Excel CONCAT function - string concatenation examples
This tutorial explores the Excel CONCAT function, a streamlined way to combine text strings from multiple cells. It also highlights key differences from its predecessor, CONCATENATE. Learn to concatenate with various delimiters (spaces, commas, line breaks), handle dates, and integrate with other functions.
Excel's CONCAT function efficiently merges text strings from different cells or ranges into a single cell. It's a Text function available in Excel 365, 2021, 2019, and online versions.
The syntax is straightforward: CONCAT(text1, [text2], ...) where text1 is required and subsequent text2 etc. are optional strings. Arguments can be text values, cell references, or ranges (up to 255). Concatenation follows the argument order.
For instance, combining "john" and "@gmail.com": =CONCAT("john","@gmail.com")

Key CONCAT Function Considerations:
- At least one text argument is needed. Invalid arguments (e.g., error-producing functions) cause errors.
- The output is always a text string, even when numbers are involved.
- Strings exceeding 32,767 characters result in a #VALUE! error.
- CONCAT doesn't have a built-in delimiter option; delimiters must be included manually within the formula.
- Empty cells are ignored.
Practical CONCAT Examples:
-
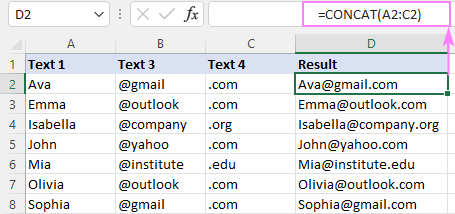
Combining Cells: Concatenate cells A2 and B2 using
=CONCAT(A2, B2). Merging A2:C2 can be done with=CONCAT(A2:C2)or=CONCAT(A2,B2,C2). Blank cells are automatically omitted.


-
Combining Columns: Concatenate columns A, B, C row-wise in column D using
=CONCAT(A2:C2)in D2, then drag down.
-
Concatenating Ranges: Combine cells A2:C3 with
=CONCAT(A2:C3). Non-adjacent ranges are also supported:=CONCAT(A2:C3, A5:C6).

-
Concatenating an Entire Column: Join all cells in column A using
=CONCAT(A:A)(or=CONCAT(A2:A1048576)to exclude headers). Remember the 32,767-character limit.

-
Using Delimiters: Add commas or spaces between concatenated strings. For example,
=CONCAT(A2, ", ", B2, ", ", C2)adds commas and spaces. UseCHAR(10)for line breaks (remember to enable Wrap Text).



-
Concatenating Dates: Convert dates to text using the
TEXTfunction before concatenation:=CONCAT(A2, CHAR(10), TEXT(B2, "d-mmm-yyyy")).

-
Combining with Other Functions: Nest other functions within CONCAT. For example,
=CONCAT("Current time: ", TEXT(NOW(), "hh:mm AM/PM"))adds the current time.
CONCAT vs. CONCATENATE:
CONCAT supersedes CONCATENATE, offering improved range handling. CONCATENATE is retained for backward compatibility. CONCAT is available in newer Excel versions only.
Downloadable practice workbook available (link omitted as per instructions).
The above is the detailed content of Excel CONCAT function - string concatenation examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1422
1422
 52
52
 1316
1316
 25
25
 1267
1267
 29
29
 1239
1239
 24
24
 MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
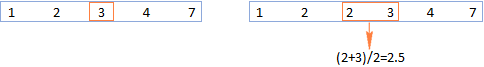
This tutorial explains how to calculate the median of numerical data in Excel using the MEDIAN function. The median, a key measure of central tendency, identifies the middle value in a dataset, offering a more robust representation of central tenden
 Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple users
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple users
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to sharing Excel workbooks, covering various methods, access control, and conflict resolution. Modern Excel versions (2010, 2013, 2016, and later) simplify collaborative editing, eliminating the need to m
 Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
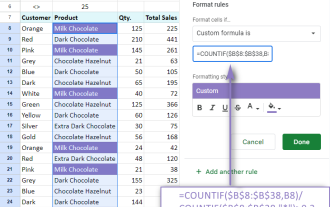
Master Google Sheets COUNTIF: A Comprehensive Guide This guide explores the versatile COUNTIF function in Google Sheets, demonstrating its applications beyond simple cell counting. We'll cover various scenarios, from exact and partial matches to han
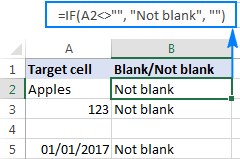 Excel: If cell contains formula examples
Apr 09, 2025 am 09:04 AM
Excel: If cell contains formula examples
Apr 09, 2025 am 09:04 AM
This tutorial demonstrates various Excel formulas to check if a cell contains specific values, including text, numbers, or parts of strings. It covers scenarios using IF, ISTEXT, ISNUMBER, SEARCH, FIND, COUNTIF, EXACT, SUMPRODUCT, VLOOKUP, and neste
 How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image file
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image file
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
This tutorial explores various methods for converting .xls files to .jpg images, encompassing both built-in Windows tools and free online converters. Need to create a presentation, share spreadsheet data securely, or design a document? Converting yo
 Google sheets chart tutorial: how to create charts in google sheets
Apr 11, 2025 am 09:06 AM
Google sheets chart tutorial: how to create charts in google sheets
Apr 11, 2025 am 09:06 AM
This tutorial shows you how to create various charts in Google Sheets, choosing the right chart type for different data scenarios. You'll also learn how to create 3D and Gantt charts, and how to edit, copy, and delete charts. Visualizing data is cru
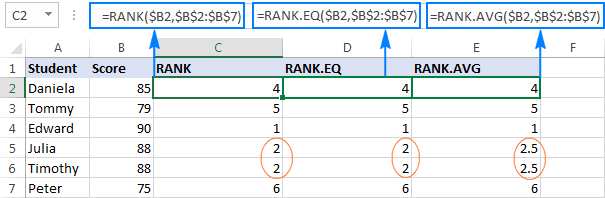 Excel RANK function and other ways to calculate rank
Apr 09, 2025 am 11:35 AM
Excel RANK function and other ways to calculate rank
Apr 09, 2025 am 11:35 AM
This Excel tutorial details the nuances of the RANK functions and demonstrates how to rank data in Excel based on multiple criteria, group data, calculate percentile rank, and more. Determining the relative position of a number within a list is easi
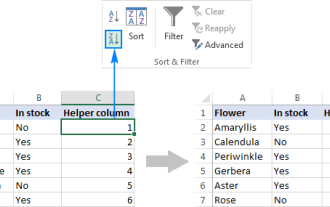 How to flip data in Excel columns and rows (vertically and horizontally)
Apr 11, 2025 am 09:05 AM
How to flip data in Excel columns and rows (vertically and horizontally)
Apr 11, 2025 am 09:05 AM
This tutorial demonstrates several efficient methods for vertically and horizontally flipping tables in Excel, preserving original formatting and formulas. While Excel lacks a direct "flip" function, several workarounds exist. Flipping Dat