How to highlight active row and column in Excel
Mar 27, 2025 am 11:05 AMThis tutorial explores three methods for dynamically highlighting the selected cell's row and column in Excel, enhancing worksheet navigation. Let's examine each approach:
Method 1: VBA for Dynamic Highlighting
This method uses VBA's SelectionChange event to programmatically highlight the active cell's row and column. The code first clears all cell background colors and then applies highlighting to the selected cell's row and column using specified ColorIndex values.
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
If Target.Cells.Count > 1 Then Exit Sub
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Cells.Interior.ColorIndex = 0
With Target
.EntireRow.Interior.ColorIndex = 38
.EntireColumn.Interior.ColorIndex = 24
End With
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End SubCustomization options include altering the ColorIndex values for different highlight colors or highlighting only the row or column. The code must be added to the worksheet's VBA module (not a standard module). Saving the file as a Macro-Enabled Workbook (.xlsm) is crucial.

Advantages: Backend operation, no user adjustments needed, compatibility across Excel versions.
Disadvantages: Clears all existing cell background colors, disables undo functionality (Ctrl Z).
Method 2: Conditional Formatting (with VBA Enhancement)
This method leverages Excel's conditional formatting with formulas referencing the CELL function. The formulas dynamically highlight the active row and/or column based on the selected cell's coordinates.
-
Highlight Active Row:
=CELL("row")=ROW() -
Highlight Active Column:
=CELL("col")=COLUMN() -
Highlight Active Row and Column:
=OR(CELL("row")=ROW(), CELL("col")=COLUMN())

Because Excel doesn't automatically recalculate on selection changes, manual recalculation (F9) or the following VBA code in the worksheet module is needed:
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
Target.Calculate
End Sub
Advantages: Preserves existing cell formatting.
Disadvantages: May impact performance on large workbooks due to recalculations, requires Excel 2007 or later.
Method 3: Conditional Formatting and VBA (Optimized)
This approach optimizes performance by using a "helper sheet" to store the active row and column numbers, which are then referenced in the conditional formatting formulas.
- Create a "Helper Sheet."
- Add this VBA code to the target worksheet's module:
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Worksheets("Helper Sheet").Cells(2, 1) = Target.Row
Worksheets("Helper Sheet").Cells(2, 2) = Target.Column
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub- Use these conditional formatting formulas:
-
Highlight Active Row:
=ROW()='Helper Sheet'!$A$2 -
Highlight Active Column:
=COLUMN()='Helper Sheet'!$B$2 -
Highlight Active Row and Column:
=OR(ROW()='Helper Sheet'!$A$2, COLUMN()='Helper Sheet'!$B$2)



Advantages: Optimized performance, works in all Excel versions.
Disadvantages: More complex setup.
Choose the method that best suits your needs and Excel version. A downloadable practice workbook is available for hands-on experience.
The above is the detailed content of How to highlight active row and column in Excel. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot Article

Hot tools Tags

Hot Article

Hot Article Tags

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
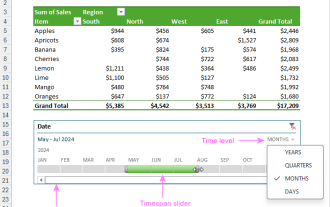 How to create timeline in Excel to filter pivot tables and charts
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:20 AM
How to create timeline in Excel to filter pivot tables and charts
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:20 AM
How to create timeline in Excel to filter pivot tables and charts