SUM, 3, 2)

Sorting Grouped Rows
Use sort_order for custom sorting (positive for ascending, negative for descending). Arrays enable multi-column sorting.
=GROUPBY(B2:B32, C2:C32, SUM, , , 2) (Sorts by values)

=GROUPBY(B2:C32, D2:D32, SUM, , , {-1,2}) (Multi-column sort)

Filtering Results
Use filter_array (Boolean array) to filter rows.
=GROUPBY(B2:B32, C2:C32, SUM, , , , B2:B32<>"Design")

Aggregating Multiple Columns
Aggregate adjacent columns directly:
=GROUPBY(B2:B32, D2:E32, AVERAGE, 3)

For non-adjacent columns, use CHOOSECOLS:
=GROUPBY(B2:B32, CHOOSECOLS(C2:E32, 1, 3), AVERAGE, 3)

Multiple Aggregations on the Same Data
Use HSTACK or VSTACK for multiple aggregations:
=GROUPBY(B3:B32, C3:C32, HSTACK(SUM, AVERAGE, PERCENTOF))
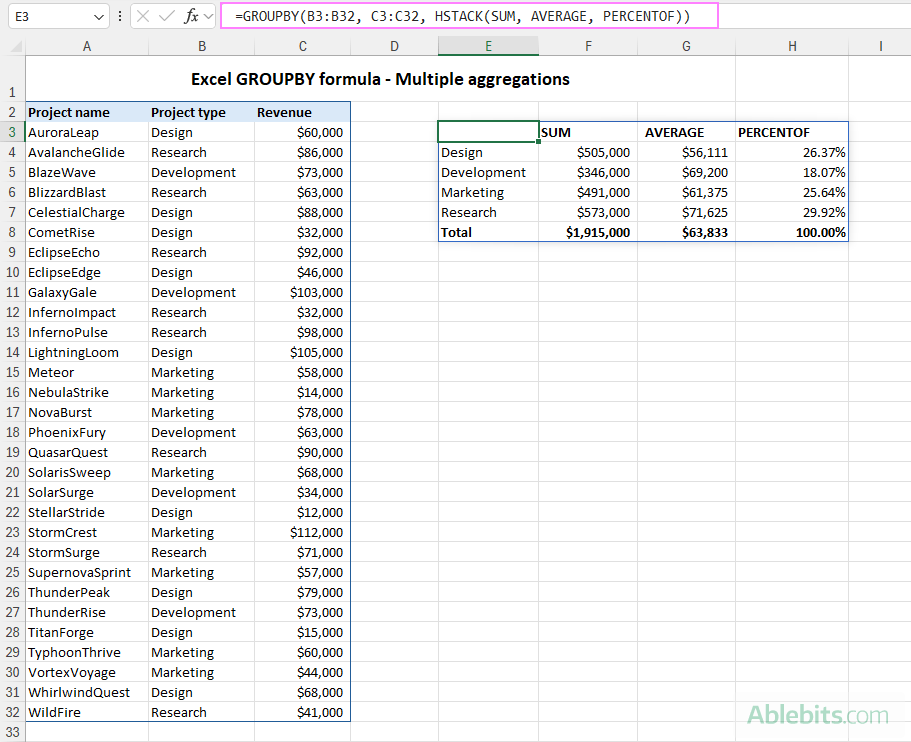
=GROUPBY(B3:B32, C3:C32, VSTACK(SUM, AVERAGE, MIN, MAX),, 0)

Grouping Comma-Separated Text Values
Use ARRAYTOTEXT to group comma-separated text:
=GROUPBY(B3:B23, A3:A23, ARRAYTOTEXT, 0, 0)

