 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Ten quick ways to improve JQuery performance to make your JQuery run faster_jquery
Ten quick ways to improve JQuery performance to make your JQuery run faster_jquery
Ten quick ways to improve JQuery performance to make your JQuery run faster_jquery
This article provides ten steps to instantly improve the performance of your scripts. Don't worry, this isn't a rocket science technique. Everyone can use it! These tips include:
Use the latest version
Merge, minimize scripts
Replace each with for
Use ID replaces class selector
Specify context for the selector
Create cache
Avoid DOM operations
Avoid using concat() and use join() to process long strings
Return false value
Use cheat sheets and reference documents
Use the latest version
jQuery is under constant development and improvement. John and his team are constantly researching new ways to improve program performance.
A little digression, a few months ago he also released Sizzle, a JS selector library that is said to improve program performance by 3 times in Firefox.
If you don’t want to keep track of whether there is a new version and then spend time downloading and uploading it, Google can help you again. There are tons of Ajax libraries stored on their servers for you to choose from.
Another simpler and faster method is to use script linking directly. If you want to use a specific version of jQuery, you can use the above method; if you want to use the latest version directly, the following code is enough:
Specific versions can also be loaded like this:
Merge and minimize scripts
Most browsers cannot handle multiple script files at the same time, so they are queued to load - load The time was extended accordingly.
Considering that every page of your site will load these scripts, you should consider putting them into a single file and minimizing them using a compression tool (such as this one from Dean Edwards). Smaller files will undoubtedly result in faster loading times.
The purpose of JavaScript and CSS compression is to reduce the number of bytes of data transfer while maintaining script execution performance (either by reducing the original file or by using gzip. Most production-level network servers use gzip as part of the HTTP protocol). Quoted from YUI compressor, a tool for compressing scripts officially recommended by jQuery.
Replace each with for
Native functions are always faster than helper components.
If you encounter a situation where you need to traverse an object (such as a JSON object received from a remote location), you'd better rewrite your (JSON) object as an array. The loop processing of the array is easier.
Using Firebug, we can measure the execution time of each function.
var array = new Array ();
for (var i=0; i<10000; i ) {
array[i] = 0;
}
console.time('native'); //Native for function
var l = array.length;
for (var i=0; i<10000; i ) {
}
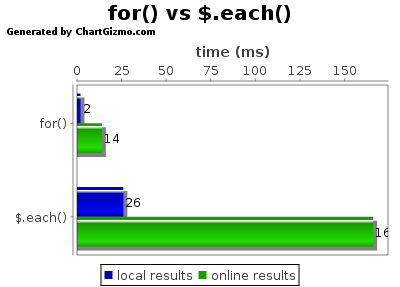
The above results show that what the native code can do in just 2 milliseconds, it takes 26 milliseconds to use jQuery's each method. And this is just the result of me testing a function that basically does nothing on this machine. When encountering more complex situations, such as setting css properties or DOM operations, the time difference is definitely greater.
Use ID instead of class selector
It is much better to use ID to select objects, because then jQuery will use the browser's native function getElementByID() to obtain the object, and the query speed is very fast.
Therefore, rather than using those convenient CSS selection techniques, it is worthwhile to use more complex selectors (jQuery also provides us with complex selectors). You can also write your own selector by hand (it's easier than you think), or specify a container with an ID for the element you want to select.
//The following example creates a list and fills in the entry content
//Then each entry is selected once
//First use class selection
console.time('class');
var list = $('#list');
var items = '
';
for (i=0; i<1000; i ) {
items = '
item
';
}
items = '
';
list.html (items);
for (i=0; i<1000; i ) {
var s = $('.item' i);
}
console.timeEnd('class');
//Then use ID to select
console.time('id');
var list = $('#list');
var items = '
';
for (i=0; i<1000; i ) {
items = '
item
';
}
items = '
';
list.html (items);
for (i=0; i<1000; i ) {
var s = $('#item' i);
}
console.timeEnd('id');
The above example nicely illustrates the significant performance difference between different selection methods. Please see the picture below. Using class to make selections, the time increases infinitely, even exceeding five seconds.
Specify context for the selector
The jQuery reference documentation says: The context of the original DOM node passed to jQuery() (if nothing is passed, the context is the entire document). The purpose is to achieve more accurate queries together with selectors.
So, if you must use class to specify the target, at least specify the context for the selector so that jQuery does not waste energy traversing the entire DOM document:
Instead of writing like this:
$('.class').css ('color' '#123456');
It is better to add context to the selector (expression: target selector; context: context):
$(expression, context)
That is to say:
$('.class', '#class-container').css ('color', '#123456');
This is much faster because it doesn’t have to traverse the entire DOM. Just find #class-container.
Build a cache
Don’t make the mistake of constantly reselecting the same thing. You should cache the element you want to process as a variable.
Don’t select the same element repeatedly in a loop! This greatly affects the speed!
$('#item').css('color ', '#123456');
$('#item').html('hello');
$('#item').css('background-color', '#ffffff') ;
// It’s better to write this way
$('#item').css('color', '#123456').html('hello').css('background-color', '# ffffff');
// Even like this
var item = $('#item');
item.css('color', '#123456');
item.html(' hello');
item.css('background-color', '#ffffff');
// This is very bad when encountering a loop
console.time('no cache');
for (var i=0; i<1000; i ) {
$('#list').append(i);
}
console.timeEnd('no cache');
// The following is much better
console.time('cache');
var item = $('#list');
for (var i=0; i<1000; i ) {
item.append (i);
}
console.timeEnd('cache');
DOM 작업 방지
prepend(),append(),after()와 같은 삽입 작업에는 시간이 많이 걸리므로 DOM 작업은 가능한 한 적어야 합니다. 위의 예는 html()을 사용하면 더 빠릅니다.
var list = '';
for (var i=0; i<1000; i ) {
list = '
' i '
'; 🎜>('# list').html (list);
긴 문자열을 처리하려면 concat() 사용을 피하고 Join()을 사용하세요.
