 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Modular programming based on RequireJS and JQuery - comprehensive analysis of common problems_javascript skills
Modular programming based on RequireJS and JQuery - comprehensive analysis of common problems_javascript skills
Modular programming based on RequireJS and JQuery - comprehensive analysis of common problems_javascript skills
As the code logic of js is getting heavier and heavier, a js file may have thousands of lines, which is very unfavorable for development and maintenance. Recently, I am splitting the logic-heavy JS into modules. When I was struggling with whether to use requirejs or seajs, I finally preferred requirejs. After all, official documents are more professional...
However, even with complete official documentation, we still encounter many problems, such as the use of jquery-ui.
The following is a step-by-step explanation of the problems I encountered and the solutions.
Understanding of AMD and CMD
A typical example of AMD (asynchronous module definition) is requirejs, while a typical example of CMD (common module definition) is Taobao's seajs.
What they have in common is that they both load js asynchronously. But the difference is that require.js will be executed immediately after loading; while seajs will not be executed until it enters the main function and needs to be executed.
If you use seajs, the initial loading and execution efficiency will be higher, but js may be fetched and executed during use, so lags may occur and affect the user experience (I have not tried it, so if I am wrong, Don’t be surprised). And requirejs executes all loaded js at the beginning. At this time, if there are some execution methods in your module, they may not be executed in the order you want.
Therefore, if you are used to asynchronous programming and want to have complete documentation, it is recommended to use requirejs; if you want to have special requirements for the execution order and facilitate development, you can also use seajs.
How to solve the circular dependency problem in requirejs
If a module a you define uses module b, and module b uses module a, then a circular dependency exception will be thrown.
For example, I wrote an example of circular dependency here.
Main page:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body> <script data-main="test.js" src="lib/require.js"></script> </body> </html>
Main method:
requirejs.config({
baseUrl: './'
});
requirejs(['js/a'],function (a){
console.log("in test");
a.testfromb();
});In the a.js module, the test() method provides the method of calling b, and the testfromb() method calls the method of b
define(function(require){
var b = require("js/b");
console.log("in a");
return {
atest:function(){
console.log("test in a");
},
testfromb:function(){
console.log("testfromb in a");
b.btest();
}
}
});In module b, the method of a is called.
define(function(require){
var a = require("js/a");
console.log("in b");
return {
btest:function(){
console.log("test in b");
a.atest();
}
}
});This is equivalent to a calling b's method, but b's method depends on a's method, which creates a circular dependency. The browser will prompt an error:
Uncaught Error: Module name "js/a" has not been loaded yet for context: _
According to the official documentation, this is a design problem and should be avoided as much as possible. So what should you do if you can't avoid it? Module b can be modified like this:
define(function(require){
// var a = require("js/a");
console.log("in b");
return {
btest:function(){
console.log("test in b");
require("js/a").atest();
}
}
});Here is to wait until the test() method is executed before loading the a module. At this time, module a has obviously been loaded. You can see the output information:
in b a.js:3 in a test.js:6 in test a.js:9 testfromb in a b.js:6 test in b a.js:6 test in a
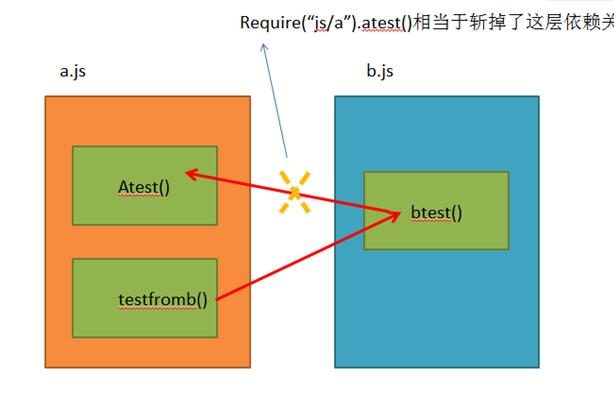
In the same way, it may not work if you modify a. This is because the order of module loading starts from b.
For source code of circular dependencies, please refer to the cloud disk
How to use jquery in requirejs
If you want to use jquery relatively easily, just add the corresponding dependencies directly to main.js:
requirejs.config({
baseUrl: './',
paths:{
'jquery':'lib/jquery'
}
});
requirejs(['jquery'],
function ($){
$('#test').html('test');
});如何在requirejs中使用jquery插件 对于jquery的插件,比较常见的做法都是传入一个jquery的对象,在这个jquery对象的基础上添加插件对应的方法。 首先需要添加jquery插件的依赖,这里用两个插件举例子——jquery-ui和jquery-datatables
requirejs.config({
baseUrl: './',
paths:{
'jquery':'lib/jquery',
'jquery-ui':'lib/jquery-ui',
'jquery-dataTables':'lib/jquery.dataTables'
},
shim:{
'jquery-ui':['jquery'],
'jquery-dataTables':['jquery']
}
});
requirejs(['jquery','jquery-ui','jquery-dataTables'],
function ($){
....