Conditional Formatting of GROUPBY Results
Enhance visual clarity using conditional formatting to highlight headers, totals, and subtotals.
Troubleshooting GROUPBY Function Issues
- Function Unavailability: Ensure you have a Microsoft 365 subscription and the latest updates.
-
#VALUE!Error: Check for equal lengths inrow_fieldsandvaluesarguments, and ensure correctfilter_arraylength. Also, verify thattotal_depthis appropriate for the number of columns inrow_fields. -
#SPILL!Error: Clear adjacent cells to allow spill range.
In conclusion, the GROUPBY function significantly enhances Excel's data analysis capabilities, providing a powerful and efficient tool for various data manipulation tasks. With practice, you'll unlock its full potential for insightful data analysis.
The above is the detailed content of Excel GROUPBY function to group rows and aggregate values. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1392
1392
 52
52
 36
36
 110
110
 How to create timeline in Excel to filter pivot tables and charts
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:20 AM
How to create timeline in Excel to filter pivot tables and charts
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:20 AM
This article will guide you through the process of creating a timeline for Excel pivot tables and charts and demonstrate how you can use it to interact with your data in a dynamic and engaging way. You've got your data organized in a pivo
 Excel formula to find top 3, 5, 10 values in column or row
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:09 AM
Excel formula to find top 3, 5, 10 values in column or row
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:09 AM
This tutorial demonstrates how to efficiently locate the top N values within a dataset and retrieve associated data using Excel formulas. Whether you need the highest, lowest, or those meeting specific criteria, this guide provides solutions. Findi
 All you need to know to sort any data in Google Sheets
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:47 AM
All you need to know to sort any data in Google Sheets
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:47 AM
Mastering Google Sheets Sorting: A Comprehensive Guide Sorting data in Google Sheets needn't be complex. This guide covers various techniques, from sorting entire sheets to specific ranges, by color, date, and multiple columns. Whether you're a novi
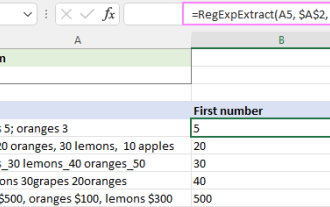 Regex to extract strings in Excel (one or all matches)
Mar 28, 2025 pm 12:19 PM
Regex to extract strings in Excel (one or all matches)
Mar 28, 2025 pm 12:19 PM
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to use regular expressions in Excel to find and extract substrings matching a given pattern. Microsoft Excel provides a number of functions to extract text from cells. Those functions can cope with most
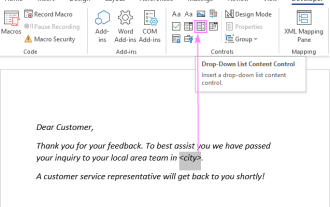 Add a dropdown list to Outlook email template
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:13 AM
Add a dropdown list to Outlook email template
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:13 AM
This tutorial shows you how to add dropdown lists to your Outlook email templates, including multiple selections and database population. While Outlook doesn't directly support dropdowns, this guide provides creative workarounds. Email templates sav
 How to customize Google Docs: guide on styles & formatting
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:24 AM
How to customize Google Docs: guide on styles & formatting
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:24 AM
In this blog post, we delve into the various techniques and features available to customize your Google Docs. Follow these tips and tricks to be well on your way to creating documents that convey your content effectively and look polished
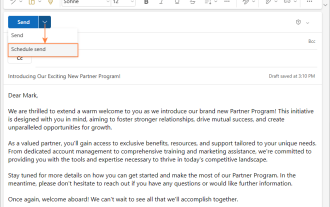 How to schedule send in Outlook
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:57 AM
How to schedule send in Outlook
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:57 AM
Wouldn't it be convenient if you could compose an email now and have it sent at a later, more opportune time? With Outlook's scheduling feature, you can do just that! Imagine that you are working late at night, inspired by a brilliant ide
 How to use Flash Fill in Excel with examples
Apr 05, 2025 am 09:15 AM
How to use Flash Fill in Excel with examples
Apr 05, 2025 am 09:15 AM
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to Excel's Flash Fill feature, a powerful tool for automating data entry tasks. It covers various aspects, from its definition and location to advanced usage and troubleshooting. Understanding Excel's Fla