' i ''
}
$('#list').html(array .join ( ''));
" = 연산자는 더 빠릅니다 - 문자열 조각을 배열에 넣은 다음 함께 결합하는 것보다 빠릅니다.", "문자열 버퍼로 배열 string.prototype보다 효율적입니다. Windows의 Firefox 2.0.0.14를 제외한 대부분의 브라우저에서 .concat.apply 메서드. " — Tom Trenka
false 값을 반환합니다.
그래서
문장을 하나 더 추가하는 것은 어떻습니까:
})
추가 팁 – 치트 시트 및 참조 문서
이 제안은 기능의 실행 속도는 빠르지만, 기꺼이 시간을 내어 이 치트 시트와 참조 문서를 공부하면 앞으로 많은 시간을 절약할 수 있습니다.
빠른 참조를 위해 항상 치트 시트를 가까이에 보관하세요.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 Windows 10 vs. Windows 11 performance comparison: Which one is better?
Mar 28, 2024 am 09:00 AM
Windows 10 vs. Windows 11 performance comparison: Which one is better?
Mar 28, 2024 am 09:00 AM
Windows 10 vs. Windows 11 performance comparison: Which one is better? With the continuous development and advancement of technology, operating systems are constantly updated and upgraded. As one of the world's largest operating system developers, Microsoft's Windows series of operating systems have always attracted much attention from users. In 2021, Microsoft released the Windows 11 operating system, which triggered widespread discussion and attention. So, what is the difference in performance between Windows 10 and Windows 11? Which
 Comparing the performance of Win11 and Win10 systems, which one is better?
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
Comparing the performance of Win11 and Win10 systems, which one is better?
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
The Windows operating system has always been one of the most widely used operating systems on personal computers, and Windows 10 has long been Microsoft's flagship operating system until recently when Microsoft launched the new Windows 11 system. With the launch of Windows 11 system, people have become interested in the performance differences between Windows 10 and Windows 11 systems. Which one is better between the two? First, let’s take a look at W
 Comparison of PHP and Go languages: big performance difference
Mar 26, 2024 am 10:48 AM
Comparison of PHP and Go languages: big performance difference
Mar 26, 2024 am 10:48 AM
PHP and Go are two commonly used programming languages, and they have different characteristics and advantages. Among them, performance difference is an issue that everyone is generally concerned about. This article will compare PHP and Go languages from a performance perspective, and demonstrate their performance differences through specific code examples. First, let us briefly introduce the basic features of PHP and Go language. PHP is a scripting language originally designed for web development. It is easy to learn and use and is widely used in the field of web development. The Go language is a compiled language developed by Google.
 Performance comparison of different Java frameworks
Jun 05, 2024 pm 07:14 PM
Performance comparison of different Java frameworks
Jun 05, 2024 pm 07:14 PM
Performance comparison of different Java frameworks: REST API request processing: Vert.x is the best, with a request rate of 2 times SpringBoot and 3 times Dropwizard. Database query: SpringBoot's HibernateORM is better than Vert.x and Dropwizard's ORM. Caching operations: Vert.x's Hazelcast client is superior to SpringBoot and Dropwizard's caching mechanisms. Suitable framework: Choose according to application requirements. Vert.x is suitable for high-performance web services, SpringBoot is suitable for data-intensive applications, and Dropwizard is suitable for microservice architecture.
 The local running performance of the Embedding service exceeds that of OpenAI Text-Embedding-Ada-002, which is so convenient!
Apr 15, 2024 am 09:01 AM
The local running performance of the Embedding service exceeds that of OpenAI Text-Embedding-Ada-002, which is so convenient!
Apr 15, 2024 am 09:01 AM
Ollama is a super practical tool that allows you to easily run open source models such as Llama2, Mistral, and Gemma locally. In this article, I will introduce how to use Ollama to vectorize text. If you have not installed Ollama locally, you can read this article. In this article we will use the nomic-embed-text[2] model. It is a text encoder that outperforms OpenAI text-embedding-ada-002 and text-embedding-3-small on short context and long context tasks. Start the nomic-embed-text service when you have successfully installed o
 PHP array key value flipping: Comparative performance analysis of different methods
May 03, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
PHP array key value flipping: Comparative performance analysis of different methods
May 03, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
The performance comparison of PHP array key value flipping methods shows that the array_flip() function performs better than the for loop in large arrays (more than 1 million elements) and takes less time. The for loop method of manually flipping key values takes a relatively long time.
 What impact do C++ functions have on program performance?
Apr 12, 2024 am 09:39 AM
What impact do C++ functions have on program performance?
Apr 12, 2024 am 09:39 AM
The impact of functions on C++ program performance includes function call overhead, local variable and object allocation overhead: Function call overhead: including stack frame allocation, parameter transfer and control transfer, which has a significant impact on small functions. Local variable and object allocation overhead: A large number of local variable or object creation and destruction can cause stack overflow and performance degradation.
 How to optimize the performance of multi-threaded programs in C++?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 02:04 PM
How to optimize the performance of multi-threaded programs in C++?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 02:04 PM
Effective techniques for optimizing C++ multi-threaded performance include limiting the number of threads to avoid resource contention. Use lightweight mutex locks to reduce contention. Optimize the scope of the lock and minimize the waiting time. Use lock-free data structures to improve concurrency. Avoid busy waiting and notify threads of resource availability through events.



