Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Linus Torvalds has released Linux Kernel 6.14 Release Candidate 6 (RC6), reporting no significant issues and keeping the release on track. The most notable change in this update addresses an AMD microcode signing issue, while the rest of the updates consist of minor fixes across multiple subsystems.
Table of Contents
Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Highlights
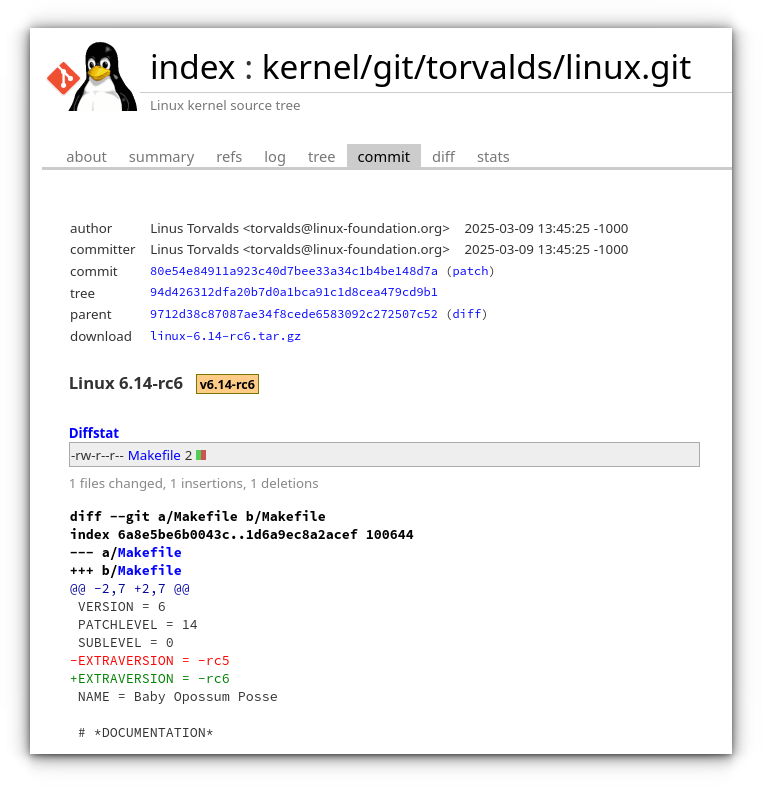
AMD Microcode Fixes
A major focus of this release candidate is the resolution of an AMD microcode signing problem. Several updates in the x86/microcode subsystem ensure that only SHA256-checksummed patches are loaded, adding an extra layer of security and validation.
Architecture-Specific Changes
x86 Updates
- Improvements in handling CPUID leaf 0x2 output validation.
- Fixes in microcode loading, including the removal of unused functions and better patch level detection.
- Refinements in speculation mitigation mechanisms.
Arm64 and LoongArch
- KVM updates for Arm64, ensuring proper initialization of SCTLR_EL1.
- Multiple LoongArch kernel virtualization fixes, including improvements in guest CSR register handling and AVEC interrupt checking.
- LoongArch-specific bug fixes in memory management and NUMA configuration.
Subsystem Fixes and Enhancements
Graphics and Display
- Various fixes for AMD GPU drivers, including KFD queue NULL pointer dereference prevention.
- Improvements in Intel and Imagination Technologies DRM drivers, particularly in timestamp accuracy and fence handling.
- Nouveau driver update to enable firmware caching for better performance.
Networking
- Fixes in Wi-Fi drivers, including mac80211 and iwlwifi, addressing issues related to TX queue cleanup, debugfs directory removal, and sparse warnings.
- Enhancements in DSA (Distributed Switch Architecture) drivers for MediaTek and Realtek chipsets.
- Patch to correct ownership handling in UDP segmentation offload (GSO).
Storage and Filesystems
- Bug fixes in XFS, including buffer readahead decoupling and buffer accounting improvements.
- Adjustments in Btrfs to resolve chunk map leaks and zoned storage issues.
- NVMe-TCP driver fixes for sporadic response drops and potential memory corruption.
- Enhancements in exFAT to prevent soft lockups and improve file write handling.
USB and Peripheral Support
- Fixes in USB Type-C UCSI drivers to prevent NULL pointer dereferences.
- Resolution of interrupt handling issues in Renesas USB host controllers.
