8 Major Problems With AI Initiatives In Enterprise

With so much enthusiasm about the rapid advancement we’ve made in using LLMs this year, some of the remaining barriers and bottlenecks tend to get lost in the shuffle.
As with all prior technologies, companies have to introduce an AI project the right way. The way I’ve heard it said is that new workflows and tools need to be a help, not a hindrance, to a company.
We often talk about this as a productivity issue – if it’s instituted correctly, the new project will help workers to be more productive, confident, and on top of their jobs. If it’s done poorly, it can mire them in low productivity, and actually inhibit the work that needs to get done.
Let’s talk about some of the specific problems that I’ve heard discussed in panels and in interviews around the AI industry, as 2025 got underway.
Lack of Buy-In and Enthusiasm
This is another way that AI follows all other prior technologies. Yes, it’s a more powerful technology with a lot more versatility for implementation – but you still need stakeholder buy-in. Otherwise, you’re starting from a position of weakness, and it’s an uphill battle.
This Substack piece talking about common challenges uses the phrase “low user adoption,” which basically means that people aren’t choosing to use a new AI tool or system.
That on its own is a core problem for enterprise AI.
Overly Broad Directives
Suppose someone in a company orders everyone to immediately “move everything to AI.”
There are a couple potential problems with this. First, there’s lack of clarity about what these directives mean. There’s also likely to be a lot of overlap and redundant efforts, as well as chaos inside of departments.
It’s better to create a detailed strategic plan and go from there.
Lack of Support and Maintenance
In some ways, it’s easier to create an initiative than it is to manage it.
That’s where this next problem comes in – suppose someone in-house or a vendor has dreamed up and built some kind of AI program, but as it is in production, there are issues with adoption and use. Users have questions – and these are often front-line people using the tools for vital business processes.
Who do you go to in order to iron these questions out?
If each department says “this isn’t our problem,” you have an intractable situation on your hands.
So that’s some thing else to look out for: not just support in the initial phases, but support later on as the AI systems become part of the workflows and business processes.
AI Agents and Human Replacement
This issue starts with a big question – will AI agents replace humans?
You can check out this input from none other than Bill Gates, where he suggests that we “won’t need humans” for most things as AI becomes ascendant.
“There will be some things we reserve for ourselves,” Gates famously said of human initiatives. “But in terms of making things and moving things and growing food, over time those will be basically solved problems.”
For more, you can listen to a recent edition of one of my favorite podcasts, AI Daily Brief with Nathaniel Whittemore.
Whittemore is talking with Nufar Gaspar, and suggests that AI agents inherently replace humans. In other words, because they’re so naturally capable, it’s easy for companies to just plug them in and get rid of the human that was doing the job before.
“I think that agents are inherently more replacing than augmenting, at least in terms of how people think about them,” he argues. “Currently, you know, with agents, the ROI that companies are looking for from agents is, ‘can they do a thing more cheaply, efficiently, more quickly than our people do it?’”
He notes that companies may choose to reinvest in human potential, or not.
“What that doesn't say is how companies are going to choose to use those new efficiency gains,” he adds. “Are they going to just slash headcount, or are they going to reinvest people's time that's now freed up in further growth like that? You know, each company has to make those decisions.”
That gap between the theory of AI as assistive, and the reality of agentic replacers, is a big potential problem in any company.
AI Washing
This is a little bit of a different issue that doesn’t have as much to do with company integration and has a lot more to do with branding and company reputation.
The basic idea is that companies have to be sincere when it comes to AI adoption and not just giving lip service to this kind of initiative. Here’s some of our own Forbes reporting on the topic from Sujai Hajela a few years ago. A lot of it is still applicable now. (and here’s more from CNN).
“AI washing” is synonymous to anything else like greenwashing, where companies might claim to be more ecological than they are. It’s just a best practice to avoid this kind of mismatch, and the idea that a company might not “practice what they preach.”
Ignoring AI Ethics
Time and time again, we see companies moving ahead with AI projects without thinking about the ethics of the thing – bias, privacy issues, etc.
Top figures in the tech world have warned against leaving ethics out of the equation. This includes voices like Bill Gates and Elon Musk early in the AI revolution, as well as others more recently who are warning about the intersection of AI with privacy and human data ownership.
Lack of Cybersecurity
AI systems also need to be used in a secure way.
Going back to the podcast, Whittemore talks about compliance with standards like HIPAA and the European GDPR. All of this is similarly important in AI implementation and design.
Lack of Good Policy
Simply put, companies need a good roadmap to be successful.
Again, AI is unique in its scope, but not unique in some of the best practices that business should apply. Anything is less effective without a good plan, so companies should make sure that AI factors into their business planning in a concrete and definable way.
That’s all for now: think about these common recommendations when it comes to AI adoption in enterprise.
The above is the detailed content of 8 Major Problems With AI Initiatives In Enterprise. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
The article reviews top AI art generators, discussing their features, suitability for creative projects, and value. It highlights Midjourney as the best value for professionals and recommends DALL-E 2 for high-quality, customizable art.
 Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Meta's Llama 3.2: A Leap Forward in Multimodal and Mobile AI Meta recently unveiled Llama 3.2, a significant advancement in AI featuring powerful vision capabilities and lightweight text models optimized for mobile devices. Building on the success o
 Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
ChatGPT 4 is currently available and widely used, demonstrating significant improvements in understanding context and generating coherent responses compared to its predecessors like ChatGPT 3.5. Future developments may include more personalized interactions and real-time data processing capabilities, further enhancing its potential for various applications.
 Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
The article compares top AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude, focusing on their unique features, customization options, and performance in natural language processing and reliability.
 Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
The article discusses top AI writing assistants like Grammarly, Jasper, Copy.ai, Writesonic, and Rytr, focusing on their unique features for content creation. It argues that Jasper excels in SEO optimization, while AI tools help maintain tone consist
 Choosing the Best AI Voice Generator: Top Options Reviewed
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
Choosing the Best AI Voice Generator: Top Options Reviewed
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
The article reviews top AI voice generators like Google Cloud, Amazon Polly, Microsoft Azure, IBM Watson, and Descript, focusing on their features, voice quality, and suitability for different needs.
 How to Access Falcon 3? - Analytics Vidhya
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:41 PM
How to Access Falcon 3? - Analytics Vidhya
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:41 PM
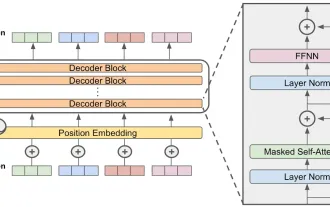
Falcon 3: A Revolutionary Open-Source Large Language Model Falcon 3, the latest iteration in the acclaimed Falcon series of LLMs, represents a significant advancement in AI technology. Developed by the Technology Innovation Institute (TII), this open
 Top 7 Agentic RAG System to Build AI Agents
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:25 PM
Top 7 Agentic RAG System to Build AI Agents
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:25 PM
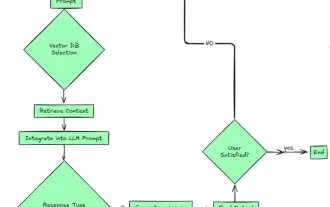
2024 witnessed a shift from simply using LLMs for content generation to understanding their inner workings. This exploration led to the discovery of AI Agents – autonomous systems handling tasks and decisions with minimal human intervention. Buildin