});由于jquery插件都需要依赖于jquery,因此可以在shim中指定依赖关系。 除了上面这种使用方法,也可以使用commonJS风格的调用:
define(function(require){
var $ = require('jquery');
require('jquery-ui');
require('jquery-dataTables');
//下面都是测试,可以忽略
var _test = $('#test');
_test.selectmenu({
width : 180,
change : function(event, ui) {
console.log('change');
}
});
return {
test:function(){
//测试jquery-ui
_test.append($('<option>test1</option><option>test1</option>'));
_test.selectmenu("refresh");
//测试jquery-datatables
var _table = $('table');
_table.dataTable();
}
}
});However, when executing the above code, an exception will be reported:
Uncaught TypeError: _table.dataTable is not a function
This is because dataTables is not a require-style module, so if it is introduced directly like this, its internal anonymous functions will not be executed. You can modify its anonymous function, passing in the $ object, in the last line:
*/ return $.fn.dataTable; //}));原来是这样 }($)));//这里增加执行这个匿名函数,并且传入$对象。 }(window, document));
This is also a method of searching on the Internet, but the principle is due to lack of experience....
You can refer to the cloud disk for the sample code. Since the imported resources are not complete, an error will be reported and can be ignored. Because being able to execute the UI plug-in means it has been successful.
Problems using jquery-ui with requirejs
Since requirejs will be executed immediately after loading the js file, if your jquery ui plug-in needs to refresh the DOM page, it may cause the page's events to fail.
For example, after your module is loaded, a click event is bound to a certain element $('#test') on the page. However, if a certain UI plug-in is used, the plug-in will re-render the DOM element, and the click event corresponding to test will become invalid.
Solution:
•Delay event binding until the DOM element is rendered and then manually trigger the binding;
•Event capture can also be used instead of event binding of DOM elements (too troublesome...not recommended).
For example, in the DOM reconstructed JS module, the code that executes rendering is as follows:
require("xxx").initEvents(); Common scenarios:
For example, I use the jquery-steps UI plug-in on the page, which will re-render the page. This caused the events I originally bound to become invalid... I could only postpone binding until the js page was reconstructed and then bind again.
The above article - Modular Programming Based on RequireJS and JQuery - Comprehensive Analysis of Frequently Asked Questions is all the content shared by the editor. I hope it can give you a reference, and I hope you will support Script Home.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 Detailed explanation of jQuery reference methods: Quick start guide
Feb 27, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
Detailed explanation of jQuery reference methods: Quick start guide
Feb 27, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
Detailed explanation of jQuery reference method: Quick start guide jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used in website development. It simplifies JavaScript programming and provides developers with rich functions and features. This article will introduce jQuery's reference method in detail and provide specific code examples to help readers get started quickly. Introducing jQuery First, we need to introduce the jQuery library into the HTML file. It can be introduced through a CDN link or downloaded
 How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 am 08:39 AM
How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 am 08:39 AM
How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery? In front-end development, we often encounter the need to manipulate the height attributes of elements. Sometimes, we may need to dynamically change the height of an element, and sometimes we need to remove the height attribute of an element. This article will introduce how to use jQuery to remove the height attribute of an element and provide specific code examples. Before using jQuery to operate the height attribute, we first need to understand the height attribute in CSS. The height attribute is used to set the height of an element
 How to use PUT request method in jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to use PUT request method in jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to use PUT request method in jQuery? In jQuery, the method of sending a PUT request is similar to sending other types of requests, but you need to pay attention to some details and parameter settings. PUT requests are typically used to update resources, such as updating data in a database or updating files on the server. The following is a specific code example using the PUT request method in jQuery. First, make sure you include the jQuery library file, then you can send a PUT request via: $.ajax({u
 jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page
Feb 28, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page
Feb 28, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Title: jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page In web development, we often need to modify and operate elements on the page. When using jQuery, sometimes you need to modify the text content of all a tags in the page at once, which can save time and energy. The following will introduce how to use jQuery to quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page, and give specific code examples. First, we need to introduce the jQuery library file and ensure that the following code is introduced into the page: <
 In-depth analysis: jQuery's advantages and disadvantages
Feb 27, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
In-depth analysis: jQuery's advantages and disadvantages
Feb 27, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
jQuery is a fast, small, feature-rich JavaScript library widely used in front-end development. Since its release in 2006, jQuery has become one of the tools of choice for many developers, but in practical applications, it also has some advantages and disadvantages. This article will deeply analyze the advantages and disadvantages of jQuery and illustrate it with specific code examples. Advantages: 1. Concise syntax jQuery's syntax design is concise and clear, which can greatly improve the readability and writing efficiency of the code. for example,
 Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags
Feb 28, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags
Feb 28, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Title: Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags. jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used to handle DOM operations. In web development, we often encounter the need to modify the text content of the link tag (a tag) on the page. This article will explain how to use jQuery to achieve this goal, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to introduce the jQuery library into the page. Add the following code in the HTML file:
 How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute? When using jQuery to operate DOM elements, you often encounter situations where you need to determine whether an element has a specific attribute. In this case, we can easily implement this function with the help of the methods provided by jQuery. The following will introduce two commonly used methods to determine whether a jQuery element has specific attributes, and attach specific code examples. Method 1: Use the attr() method and typeof operator // to determine whether the element has a specific attribute
 Understand the role and application scenarios of eq in jQuery
Feb 28, 2024 pm 01:15 PM
Understand the role and application scenarios of eq in jQuery
Feb 28, 2024 pm 01:15 PM
jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used to handle DOM manipulation and event handling in web pages. In jQuery, the eq() method is used to select elements at a specified index position. The specific usage and application scenarios are as follows. In jQuery, the eq() method selects the element at a specified index position. Index positions start counting from 0, i.e. the index of the first element is 0, the index of the second element is 1, and so on. The syntax of the eq() method is as follows: $("s



