Why your Mac won't connect to Wi-Fi and how to fix it
A practical guide to solving Mac Wi-Fi connectivity problems
Wi-Fi is so convenient that we usually only notice it when it is interrupted. However, your day can quickly get bad when your Mac can't connect to Wi-Fi. Follow these simple steps to quickly resolve Wi-Fi connectivity issues and get back online immediately.

Use NetSpot to analyze and troubleshoot networks and find other utilities in the Setapp library.
Free trial security test
What are the reasons why Macs cannot connect to Wi-Fi?
If the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar turns grayed out or shows an exclamation mark, it means your network is disconnected. However, sometimes the icon appears bright blue, and it looks like the MacBook is connected to Wi-Fi, but the network is not available.
Three main reasons why Wi-Fi doesn't work:
- Mac software issues. From macOS to settings to conflicting applications, software can be the root cause of Mac Wi-Fi not working.
- Router problem. If your router has not been updated for a long time, it may be the problem.
- Internet Service Provider (ISP) Problem. Your ISP may experience an outage or other temporary network problems. Also, make sure you have paid your internet bill!
If you have problems with your internet, it is likely that one of these three reasons (or more) is not working properly. For example, you might see your Wi-Fi icon appearing bright blue, but it cannot connect because you need to authenticate inside the network (just like at an airport).
How to force my Mac to connect to Wi-Fi
Let me give you a quick overview of the solution first. If you need a more detailed description of each solution, scroll down.
| How to solve Wi-Fi problems? | illustrate |
|---|---|
| Check your Wi-Fi signal | Use the WiFi Signal application to get detailed information, or use the Activity Monitor to get a general overview. |
