Excel MIRR function to calculate modified internal rate of return
This tutorial clarifies the modified internal rate of return (MIRR), its distinctions from IRR, and its Excel calculation. For years, financial experts have highlighted IRR's shortcomings, yet many still rely on it. While not perfect, MIRR addresses key IRR flaws, offering a more realistic project evaluation. Let's explore the Excel MIRR function.
- The Excel MIRR Function
- Calculating MIRR in Excel: A Formula Example
- An Excel MIRR Template
- MIRR vs. IRR: Which is Superior?
- Troubleshooting the Excel MIRR Function
What is MIRR?
The modified internal rate of return (MIRR) is a financial metric assessing project profitability and ranking similarly-sized investments. A refined version of IRR, MIRR aims to correct IRR's deficiencies.
MIRR represents the return rate where the terminal inflow's net present value (NPV) equals the initial investment (outflow); IRR, conversely, finds the rate making NPV zero.
Crucially, IRR assumes all positive cash flows reinvest at the project's IRR, while MIRR lets you specify a separate reinvestment rate. (See MIRR vs. IRR for details).
A higher MIRR is preferable. Using MIRR as the sole criterion, accept projects with MIRR exceeding the cost of capital (hurdle rate); reject those falling below.
Excel MIRR Function
Excel's MIRR function calculates the modified internal rate of return for regularly-spaced cash flows.
Syntax:
MIRR(values, finance_rate, reinvest_rate)
Where:
- values (required): An array or cell range containing cash flows.
- finance_rate (required): The interest rate paid to finance the investment (cost of borrowing for negative cash flows). Enter as a percentage or decimal.
- reinvest_rate (required): The compounding return rate for reinvesting positive cash flows. Enter as a percentage or decimal.
MIRR is available in Excel 2007 and later versions.
Key Considerations for Excel's MIRR Function
Before calculating MIRR, remember:
- At least one positive (income) and one negative (outlay) value is needed in values; otherwise, a #DIV/0! error results.
- Cash flows are assumed to occur at regular intervals, with their order determining the cash flow sequence. Input values chronologically.
- Cash flows are assumed to occur at the end of each period.
- Only numeric values are processed. Text, logical values, and empty cells are ignored; zeros are included.
- The weighted average cost of capital is often used as the reinvest_rate, but any appropriate rate can be used.
Calculating MIRR in Excel: A Formula Example
Calculating MIRR is straightforward: input cash flows, borrowing cost, and reinvestment rate into the function's arguments.
For example, to find the MIRR for cash flows in A2:A8, with the finance rate in D1 and reinvestment rate in D2, use:
=MIRR(A2:A8,D1,D2)

Tip: Format the formula cell as a percentage if the result is a decimal.
An Excel MIRR Template
To efficiently evaluate projects of varying sizes, create a MIRR template:
- Create a dynamic named range for cash flow values using:
=OFFSET(Sheet1!$A$2,0,0,COUNT(Sheet1!$A:$A),1)(ReplaceSheet1!$A$2with your worksheet and starting cell). Name this range (e.g., "Values"). - (Optional) Name cells containing finance and reinvest rates.
- Use the named ranges in your MIRR formula (e.g.,
=MIRR(Values, Finance_rate, Reinvest_rate)).
This allows for flexible input of values in column A (starting at A2), dynamically updating the MIRR calculation.

Note: Values must be in adjacent cells without gaps for the template to function correctly. Blank finance and reinvest rate cells default to zero.
MIRR vs. IRR: Which is Superior?
While MIRR's theoretical basis is debated, it's generally considered a more robust alternative to IRR. Calculating both can be a useful compromise, understanding their limitations:
IRR Limitations
Despite its popularity, IRR has flaws:
1. Reinvestment Rate Assumption
IRR assumes interim cash flows reinvest at the IRR itself. Realistically, reinvestment rates are often lower, closer to the cost of capital, and may fluctuate. This leads to IRR overestimating project potential. MIRR provides a more accurate reflection by considering finance and reinvestment rates, allowing for varied return rates across project stages.