- HID driver updates for various peripherals, including Apple, Nintendo, and Intel devices.
Virtualization and Kernel Security
- Several KVM fixes for x86 and Arm64, focusing on debug control registers, event injection, and virtual machine run state handling.
- SEV-Guest improvements, optimizing request data allocation.
- Fixes in userfaultfd to avoid blocking on large folios with raised reference counts.
Filesystem and Memory Management
- Fixes in memory-hotplug and swap mechanisms, ensuring stable migration and recovery.
- Adjustments in userfaultfd behavior to prevent unexpected page table entry unmapping.
- Refinements in pipe buffer logic to fix race conditions and improve performance.
Try Kernel 6.14-rc6
Developers and testers are encouraged to review the shortlog for more details and report any regressions to ensure a smooth release process.
If you want to test this release, you can download the Kernel 6.14-rc6 from the Kernel.org website or the Linus Torvalds's git tree.
Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 is a minor release. The majority of updates include security patches, performance improvements, and bug fixes across different subsystems.
With no major roadblocks, the release schedule remains on track. The next few weeks will focus on stabilizing the kernel further before the final release.
The above is the detailed content of Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1422
1422
 52
52
 1316
1316
 25
25
 1266
1266
 29
29
 1239
1239
 24
24
 What is the most use of Linux?
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:02 AM
What is the most use of Linux?
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Linux is widely used in servers, embedded systems and desktop environments. 1) In the server field, Linux has become an ideal choice for hosting websites, databases and applications due to its stability and security. 2) In embedded systems, Linux is popular for its high customization and efficiency. 3) In the desktop environment, Linux provides a variety of desktop environments to meet the needs of different users.
 How to learn Linux basics?
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:32 AM
How to learn Linux basics?
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:32 AM
The methods for basic Linux learning from scratch include: 1. Understand the file system and command line interface, 2. Master basic commands such as ls, cd, mkdir, 3. Learn file operations, such as creating and editing files, 4. Explore advanced usage such as pipelines and grep commands, 5. Master debugging skills and performance optimization, 6. Continuously improve skills through practice and exploration.
 Does the internet run on Linux?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Does the internet run on Linux?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:03 AM
The Internet does not rely on a single operating system, but Linux plays an important role in it. Linux is widely used in servers and network devices and is popular for its stability, security and scalability.
 What are Linux operations?
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
What are Linux operations?
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
The core of the Linux operating system is its command line interface, which can perform various operations through the command line. 1. File and directory operations use ls, cd, mkdir, rm and other commands to manage files and directories. 2. User and permission management ensures system security and resource allocation through useradd, passwd, chmod and other commands. 3. Process management uses ps, kill and other commands to monitor and control system processes. 4. Network operations include ping, ifconfig, ssh and other commands to configure and manage network connections. 5. System monitoring and maintenance use commands such as top, df, du to understand the system's operating status and resource usage.
 What is the salary of Linux administrator?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:24 AM
What is the salary of Linux administrator?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:24 AM
The average annual salary of Linux administrators is $75,000 to $95,000 in the United States and €40,000 to €60,000 in Europe. To increase salary, you can: 1. Continuously learn new technologies, such as cloud computing and container technology; 2. Accumulate project experience and establish Portfolio; 3. Establish a professional network and expand your network.
 What are the main tasks of a Linux system administrator?
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:23 AM
What are the main tasks of a Linux system administrator?
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:23 AM
The main tasks of Linux system administrators include system monitoring and performance tuning, user management, software package management, security management and backup, troubleshooting and resolution, performance optimization and best practices. 1. Use top, htop and other tools to monitor system performance and tune it. 2. Manage user accounts and permissions through useradd commands and other commands. 3. Use apt and yum to manage software packages to ensure system updates and security. 4. Configure a firewall, monitor logs, and perform data backup to ensure system security. 5. Troubleshoot and resolve through log analysis and tool use. 6. Optimize kernel parameters and application configuration, and follow best practices to improve system performance and stability.
 Boost Productivity with Custom Command Shortcuts Using Linux Aliases
Apr 12, 2025 am 11:43 AM
Boost Productivity with Custom Command Shortcuts Using Linux Aliases
Apr 12, 2025 am 11:43 AM
Introduction Linux is a powerful operating system favored by developers, system administrators, and power users due to its flexibility and efficiency. However, frequently using long and complex commands can be tedious and er
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.