| Restart your Mac | Apple icon > Restart. |
| Restart your Wi-Fi router | Press the button on the router, wait for 10 seconds, and press the button again. |
| Forgot and reconnect to the network | Go to System Settings > Network > Wi-Fi. Click "Details" > "Forgot this network" next to your network. Then reconnect. |
| Renew DHCP lease | Go to System Settings > Network > Wi-Fi. Click "Details" > "TCP/IP" > "Renew DHCP Lease" next to your network. |
| Update macOS | Go to System Settings > General > Software Updates. |
| Update Wi-Fi drivers | Use tools like CleanMyMac X to make sure all drivers on your Mac are up to date. |
If you follow the steps below, in 99% of the cases, you should be able to resolve network issues in a few minutes. Most of the problems are simple failures or software update errors.
1. Check your Wi-Fi signal
When your Wi-Fi is not working properly, it is best to check the Wi-Fi signal strength. The best way is to use the WiFi Signal app for your Mac.
WiFi Signal is a lightweight utility that runs in the menu bar and monitors your network for real-time updates. You can click on the WiFi Signal icon at any time, which will display the current Wi-Fi speed, frequency band, signal quality, noise level, and more. The app allows you to set up notifications and tag networks, which is very useful for troubleshooting.
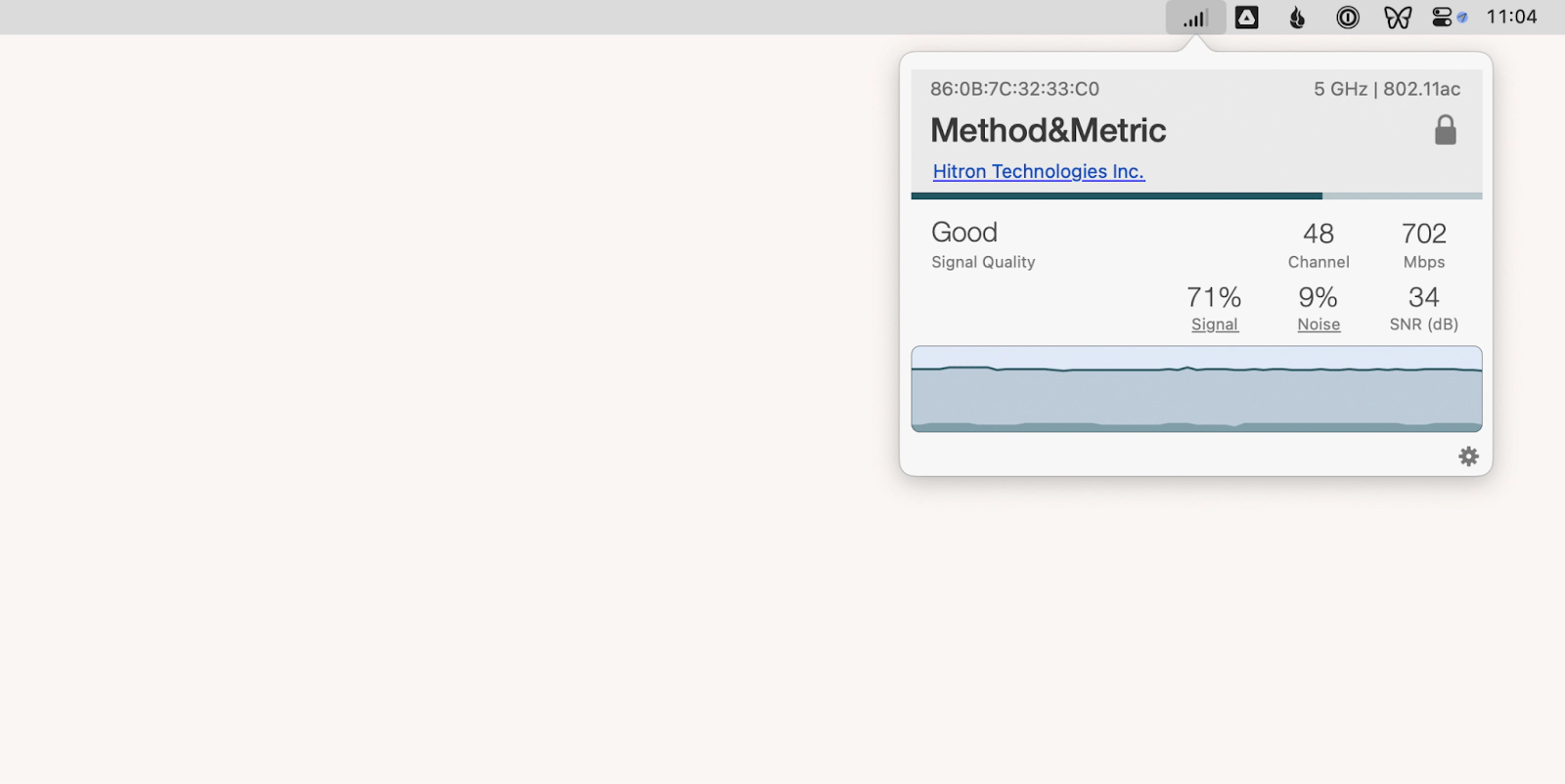
Or, there is no good way to measure your precise Wi-Fi signal using the default Mac utility. The best thing you can do without installing extra apps is to check out the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar to see the signal strength based on the full number of bars. In addition, try starting Activity Monitor from the Utilities folder and navigating to the Network tab. If you see packets being transferred in and out in real time, your connection is working.

