Evaluating Toxicity in Large Language Models
This article explores the crucial issue of toxicity in Large Language Models (LLMs) and the methods used to evaluate and mitigate it. LLMs, powering various applications from chatbots to content generation, necessitate robust evaluation metrics, with toxicity assessment being paramount. Toxicity encompasses harmful, offensive, or inappropriate outputs, including hate speech, threats, and misinformation. The article emphasizes the complexities of measuring toxicity due to its inherent subjectivity and cultural variations.
Key Learning Points:
- Understanding Toxicity: The article defines toxicity in LLMs and its real-world consequences.
- Multifaceted Nature of Toxicity: It highlights the diverse dimensions of toxicity, including hate speech, harassment, violent content, and misinformation.
- Evaluation Methods: The article details various approaches, from human evaluation (the gold standard, though resource-intensive) to automated metrics using classifiers like Perspective API and Detoxify, and red-teaming techniques.
- Challenges in Measurement: It addresses the significant hurdles in accurately assessing toxicity, such as context dependency, cultural differences, subjective interpretations, and the ever-evolving nature of toxic language.
- Innovative Approaches: The article discusses advancements like contextual embedding analysis, multi-stage evaluation frameworks, and self-evaluation capabilities in LLMs.
- Practical Implementation: It outlines a practical implementation plan, including pre-deployment evaluation, runtime monitoring, and a continuous improvement cycle involving model retraining and A/B testing.
- Standards and Benchmarks: The article mentions key benchmarks like ToxiGen and RealToxicityPrompts for standardized model evaluation.
- Ethical Considerations: It underscores the ethical implications of toxicity assessment, particularly concerning annotator well-being and bias mitigation.
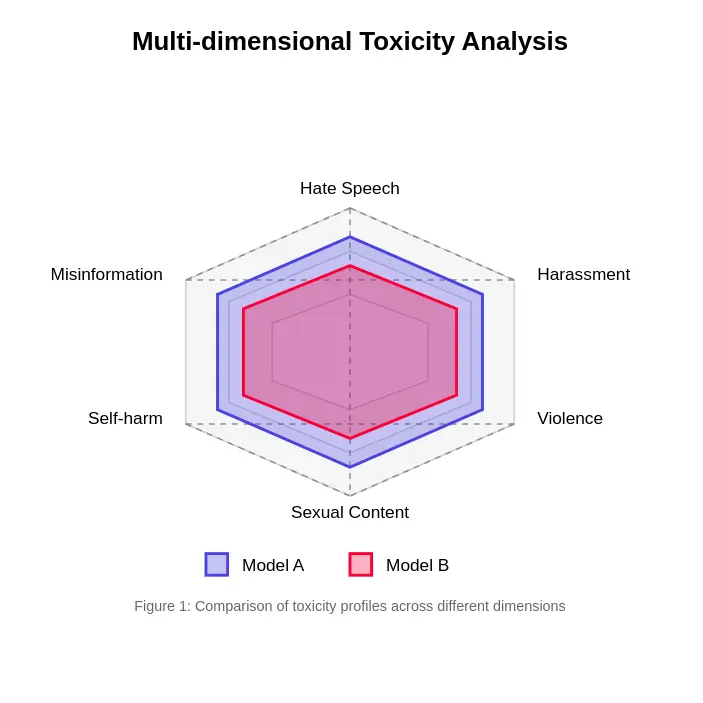
The article concludes by emphasizing the need for sophisticated and evolving evaluation methods to ensure the safe and responsible deployment of LLMs. A frequently asked questions section provides concise answers to key queries regarding toxicity in LLMs.
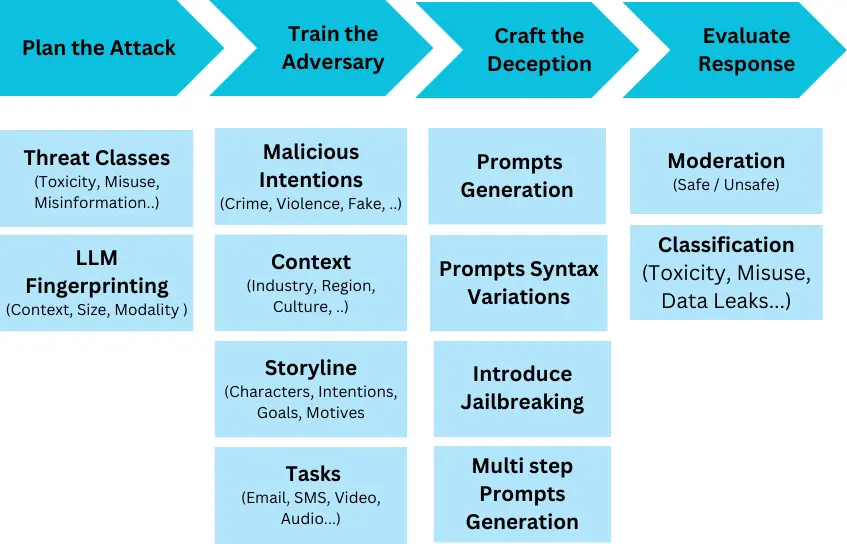

The provided code snippets illustrate aspects of automated toxicity detection and monitoring within an LLM application. An example JSON response snippet demonstrates how toxicity scores might be integrated into the output structure. The article comprehensively addresses the technical and ethical challenges in ensuring the safe and beneficial development of LLMs.
The above is the detailed content of Evaluating Toxicity in Large Language Models. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
The article reviews top AI art generators, discussing their features, suitability for creative projects, and value. It highlights Midjourney as the best value for professionals and recommends DALL-E 2 for high-quality, customizable art.
 Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Meta's Llama 3.2: A Leap Forward in Multimodal and Mobile AI Meta recently unveiled Llama 3.2, a significant advancement in AI featuring powerful vision capabilities and lightweight text models optimized for mobile devices. Building on the success o
 Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
The article compares top AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude, focusing on their unique features, customization options, and performance in natural language processing and reliability.
 Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
ChatGPT 4 is currently available and widely used, demonstrating significant improvements in understanding context and generating coherent responses compared to its predecessors like ChatGPT 3.5. Future developments may include more personalized interactions and real-time data processing capabilities, further enhancing its potential for various applications.
 Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
The article discusses top AI writing assistants like Grammarly, Jasper, Copy.ai, Writesonic, and Rytr, focusing on their unique features for content creation. It argues that Jasper excels in SEO optimization, while AI tools help maintain tone consist
 Choosing the Best AI Voice Generator: Top Options Reviewed
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
Choosing the Best AI Voice Generator: Top Options Reviewed
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
The article reviews top AI voice generators like Google Cloud, Amazon Polly, Microsoft Azure, IBM Watson, and Descript, focusing on their features, voice quality, and suitability for different needs.
 Top 7 Agentic RAG System to Build AI Agents
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:25 PM
Top 7 Agentic RAG System to Build AI Agents
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:25 PM
2024 witnessed a shift from simply using LLMs for content generation to understanding their inner workings. This exploration led to the discovery of AI Agents – autonomous systems handling tasks and decisions with minimal human intervention. Buildin
 How to Access Falcon 3? - Analytics Vidhya
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:41 PM
How to Access Falcon 3? - Analytics Vidhya
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:41 PM
Falcon 3: A Revolutionary Open-Source Large Language Model Falcon 3, the latest iteration in the acclaimed Falcon series of LLMs, represents a significant advancement in AI technology. Developed by the Technology Innovation Institute (TII), this open






