Boost Productivity with Custom Command Shortcuts Using Linux Aliases

Introduction
Linux is a powerful operating system favored by developers, system administrators, and power users due to its flexibility and efficiency. However, frequently using long and complex commands can be tedious and error-prone. This is where aliases come into play.
Aliases allow users to create shortcuts for commonly used commands, reducing typing effort and improving workflow efficiency. By customizing commands with aliases, users can speed up tasks and tailor their terminal experience to suit their needs.
In this article, we'll explore how aliases work, the different types of aliases, and how to effectively manage and utilize them. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced Linux user, mastering aliases will significantly enhance your productivity.
What is an Alias in Linux?
An alias in Linux is a user-defined shortcut for a command or a sequence of commands. Instead of typing a long command every time, users can assign a simple keyword to execute it.
For example, the command:
ls -la
displays all files (including hidden ones) in long format. This can be shortened by creating an alias:
alias ll='ls -la'
Now, whenever the user types ll, it will execute ls -la.
Aliases help streamline command-line interactions, minimize errors, and speed up repetitive tasks.
Types of Aliases in Linux
There are two main types of aliases in Linux:
Temporary Aliases- Exist only during the current terminal session.
- Disappear once the terminal is closed or restarted.
- Stored in shell configuration files (~/.bashrc, ~/.bash_profile, or ~/.zshrc).
- Persist across terminal sessions and system reboots.
Understanding the difference between temporary and permanent aliases is crucial for effective alias management.
Creating Temporary Aliases
Temporary aliases are quick to set up and useful for short-term tasks.
Syntax for Creating a Temporary Aliasalias alias_name='command_to_run'
Examples-
Shortcut for ls -la:
alias ll='ls -la'
-
Quick access to git status:
alias gs='git status'
-
Updating system (for Debian-based systems):
alias update='sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y'
After defining an alias, simply typing alias_name in the terminal will execute the corresponding command.
Checking Active AliasesTo view all currently defined aliases, run:
alias
Removing a Temporary AliasTo delete a temporary alias, use:
unalias alias_name
Example:
unalias ll
This removes the ll alias from the current session. However, it will still exist in the configuration file if defined as a permanent alias.
Creating Permanent Aliases
Since temporary aliases are lost when the terminal is closed, it's often necessary to create permanent aliases for frequently used commands.
Steps to Create a Permanent Alias-
Open the shell configuration file (.bashrc, .bash_profile, or .zshrc):
nano ~/.bashrc
-
Add the alias at the end of the file:
alias ll='ls -la' alias gs='git status'
-
Save and exit (CTRL X, then Y, then Enter).
-
Apply the changes immediately without restarting the terminal:
source ~/.bashrc
Now, these aliases will persist across sessions.
Using a Dedicated Alias FileFor better organization, some users prefer to store aliases in a separate file (~/.bash_aliases) and reference it in .bashrc:
- Create the alias file:
nano ~/.bash_aliases
- Add aliases to the file.
- Modify .bashrc to include:
if [ -f ~/.bash_aliases ]; then . ~/.bash_aliases fi
- Reload the configuration:
source ~/.bashrc
This method helps maintain a cleaner .bashrc file.
Managing and Troubleshooting Aliases
Listing All AliasesTo see all defined aliases, run:
alias
Checking for ConflictsSometimes an alias may conflict with an existing command. To check what a command is executing, use:
type command_name
Example:
type ll
Unsetting an AliasTo remove an alias permanently, delete it from .bashrc or .bash_aliases, then reload the file:
unalias alias_name source ~/.bashrc
Advanced Aliases
Aliases can be more than just simple command substitutions. They can incorporate multiple commands and even use functions for enhanced functionality.
Chaining CommandsAliases can execute multiple commands using && or ;.
Example:
alias cleanup='rm -rf ~/Downloads/* && echo "Downloads folder cleaned!"'
Using Functions for More FlexibilitySince aliases do not accept arguments, functions can be used instead.
Example:
function mkcd() { mkdir -p "$1" && cd "$1" }
Save this function in .bashrc or .zshrc, then use:
mkcd new_directory
This creates a directory and navigates into it in one step.
Best Practices for Using Aliases
- Keep them intuitive: Use short and memorable names.
- Avoid overwriting essential commands: Be cautious not to redefine critical system commands.
- Organize aliases: Store them in ~/.bash_aliases for easier management.
- Document custom aliases: If working in a team, share commonly used aliases to maintain consistency.
Conclusion
Aliases are an invaluable feature of the Linux shell, allowing users to streamline their workflow, reduce typing effort, and automate repetitive tasks. By mastering aliases, both beginners and experienced users can significantly enhance their efficiency in the terminal.
Start by defining a few simple aliases and gradually experiment with more complex ones to suit your workflow. As you become more comfortable, integrating aliases into shell scripts and functions will further optimize your Linux experience.
The above is the detailed content of Boost Productivity with Custom Command Shortcuts Using Linux Aliases. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
The Linux command line interface provides a wealth of text processing tools, one of the most powerful tools is the sed command. sed is the abbreviation of Stream EDitor, a multi-functional tool that allows complex processing of text files and streams. What is Sed? sed is a non-interactive text editor that operates on pipeline inputs or text files. By providing directives, you can let it modify and process text in a file or stream. The most common use cases of sed include selecting text, replacing text, modifying original files, adding lines to text, or removing lines from text. It can be used from the command line in Bash and other command line shells. Sed command syntax sed
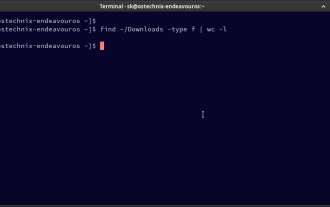 How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
Efficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-l
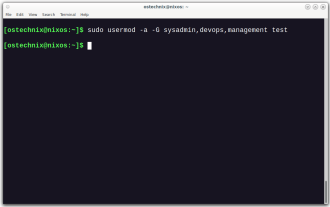 How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Efficiently managing user accounts and group memberships is crucial for Linux/Unix system administration. This ensures proper resource and data access control. This tutorial details how to add a user to multiple groups in Linux and Unix systems. We
 Locating Leviathan Files in Linux
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Locating Leviathan Files in Linux
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Introduction In the realm of Linux, where the command line is often the compass by which we navigate, the efficient management of disk space is crucial. Whether you’re sailing through personal projects or steering the ship o
 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
Linux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
This brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
 LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
If you're familiar with AirDrop, you know it's a popular feature developed by Apple Inc. that enables seamless file transfer between supported Macintosh computers and iOS devices using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. However, if you're using Linux and missing o
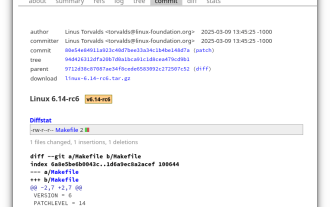 Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linus Torvalds has released Linux Kernel 6.14 Release Candidate 6 (RC6), reporting no significant issues and keeping the release on track. The most notable change in this update addresses an AMD microcode signing issue, while the rest of the updates