2. Multiple Solutions
With alternating positive and negative cash flows, IRR can yield multiple solutions, causing ambiguity. MIRR avoids this by producing a single value.
MIRR Limitations
Some argue MIRR's return rate is less reliable as project earnings aren't always fully reinvested. However, adjusting the reinvest_rate compensates for partial reinvestments (e.g., use a 3% reinvest_rate if only half of a 6% return is reinvested).
Troubleshooting the Excel MIRR Function
Error handling:
- #DIV/0! error: Insufficient positive and negative values in the values argument.
- #VALUE! error: Non-numeric finance_rate or reinvest_rate.
Mastering Excel's MIRR function enhances project evaluation accuracy. For further practice, consider downloading a sample workbook on calculating MIRR in Excel.
The above is the detailed content of Excel MIRR function to calculate modified internal rate of return. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Excel formula to find top 3, 5, 10 values in column or row
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:09 AM
Excel formula to find top 3, 5, 10 values in column or row
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:09 AM
This tutorial demonstrates how to efficiently locate the top N values within a dataset and retrieve associated data using Excel formulas. Whether you need the highest, lowest, or those meeting specific criteria, this guide provides solutions. Findi
 Add a dropdown list to Outlook email template
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:13 AM
Add a dropdown list to Outlook email template
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:13 AM
This tutorial shows you how to add dropdown lists to your Outlook email templates, including multiple selections and database population. While Outlook doesn't directly support dropdowns, this guide provides creative workarounds. Email templates sav
 How to use Flash Fill in Excel with examples
Apr 05, 2025 am 09:15 AM
How to use Flash Fill in Excel with examples
Apr 05, 2025 am 09:15 AM
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to Excel's Flash Fill feature, a powerful tool for automating data entry tasks. It covers various aspects, from its definition and location to advanced usage and troubleshooting. Understanding Excel's Fla
 Regex to extract strings in Excel (one or all matches)
Mar 28, 2025 pm 12:19 PM
Regex to extract strings in Excel (one or all matches)
Mar 28, 2025 pm 12:19 PM
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to use regular expressions in Excel to find and extract substrings matching a given pattern. Microsoft Excel provides a number of functions to extract text from cells. Those functions can cope with most
 How to add calendar to Outlook: shared, Internet calendar, iCal file
Apr 03, 2025 am 09:06 AM
How to add calendar to Outlook: shared, Internet calendar, iCal file
Apr 03, 2025 am 09:06 AM
This article explains how to access and utilize shared calendars within the Outlook desktop application, including importing iCalendar files. Previously, we covered sharing your Outlook calendar. Now, let's explore how to view calendars shared with
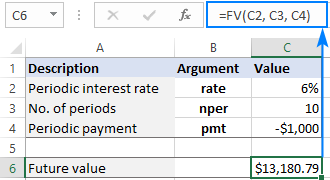 FV function in Excel to calculate future value
Apr 01, 2025 am 04:57 AM
FV function in Excel to calculate future value
Apr 01, 2025 am 04:57 AM
This tutorial explains how to use Excel's FV function to determine the future value of investments, encompassing both regular payments and lump-sum deposits. Effective financial planning hinges on understanding investment growth, and this guide prov
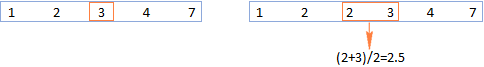 MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
This tutorial explains how to calculate the median of numerical data in Excel using the MEDIAN function. The median, a key measure of central tendency, identifies the middle value in a dataset, offering a more robust representation of central tenden
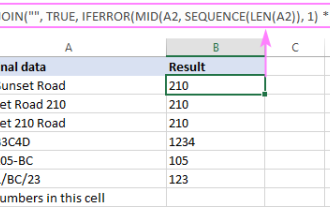 How to remove / split text and numbers in Excel cell
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:07 AM
How to remove / split text and numbers in Excel cell
Apr 01, 2025 am 05:07 AM
This tutorial demonstrates several methods for separating text and numbers within Excel cells, utilizing both built-in functions and custom VBA functions. You'll learn how to extract numbers while removing text, isolate text while discarding numbers






