Who actually owns Google?
Google is owned by Alphabet Inc., which is controlled by Larry Page and Sergey Bring: 1) The founder ensures control of the company by holding Class B shares (10 votes per share); 2) Alphabet's Class A and Class C shares are circulated in the open market and employee stock ownership plans, respectively, but do not affect the founder's control.

introduction
Google, the name is almost synonymous with the Internet, but do you know who really owns this tech giant? This article will uncover the mystery of Google's ownership and explore the story behind it in depth. After reading this article, you will not only understand Google's owners, but also have a deeper understanding of its development history and influence.
Review of basic knowledge
Google was founded in 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin in a dormitory at Stanford University. Initially, Google was just a search engine, but it quickly grew into a tech empire covering a variety of services. To understand Google's ownership needs to start with its founder and company structure.
Core concept or function analysis
Google's ownership structure
Google's ownership is primarily achieved through its parent company, Alphabet Inc. In 2015, Google reorganized and established Alphabet Inc. as a holding company, which became a subsidiary of Alphabet. Alphabet's equity structure is very complex, but it mainly consists of the following parts:
- Founder shares : Larry Page and Sergey Brin hold Class A and Class B shares of Alphabet. Class B shares have 10 votes per share, while Class A shares have only 1 votes per share. This means that even if they hold a low shareholding, they are still able to control most of the company’s decisions.
- Open Market Shares : Alphabet's Class C shares (no voting rights) are traded on the open market and can be purchased by anyone, but these stocks do not come with voting rights.
- Employee shares : Alphabet employees hold shares in the company through stock option plans, which are usually Class A or Class C shares.
How it works
Alphabet's equity structure is designed to ensure that the founder can continue to control the company's development direction, even if the company's shares are diluted after listing. Through high voting rights in Class B stocks, Larry Page and Sergey Brin were able to maintain absolute control in corporate decision-making. This structure is not uncommon among technology companies, but the specific implementation of Alphabet is very unique.
Example of usage
Basic usage
Let's look at a simple example of how to control a company through the stock structure:
class Share:
def __init__(self, type, votes):
self.type = type
self.votes = votes
class Company:
def __init__(self):
self.shares = []
def add_share(self, share):
self.shares.append(share)
def total_votes(self):
return sum(share.votes for share in self.shares)
# Create Alphabet Alphabet = Company()
# Add founder_share = Share('B', 10)
alphabet.add_share(founder_share)
# Add public_share = Share('A', 1)
alphabet.add_share(public_share)
# Calculate total voting rights total_votes = alphabet.total_votes()
print(f"Total voting rights: {total_votes}")This code shows how to control a company's voting rights through different types of shares. Founders hold Class B shares with higher voting rights, thus ensuring their dominance in corporate decision-making.
Advanced Usage
In actual operations, Alphabet's equity structure is more complex. We can further extend the code to simulate this complexity:
class Share:
def __init__(self, type, votes, quantity):
self.type = type
self.votes = votes
self.quantity = quantity
class Company:
def __init__(self):
self.shares = []
def add_share(self, share):
self.shares.append(share)
def total_votes(self):
return sum(share.votes * share.quantity for share in self.shares)
# Create Alphabet Alphabet = Company()
# Add founder_share = Share('B', 10, 1000000) # 1 million shares, 10 votes per share alphabet.add_share(founder_share)
# Add public_share_a = Share('A', 1, 50000000) # 50 million shares, 1 vote per share public_share_c = Share('C', 0, 10000000) # 100 million shares, no voting rights alphabet.add_share(public_share_a)
alphabet.add_share(public_share_c)
# Calculate total voting rights total_votes = alphabet.total_votes()
print(f"Total voting rights: {total_votes}")This code shows how to simulate the actual equity structure of Alphabet by increasing the number and type of shares. The founder ensured control of the company by holding a large number of Class B shares.
Common Errors and Debugging Tips
Common mistakes when simulating equity structures include:
- Voting rights calculation error : Ensure that the voting rights of each stock are calculated correctly, especially when the stock type and quantity are complex.
- Share type confusion : clearly distinguish different types of stocks and their voting rights to avoid confusion.
Debugging Tips:
- Step by step Verification : Step by step Verify the voting rights calculations of each stock to ensure there are no omissions or errors.
- Use debugging tools : Use Python's debugging tools, such as pdb, to track the code execution process and find out the problem.
Performance optimization and best practices
Performance optimization is very important when simulating complex equity structures. Here are some suggestions:
- Using efficient data structures : For example, using dictionaries to store stock types and quantities can improve query and computational efficiency.
- Avoid repeated calculations : When calculating the total voting rights, avoid repeatedly calculating the voting rights of each stock, which can be optimized through cache or pre-calculation.
Best Practices:
- Code readability : Ensure the code structure is clear and the variable naming is meaningful, making it easy for others to understand and maintain.
