 Software Tutorial
Software Tutorial
 Office Software
Office Software
 The PIVOTBY Function vs PivotTables: Which Should You Use in Excel?
The PIVOTBY Function vs PivotTables: Which Should You Use in Excel?
The PIVOTBY Function vs PivotTables: Which Should You Use in Excel?
Excel's PIVOTBY Function vs. PivotTables: A Detailed Comparison
Excel offers two powerful tools for data summarization and reorganization: the PIVOTBY function and PivotTables. Both group and aggregate data for detailed analysis, but their usage differs significantly. This article explores their strengths and weaknesses to help you choose the best tool for your needs.
Excel's PIVOTBY Function: Dynamic Array Power
PIVOTBY, a dynamic array function, uses formulas to create tabular summaries by grouping data rows and columns. Key features include:

Limited Compatibility: Introduced relatively recently (September 2024), PIVOTBY is currently only available in Excel for Microsoft 365 (Windows and Mac). Older Excel versions will display a #NAME? error.

Automatic Refresh: A major advantage is its automatic recalculation and resizing whenever the source data changes. This eliminates the need for manual refreshes (unlike PivotTables), ensuring you always see the latest data.
Extensive Customization: PIVOTBY offers unparalleled flexibility:
- Define row and column variables.
- Include or exclude headers.
- Use various Excel functions (including custom LAMBDA functions) for aggregation.
- Create hierarchical groupings.
- Sort data by rows and columns.
- Filter unwanted data.
- Convert totals to percentages.
This customization is all within a single function, unlike PivotTables which require navigating different panes and ribbon options. Furthermore, PIVOTBY works with both columnar and row-oriented source data, unlike PivotTables which require columnar data.
Formula Dependency: PIVOTBY's strength—its formula-based nature—can also be a limitation. Sharing a workbook with users unfamiliar with the function can cause issues if adjustments are needed. It's ideal for personal use or sharing with users who understand its functionality.

Excel PivotTables: The Established Champion
PivotTables are a long-standing and widely recognized Excel feature for analyzing large datasets. Key aspects include:

Wide Compatibility: Available in most Excel versions (Excel 2016 and later), including Microsoft Office, Excel for the web, and Excel for Microsoft 365, ensuring broad compatibility.
Designated User Interface: The intuitive PivotTable Fields pane simplifies data selection and organization into rows and columns. The Design and Analyze tabs provide easy access to customization options.


Manual Refresh: While requiring manual refreshes, this prevents the performance drain that constant recalculation in multiple PIVOTBY formulas can cause.

Efficient Formatting: Built-in formatting options clearly distinguish headers, data rows, subtotals, and grand totals. The Design tab offers quick style modifications.


Added Visualization: PivotTables integrate seamlessly with Timeline filters and PivotCharts for dynamic data visualization.

Diverse Data Sources: Excel 2016 and later versions allow PivotTables to connect to external data sources (databases, CSV, web pages, etc.), offering greater flexibility.

