 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 4 methods of Javascript asynchronous programming to help you write better programs_javascript skills
4 methods of Javascript asynchronous programming to help you write better programs_javascript skills
4 methods of Javascript asynchronous programming to help you write better programs_javascript skills
As you may know, the execution environment of the Javascript language is "single thread".
The so-called "single thread" means that only one task can be completed at a time. If there are multiple tasks, they must be queued. After the previous task is completed, the next task will be executed, and so on. 
The advantage of this mode is that it is relatively simple to implement and the execution environment is relatively simple; the disadvantage is that as long as one task takes a long time, subsequent tasks must be queued up, which will delay the entire program. implement. Common browser unresponsiveness (suspended death) is often caused by a certain piece of Javascript code running for a long time (such as an infinite loop), causing the entire page to get stuck in this place and other tasks cannot be performed.
In order to solve this problem, the Javascript language divides the task execution mode into two types: Synchronous (Synchronous) and asynchronous (Asynchronous) .
"Synchronous mode" is the mode in the previous paragraph. The latter task waits for the previous task to end before executing it. The execution order of the program is consistent and synchronous with the order of tasks; "Asynchronous mode" is Completely different. Each task has one or more callback functions. After the previous task ends, the callback function is executed instead of the next task. The latter task is executed before the previous task ends, so The execution order of the program is inconsistent and asynchronous with the order of tasks. 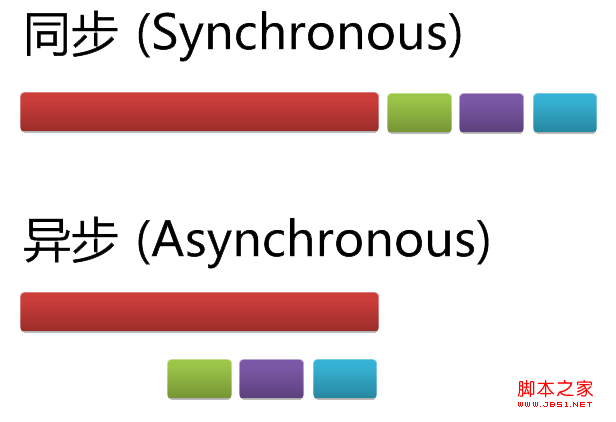
"Asynchronous mode" is very important. On the browser side, long-running operations should be performed asynchronously to avoid the browser becoming unresponsive. The best example is Ajax operations. On the server side, "asynchronous mode" is even the only mode, because the execution environment is single-threaded, and if all http requests are allowed to be executed synchronously, the server performance will drop drastically and it will become unresponsive very quickly.
This article summarizes 4 methods of "asynchronous mode" programming. Understanding them will allow you to write Javascript programs with a more reasonable structure, better performance, and easier maintenance.
1. Callback function
This is the most basic method of asynchronous programming.
Suppose there are two functions f1 and f2, and the latter waits for the execution result of the former.
f1();
f2();
If f1 is a time-consuming task, you can consider rewriting f1 and writing f2 as the callback function of f1.
function f1(callback){
setTimeout(function () {
// f1’s task code
callback();
}, 1000);
}
The execution code becomes as follows:
f1(f2);
In this way, we turn the synchronous operation into an asynchronous operation. F1 will not block the running of the program. It is equivalent to executing the main logic of the program first and postponing the execution of time-consuming operations.
The advantage of the callback function is that it is simple, easy to understand and deploy. The disadvantage is that it is not conducive to the reading and maintenance of the code. The various parts are highly coupled (Coupling), the process will be very confusing, and each task can only be specified A callback function.
2. Event monitoring
Another way of thinking is to use the event-driven model. The execution of a task does not depend on the order of the code, but on whether an event occurs.
Let’s take f1 and f2 as an example. First, bind an event to f1 (jQuery is used here).
f1.on('done', f2);
The above line of code means that when the done event occurs in f1, f2 will be executed. Then, rewrite f1:
function f1(){
SetTimeout(function () {
// f1’s task code
f1.trigger('done');
}, 1000);
f1.trigger('done') means that after the execution is completed, the done event will be triggered immediately to start executing f2.
The advantage of this method is that it is relatively easy to understand, can bind multiple events, each event can specify multiple callback functions, and can be "decoupled", which is conducive to modularization. The disadvantage is that the entire program must become event-driven, and the running process will become very unclear.
3. Publish/Subscribe
The "event" in the previous section can be understood as a "signal".
We assume that there is a "signal center". When a certain task is executed, it "publish" a signal to the signal center. Other tasks can "subscribe" to the signal from the signal center to know what it is. You can start executing it yourself. This is called the "publish-subscribe pattern" (publish-subscribe pattern), also known as the "observer pattern" (observer pattern).
There are many implementations of this pattern. The one used below is Ben Alman’s Tiny Pub/Sub, which is a plug-in for jQuery.
First, f2 subscribes to the "done" signal from "Signal Center" jQuery.
jQuery.subscribe("done", f2);
Then, f1 is rewritten as follows:
function f1(){
setTimeout(function () {
// f1’s task code
jQuery.publish("done");
jQuery.publish("done") means that after the execution of f1 is completed, the "done" signal is released to the "signal center" jQuery, thereby triggering the execution of f2.
The nature of this method is similar to "event listening", but it is obviously better than the latter. Because we can monitor the operation of the program by looking at the "Message Center" to see how many signals exist and how many subscribers each signal has.