- Modular design : modularize different functions for easy reuse and maintenance.
Through the above analysis and code examples, we not only understand Google's ownership structure, but also explore in-depth how to simulate and understand this complex equity structure through programming. Hopefully these insights and practices will help you better understand Google ownership and apply this knowledge in programming.
The above is the detailed content of Who actually owns Google?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1662
1662
 14
14
 1419
1419
 52
52
 1313
1313
 25
25
 1262
1262
 29
29
 1235
1235
 24
24
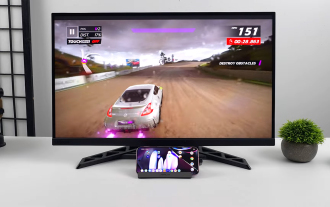 Google Pixel 9 Pro XL gets tested with desktop mode
Aug 29, 2024 pm 01:09 PM
Google Pixel 9 Pro XL gets tested with desktop mode
Aug 29, 2024 pm 01:09 PM
Google has introduced DisplayPort Alternate Mode with the Pixel 8 series, and it's present on the newly launched Pixel 9 lineup. While it's mainly there to let you mirror the smartphone display with a connected screen, you can also use it for desktop
 Google Pixel 9 and Pixel 9 Pro rumoured to gain Creative Assistant AI upon release
Jun 22, 2024 am 10:50 AM
Google Pixel 9 and Pixel 9 Pro rumoured to gain Creative Assistant AI upon release
Jun 22, 2024 am 10:50 AM
Currently, four new Pixel smartphones are anticipated to land this autumn. To recap, the series is rumoured to feature thePixel 9 and Pixel 9 Pro at launch. However, the Pixel 9 Pro will be a rival to the iPhone 16 Pro rather than a Pixel 8 Pro (curr
 Google AI announces Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemma 2 for developers
Jul 01, 2024 am 07:22 AM
Google AI announces Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemma 2 for developers
Jul 01, 2024 am 07:22 AM
Google AI has started to provide developers with access to extended context windows and cost-saving features, starting with the Gemini 1.5 Pro large language model (LLM). Previously available through a waitlist, the full 2 million token context windo
 Google Tensor G4 of Pixel 9 Pro XL lags behind Tensor G2 in Genshin Impact
Aug 24, 2024 am 06:43 AM
Google Tensor G4 of Pixel 9 Pro XL lags behind Tensor G2 in Genshin Impact
Aug 24, 2024 am 06:43 AM
Google recently responded to the performance concerns about the Tensor G4 of the Pixel 9 line. The company said that the SoC wasn't designed to beat benchmarks. Instead, the team focused on making it perform well in the areas where Google wants the c
 Google app beta APK teardown reveals new extensions coming to Gemini AI assistant
Jul 30, 2024 pm 01:06 PM
Google app beta APK teardown reveals new extensions coming to Gemini AI assistant
Jul 30, 2024 pm 01:06 PM
Google's AI assistant, Gemini, is set to become even more capable, if the APK teardown of the latest update (v15.29.34.29 beta) is to be considered. The tech behemoth's new AI assistant could reportedly get several new extensions. These extensions wi
 Google Pixel 9 smartphones will not launch with Android 15 despite seven-year update commitment
Aug 01, 2024 pm 02:56 PM
Google Pixel 9 smartphones will not launch with Android 15 despite seven-year update commitment
Aug 01, 2024 pm 02:56 PM
The Pixel 9 series is almost here, having been scheduled for an August 13 release. Based on recent rumours, the Pixel 9, Pixel 9 Pro and Pixel 9 Pro XL will mirror the Pixel 8 and Pixel 8 Pro (curr. $749 on Amazon) by starting with 128 GB of storage.
 Google\'s new Chromecast \'TV Streamer\' rumoured to launch with Ethernet and Thread connectivity
Aug 01, 2024 am 10:21 AM
Google\'s new Chromecast \'TV Streamer\' rumoured to launch with Ethernet and Thread connectivity
Aug 01, 2024 am 10:21 AM
Google is roughly a fortnight away from fully revealing new hardware. As usual, countless sources have leaked details about new Pixel devices, whether that be the Pixel Watch 3, Pixel Buds Pro 2 or Pixel 9 smartphones. It also seems that the company
 Leaked Google Pixel 9 adverts show new AI features including \'Add Me\' camera functionality
Jul 30, 2024 am 11:18 AM
Leaked Google Pixel 9 adverts show new AI features including \'Add Me\' camera functionality
Jul 30, 2024 am 11:18 AM
More promotional materials relating to the Pixel 9 series have leaked online. For reference, the new leak arrived shortly after 91mobiles shared multiple images that also showcased the Pixel Buds Pro 2 and Pixel Watch 3 or Pixel Watch 3 XL. This time