Finally, you can start the Wi-Fi diagnostic test from your Mac's wireless diagnostic tool (found in the Utilities folder). If you eventually need to contact a technician to fix your Wi-Fi, this tool can generate technical reports that may be useful.

2. Restart Wi-Fi router and Mac
If you have identified a network problem, the first step to fixing it is always to restart your device.
To restart your Mac:
- Click the Apple icon in the menu bar.
- Click "Restart".
- Click "Restart" again.

If your Mac still cannot connect to Wi-Fi after restarting, you need to restart the router. Find the router in your space and press the Restart button twice (usually located on the back). Wait for a few minutes.
3. Forgot Wi-Fi and reconnect your Mac to the network
Another common failure is the way your Mac connects to the network at the software level. In these cases, forgetting the network and reconnecting from scratch may help.
To forget about Wi-Fi network:
- Open System Settings.
- Select Network > Wi-Fi.
- Click "Details" next to your network.
- Click "Forgot this network".
- Click "Remove".

Once done, reconnect to your Wi-Fi network via the menu bar (you have to enter your router/network password again).
4. Check Wi-Fi network configuration
The physical configuration of your Wi-Fi network has a big impact on performance. The further you are from the router, or the more walls in the middle, the weaker your Wi-Fi signal will be. This is why Wi-Fi router extensions are often used.
In fact, it's hard to know how many Wi-Fi extensions you need without looking at some kind of map. But there is NetSpot.
NetSpot is one of the best applications to analyze, manage, and fix network connectivity issues. In addition to detailed statistics for all Wi-Fi networks around you, NetSpot allows you to upload or draw a map of your space and test signals throughout the space so that you can identify weak links and expand Wi-Fi coverage accordingly.

Another quick tip is to make sure your Wi-Fi allows for 5 GHz band frequency, which is usually faster and less susceptible to interference. If two networks (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) are not enabled by default, you can change it by logging into the router settings. Check the back of the router for more information. However, if you only have one Wi-Fi router and it's a long distance, switching to the 2.4 GHz band may improve your signal because that band has better range.
My experience personally, I use 5GHz as much as possible. The 2.4GHz frequency band has a larger coverage area and better ability to penetrate walls, but it has poor resistance to interference. The 5GHz band covers a shorter distance, but faster. So if I get close to the router, I'd choose 5GHz. You can read more about how to find the best Wi-Fi channels in our guide.
5. Renew DHCP lease
One of the more technical solutions to the "Why my MacBook can't connect to Wi-Fi" issue is to renew the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Agreement) lease. DHCP is a network management protocol used to assign IP addresses to your device.
When you renew your DHCP lease, your Mac will be forced to acquire a new IP address, which can solve a large number of network-level failures.
Renewing a DHCP lease is easy:
- Open System Settings.
- Select Network > Wi-Fi.
- Click "Details" next to your Wi-Fi network.
- Go to TCP/IP.
- Click “Renew DHCP Lease”.

6. Update Mac software
Most of the errors and security issues with Macs stem from not running the latest stable version of macOS. That's why it's very important to keep your Mac updated.
Here is how to update your macOS:
- Open System Settings.
- Go to General > Software Updates.
- Turn on automatic update.
- If a new macOS version is available, click "Update".

7. Update Wi-Fi Driver
Anyone with experience using Windows will remember that drivers need to be installed for everything. But this is not usually the case on Macs. By keeping your application updated, you should get everything you need to run your application.
Check if your router or modem has its own software and learn how to update it regularly. Also, if possible, look for software on how to upgrade the router itself.
The easiest way to update software is to use Mac optimization applications like CleanMyMac X.
CleanMyMac X improves every aspect of your Mac, from removing junk to removing malware to protecting your privacy, uninstalling apps, updating them – all in just a few clicks.
Here is how to update all software using CleanMyMac X:
- Open CleanMyMac X.
- Click "Update Programs" in the sidebar.
- Select the application you want to update.
- Click "Update".

