 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Determine whether reference type objects such as Object, Array, and Function are equal in js_javascript skills
Determine whether reference type objects such as Object, Array, and Function are equal in js_javascript skills
Determine whether reference type objects such as Object, Array, and Function are equal in js_javascript skills
During iteration, we also need to note that the element in the object or array may be an arbitrary value - in addition to primitive type values, objects, arrray, this value may also be a method, a DOM object or a window object, possibly You have noticed that some reference types cannot be iterated and require branch judgment. The code is as follows:
function compare(a,b){
var
pt = /undefined|number|string|boolean/,
fn = /^(functions*)(w *b)/,
cr = "constructor",
cn = "childNodes",
pn = "parentNode",
ce = arguments.callee;
if(pt.test( typeof a) || pt.test(typeof b) || a === null || b === null){
return a === b || (isNaN(a) && isNaN(b)) ; //For convenience, it is assumed here that NaN == NaN
}
if(a[cr] !== b[cr]){
return false;
}
switch( a[cr]){
case Date : {
return a.valueOf() === b.valueOf();
};
case Function : {
return a.toString ().replace(fn,'$1') === b.toString().replace(fn,'$1'); //The way the function is declared in hard coding will affect the result of toString, so use regular formatting
};
case Array : {
if(a.length !== b.length){
return false;
}
for(var i=0;i< ;a.length;i ){
if(!ce(a[i],b[i])){
return false;
}
}
break;
};
default : {
var alen = 0, blen = 0, d;
if(a === b){
return true;
}
if(a [cn] || a[pn] || b[cn] || b[pn]){
return a === b;
}
for(d in a){
alen ;
}
for(d in b){
blen ;
}
if(alen !== blen){
return false;
}
for(d in a){
if(!ce(a[d],b[d])){
return false;
}
}
break;
} ;
}
return true;
}
console.log(compare({},{a:1})); //false
console.log(compare({a: 1},{b:2})); //false
console.log(compare({b:2,a:1},{a:1,b:2})); //true
console.log(compare({a:function(){return false;},b:2},{a:function(){return false;},b:2})); //true
console .log(compare([],[])); //true
console.log(compare([2,1],[1,2])); //false
console.log(compare (function(){alert(1)},function(){})); //false
console.log(compare(function aaa(){alert(1)},function(){alert(1) })); //true
console.log(compare(document.getElementsByTagName("a")[0],document.getElementsByTagName("a")[1])); //false
console. log(compare(document.getElementsByTagName("a")[0],document.getElementsByTagName("a")[0])); //true

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 What does function mean?
Aug 04, 2023 am 10:33 AM
What does function mean?
Aug 04, 2023 am 10:33 AM
Function means function. It is a reusable code block with specific functions. It is one of the basic components of a program. It can accept input parameters, perform specific operations, and return results. Its purpose is to encapsulate a reusable block of code. code to improve code reusability and maintainability.
 Sort array using Array.Sort function in C#
Nov 18, 2023 am 10:37 AM
Sort array using Array.Sort function in C#
Nov 18, 2023 am 10:37 AM
Title: Example of using the Array.Sort function to sort an array in C# Text: In C#, array is a commonly used data structure, and it is often necessary to sort the array. C# provides the Array class, which has the Sort method to conveniently sort arrays. This article will demonstrate how to use the Array.Sort function in C# to sort an array and provide specific code examples. First, we need to understand the basic usage of the Array.Sort function. Array.So
 What is the purpose of the 'enumerate()' function in Python?
Sep 01, 2023 am 11:29 AM
What is the purpose of the 'enumerate()' function in Python?
Sep 01, 2023 am 11:29 AM
In this article, we will learn about enumerate() function and the purpose of “enumerate()” function in Python. What is the enumerate() function? Python's enumerate() function accepts a data collection as a parameter and returns an enumeration object. Enumeration objects are returned as key-value pairs. The key is the index corresponding to each item, and the value is the items. Syntax enumerate(iterable,start) Parameters iterable - The passed in data collection can be returned as an enumeration object, called iterablestart - As the name suggests, the starting index of the enumeration object is defined by start. if we ignore
 Detailed explanation of the role and function of the MySQL.proc table
Mar 16, 2024 am 09:03 AM
Detailed explanation of the role and function of the MySQL.proc table
Mar 16, 2024 am 09:03 AM
Detailed explanation of the role and function of the MySQL.proc table. MySQL is a popular relational database management system. When developers use MySQL, they often involve the creation and management of stored procedures (StoredProcedure). The MySQL.proc table is a very important system table. It stores information related to all stored procedures in the database, including the name, definition, parameters, etc. of the stored procedures. In this article, we will explain in detail the role and functionality of the MySQL.proc table
 Simple and clear method to use PHP array_merge_recursive() function
Jun 27, 2023 pm 01:48 PM
Simple and clear method to use PHP array_merge_recursive() function
Jun 27, 2023 pm 01:48 PM
When programming in PHP, we often need to merge arrays. PHP provides the array_merge() function to complete array merging, but when the same key exists in the array, this function will overwrite the original value. In order to solve this problem, PHP also provides an array_merge_recursive() function in the language, which can merge arrays and retain the values of the same keys, making the program design more flexible. array_merge
 How to use the array_combine function in PHP to combine two arrays into an associative array
Jun 26, 2023 pm 01:41 PM
How to use the array_combine function in PHP to combine two arrays into an associative array
Jun 26, 2023 pm 01:41 PM
In PHP, there are many powerful array functions that can make array operations more convenient and faster. When we need to combine two arrays into an associative array, we can use PHP's array_combine function to achieve this operation. This function is actually used to combine the keys of one array as the values of another array into a new associative array. Next, we will explain how to use the array_combine function in PHP to combine two arrays into an associative array. Learn about array_comb
 What are the methods of converting java Object to byte and byte to Object?
Apr 20, 2023 am 11:37 AM
What are the methods of converting java Object to byte and byte to Object?
Apr 20, 2023 am 11:37 AM
Object to byte and byte to Object Today we will realize how to convert from Object to byte and how to convert from byte to Object. First, define a class student: packagecom.byteToObject;importjava.io.Serializable;publicclassstudentimplementsSerializable{privateintsid;privateStringname;publicintgetSid(){returnsid;}publicvoidsetSid(in
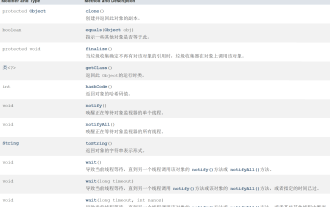 How to use methods in Java Object class
Apr 18, 2023 pm 06:13 PM
How to use methods in Java Object class
Apr 18, 2023 pm 06:13 PM
1. Introduction to the Object class Object is a class provided by Java by default. Except for the Object class, all classes in Java have inheritance relationships. By default, it will inherit the Object parent class. That is, objects of all classes can be received using the reference of Object. Example: Use Object to receive objects of all classes classPerson{}classStudent{}publicclassTest{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){function(newPerson());function(newStudent());}public