PIVOTBY vs. PivotTables: When to Use Which
PIVOTBY and PivotTables serve different purposes and aren't mutually exclusive. Consider these factors when choosing:
Use PIVOTBY if:
- Automatic data refresh is crucial.
- You prefer formula-based manipulation.
- Extensive customization is needed.
- You're comfortable with advanced Excel functions.
Use PivotTables if:
- Ease of use and quick data organization are priorities.
- Visualizations are important.
- Data sharing with less experienced users is necessary.
- You need to connect to diverse data sources.
The GROUPBY function, while also useful for data grouping, only works with rows, making it less versatile than PIVOTBY for creating comprehensive summaries.
The above is the detailed content of The PIVOTBY Function vs PivotTables: Which Should You Use in Excel?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1205
1205
 24
24
 How to Create a Timeline Filter in Excel
Apr 03, 2025 am 03:51 AM
How to Create a Timeline Filter in Excel
Apr 03, 2025 am 03:51 AM
In Excel, using the timeline filter can display data by time period more efficiently, which is more convenient than using the filter button. The Timeline is a dynamic filtering option that allows you to quickly display data for a single date, month, quarter, or year. Step 1: Convert data to pivot table First, convert the original Excel data into a pivot table. Select any cell in the data table (formatted or not) and click PivotTable on the Insert tab of the ribbon. Related: How to Create Pivot Tables in Microsoft Excel Don't be intimidated by the pivot table! We will teach you basic skills that you can master in minutes. Related Articles In the dialog box, make sure the entire data range is selected (
 If You Don't Use Excel's Hidden Camera Tool, You're Missing a Trick
Mar 25, 2025 am 02:48 AM
If You Don't Use Excel's Hidden Camera Tool, You're Missing a Trick
Mar 25, 2025 am 02:48 AM
Quick Links Why Use the Camera Tool?
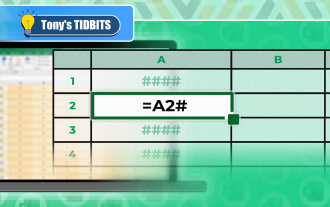 You Need to Know What the Hash Sign Does in Excel Formulas
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:55 AM
You Need to Know What the Hash Sign Does in Excel Formulas
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:55 AM
Excel Overflow Range Operator (#) enables formulas to be automatically adjusted to accommodate changes in overflow range size. This feature is only available for Microsoft 365 Excel for Windows or Mac. Common functions such as UNIQUE, COUNTIF, and SORTBY can be used in conjunction with overflow range operators to generate dynamic sortable lists. The pound sign (#) in the Excel formula is also called the overflow range operator, which instructs the program to consider all results in the overflow range. Therefore, even if the overflow range increases or decreases, the formula containing # will automatically reflect this change. How to list and sort unique values in Microsoft Excel
 Use the PERCENTOF Function to Simplify Percentage Calculations in Excel
Mar 27, 2025 am 03:03 AM
Use the PERCENTOF Function to Simplify Percentage Calculations in Excel
Mar 27, 2025 am 03:03 AM
Excel's PERCENTOF function: Easily calculate the proportion of data subsets Excel's PERCENTOF function can quickly calculate the proportion of data subsets in the entire data set, avoiding the hassle of creating complex formulas. PERCENTOF function syntax The PERCENTOF function has two parameters: =PERCENTOF(a,b) in: a (required) is a subset of data that forms part of the entire data set; b (required) is the entire dataset. In other words, the PERCENTOF function calculates the percentage of the subset a to the total dataset b. Calculate the proportion of individual values using PERCENTOF The easiest way to use the PERCENTOF function is to calculate the single
 If You Don't Rename Tables in Excel, Today's the Day to Start
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:58 AM
If You Don't Rename Tables in Excel, Today's the Day to Start
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:58 AM
Quick link Why should tables be named in Excel How to name a table in Excel Excel table naming rules and techniques By default, tables in Excel are named Table1, Table2, Table3, and so on. However, you don't have to stick to these tags. In fact, it would be better if you don't! In this quick guide, I will explain why you should always rename tables in Excel and show you how to do this. Why should tables be named in Excel While it may take some time to develop the habit of naming tables in Excel (if you don't usually do this), the following reasons illustrate today
 How to Format a Spilled Array in Excel
Apr 10, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
How to Format a Spilled Array in Excel
Apr 10, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
Use formula conditional formatting to handle overflow arrays in Excel Direct formatting of overflow arrays in Excel can cause problems, especially when the data shape or size changes. Formula-based conditional formatting rules allow automatic formatting to be adjusted when data parameters change. Adding a dollar sign ($) before a column reference applies a rule to all rows in the data. In Excel, you can apply direct formatting to the values or background of a cell to make the spreadsheet easier to read. However, when an Excel formula returns a set of values (called overflow arrays), applying direct formatting will cause problems if the size or shape of the data changes. Suppose you have this spreadsheet with overflow results from the PIVOTBY formula,
 How to Use Excel's AGGREGATE Function to Refine Calculations
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:54 AM
How to Use Excel's AGGREGATE Function to Refine Calculations
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:54 AM
Quick Links The AGGREGATE Syntax