4. Promises object
The Promises object is a specification proposed by the CommonJS working group to provide a unified interface for asynchronous programming. Simply put, the idea is that each asynchronous task returns a Promise object, which has a then method that allows a callback function to be specified. For example, the callback function f2 of f1 can be written as:
f1 needs to be rewritten as follows (the jQuery implementation is used here):
setTimeout(function () {
/ / f1’s task code
dfd.resolve();
}, 500);
return dfd.promise; The function has become a chain writing method, the program flow can be seen clearly, and there is a complete set of supporting methods that can realize many powerful functions.
For example, specify multiple callback functions:
Copy the code

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to implement asynchronous programming with C++ functions?
Apr 27, 2024 pm 09:09 PM
How to implement asynchronous programming with C++ functions?
Apr 27, 2024 pm 09:09 PM
Summary: Asynchronous programming in C++ allows multitasking without waiting for time-consuming operations. Use function pointers to create pointers to functions. The callback function is called when the asynchronous operation completes. Libraries such as boost::asio provide asynchronous programming support. The practical case demonstrates how to use function pointers and boost::asio to implement asynchronous network requests.
 How to use ReactPHP for asynchronous programming in PHP
Jun 27, 2023 am 09:14 AM
How to use ReactPHP for asynchronous programming in PHP
Jun 27, 2023 am 09:14 AM
As web applications become more complex, programmers are forced to adopt asynchronous programming to handle large numbers of requests and I/O operations. PHP: HypertextPreprocessor is no exception. To meet this need, ReactPHP has become one of the most popular asynchronous programming frameworks for PHP. In this article, we will discuss how to do asynchronous programming in PHP using ReactPHP. 1. Introduction to ReactPHP ReactPHP is an event-driven programming
 Asynchronous Programming of JavaScript Functions: Essential Tips for Handling Complex Tasks
Nov 18, 2023 am 10:06 AM
Asynchronous Programming of JavaScript Functions: Essential Tips for Handling Complex Tasks
Nov 18, 2023 am 10:06 AM
JavaScript Function Asynchronous Programming: Essential Skills for Handling Complex Tasks Introduction: In modern front-end development, handling complex tasks has become an indispensable part. JavaScript function asynchronous programming skills are the key to solving these complex tasks. This article will introduce the basic concepts and common practical methods of JavaScript function asynchronous programming, and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand and use these techniques. 1. Basic concepts of asynchronous programming In traditional synchronous programming, the code is
 How to implement asynchronous message handling in PHP
Jul 10, 2023 am 08:19 AM
How to implement asynchronous message handling in PHP
Jul 10, 2023 am 08:19 AM
How to implement asynchronous message processing in PHP Introduction: In modern web applications, asynchronous message processing is becoming more and more important. Asynchronous message processing can improve the performance and scalability of the system and improve the user experience. As a commonly used server-side programming language, PHP can also implement asynchronous message processing through some technologies. In this article, we will introduce some methods of implementing asynchronous message processing in PHP and provide code examples. Using Message Queuing Message Queuing is a way of decoupling system components, allowing different components to
 In-depth understanding of the new features of PHP8: How to use asynchronous programming and code efficiently?
Sep 11, 2023 pm 01:52 PM
In-depth understanding of the new features of PHP8: How to use asynchronous programming and code efficiently?
Sep 11, 2023 pm 01:52 PM
In-depth understanding of the new features of PHP8: How to use asynchronous programming and code efficiently? PHP8 is the latest major version of the PHP programming language, bringing many exciting new features and improvements. One of the most prominent features is support for asynchronous programming. Asynchronous programming allows us to improve performance and responsiveness when dealing with concurrent tasks. This article will take an in-depth look at PHP8’s asynchronous programming features and introduce how to use them efficiently. First, let’s understand what asynchronous programming is. In the traditional synchronous programming model, code follows a linear sequence
 Common problems and solutions in asynchronous programming in Java framework
Jun 04, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
Common problems and solutions in asynchronous programming in Java framework
Jun 04, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
3 common problems and solutions in asynchronous programming in Java frameworks: Callback Hell: Use Promise or CompletableFuture to manage callbacks in a more intuitive style. Resource contention: Use synchronization primitives (such as locks) to protect shared resources, and consider using thread-safe collections (such as ConcurrentHashMap). Unhandled exceptions: Explicitly handle exceptions in tasks and use an exception handling framework (such as CompletableFuture.exceptionally()) to handle exceptions.
 How does the golang framework handle concurrency and asynchronous programming?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 07:49 PM
How does the golang framework handle concurrency and asynchronous programming?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 07:49 PM
The Go framework uses Go's concurrency and asynchronous features to provide a mechanism for efficiently handling concurrent and asynchronous tasks: 1. Concurrency is achieved through Goroutine, allowing multiple tasks to be executed at the same time; 2. Asynchronous programming is implemented through channels, which can be executed without blocking the main thread. Task; 3. Suitable for practical scenarios, such as concurrent processing of HTTP requests, asynchronous acquisition of database data, etc.
 Python asynchronous programming: A way to achieve efficient concurrency in asynchronous code
Feb 26, 2024 am 10:00 AM
Python asynchronous programming: A way to achieve efficient concurrency in asynchronous code
Feb 26, 2024 am 10:00 AM
1. Why use asynchronous programming? Traditional programming uses blocking I/O, which means that the program waits for an operation to complete before continuing. This may work well for a single task, but may cause the program to slow down when processing a large number of tasks. Asynchronous programming breaks the limitations of traditional blocking I/O and uses non-blocking I/O, which means that the program can distribute tasks to different threads or event loops for execution without waiting for the task to complete. This allows the program to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, improving the program's performance and efficiency. 2. The basis of Python asynchronous programming The basis of Python asynchronous programming is coroutines and event loops. Coroutines are functions that allow a function to switch between suspending and resuming. The event loop is responsible for scheduling