Summary: The best solution when Mac Wi-Fi doesn't work
Following the above steps should quickly resolve your "My Wi-Fi is not working" issue. As you can see, you just need to have a few applications in the toolkit, such as WiFi Signal for real-time connection details, NetSpot for visualizing network signal representations, and CleanMyMac X for updating and solving software problems.
When you find that your MacBook cannot connect to Wi-Fi, try WiFi Signal, NetSpot, and CleanMyMac X for free during the seven-day trial of Setapp. Setapp is a platform with over 240 Mac and iOS apps covering all categories you can think of, from writing prose to editing photos. Download any app in Setapp for free now and find the practical tools you've been missing.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to force my Mac to connect to Wi-Fi?
Go to the WiFi icon in the menu bar and select the network you want to join. If the system prompts, please enter the network password and your Mac should be available online.
Why does my Mac Wi-Fi have exclamation marks?
A Wi-Fi icon with an exclamation mark indicates that the router and IP address cannot be assigned to the Wi-Fi interface, so your Mac cannot connect to the Internet.
How to fix exclamation marks on Wi-Fi?
An exclamation mark on the Mac Wi-Fi icon indicates an issue with the internet connection. To fix it, try the following:
- Troubleshooting with WiFi Signal.
- Restart your Wi-Fi router and your Mac.
- Forgot Wi-Fi network and reconnect your Mac to it.
- Check the Wi-Fi network configuration.
- Renew the DHCP lease.
- Update Wi-Fi drivers with CleanMyMac X.
What does it mean to dim the Mac Wi-Fi menu in the menu bar?
Often, there are two reasons: your Wi-Fi is turned off, or it doesn't work properly.
Why is my Mac constantly disconnecting from Wi-Fi?
The most common reasons why your Mac keeps disconnecting from Wi-Fi are:
- Weak signal.
- Router problem.
- Network configuration issues.
- macOS or driver has expired.
- Interference from other networks.
- Wi-Fi hardware failure.
To start troubleshooting, try using WiFi Signal.
The above is the detailed content of Why your Mac won't connect to Wi-Fi and how to fix it. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1422
1422
 52
52
 1316
1316
 25
25
 1267
1267
 29
29
 1239
1239
 24
24
 Fix your Mac running slow after update to Sequoia
Apr 14, 2025 am 09:30 AM
Fix your Mac running slow after update to Sequoia
Apr 14, 2025 am 09:30 AM
After upgrading to the latest macOS, does the Mac run slower? Don't worry, you are not alone! This article will share my experience in solving slow Mac running problems after upgrading to macOS Sequoia. After the upgrade, I can’t wait to experience new features such as recording and transcription of voice notes and improved trail map planning capabilities. But after installation, my Mac started running slowly. Causes and solutions for slow Mac running after macOS update Here is my summary of my experience, I hope it can help you solve the problem of slow Mac running after macOS Sequoia update: Cause of the problem Solution Performance issues Using Novabe
 How to make a video into a live photo on Mac and iPhone: Detailed steps
Apr 11, 2025 am 10:59 AM
How to make a video into a live photo on Mac and iPhone: Detailed steps
Apr 11, 2025 am 10:59 AM
This guide explains how to convert between Live Photos, videos, and GIFs on iPhones and Macs. Modern iPhones excel at image processing, but managing different media formats can be tricky. This tutorial provides solutions for various conversions, al
 How to reduce WindowServer Mac CPU usage
Apr 16, 2025 pm 12:07 PM
How to reduce WindowServer Mac CPU usage
Apr 16, 2025 pm 12:07 PM
macOS WindowServer: Understanding High CPU Usage and Solutions Have you noticed WindowServer consuming significant CPU resources on your Mac? This process is crucial for your Mac's graphical interface, rendering everything you see on screen. High C
 How to type hashtag on Mac
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:43 AM
How to type hashtag on Mac
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:43 AM
You can’t really use the internet nowadays without encountering the hashtag symbol that looks like this — #. Popularized on a global scale by Twitter as a way to define common tweet themes and later adopted by Instagram and other apps to c
 Mac Disk Utility: How to Repair Disk with First Aid? How to Recover It?
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:49 AM
Mac Disk Utility: How to Repair Disk with First Aid? How to Recover It?
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:49 AM
You might need to repair your Mac disk if your computer won’t start up, apps keep freezing, you can’t open certain documents, or the performance has slowed to a halt. Luckily, Apple includes a handy tool you can use to
 Is Google Chrome Not Working on Mac? Why Are Websites Not Loading?
Apr 12, 2025 am 11:36 AM
Is Google Chrome Not Working on Mac? Why Are Websites Not Loading?
Apr 12, 2025 am 11:36 AM
With a market share of over 65.7%, Google Chrome is the biggest web browser in the world. You can use it if you use other operating systems like Windows and Android, but many Mac users also prefer Chrome over Safari. Mo
 How to delete files on Mac
Apr 15, 2025 am 10:22 AM
How to delete files on Mac
Apr 15, 2025 am 10:22 AM
Managing Mac storage: A comprehensive guide to deleting files Daily Mac usage involves installing apps, creating files, and downloading data. However, even high-end Macs have limited storage. This guide provides various methods for deleting unneces
 How to connect bluetooth headphones to Mac?
Apr 12, 2025 pm 12:38 PM
How to connect bluetooth headphones to Mac?
Apr 12, 2025 pm 12:38 PM
From the dawn of time to just about a few years ago, all of us sported a pair of wired headphones and were convinced that this is simply how it will be done forever. After all, they are the easiest technology around: just plug them in, put them




