 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Use the most understandable code to help novices understand javascript closures. Recommended_javascript skills
Use the most understandable code to help novices understand javascript closures. Recommended_javascript skills
Use the most understandable code to help novices understand javascript closures. Recommended_javascript skills
I have recently read several articles about JavaScript closures, including the recently popular Uncle Tom series, and articles in "Javascript Advanced Programming"... I can't understand it. Some of the codes in it are from college textbooks. If you haven’t read it, it’s like a book from heaven. Fortunately, I recently came across two good books "ppk on javascript" and "object-oriented JavaScript". I am currently reading the latter. The latter does not have a Chinese version yet, but the former is still recommended to read the original version. The writing is not complicated. Friends who are interested can read it. Look, it’s suitable for friends who want to advance.
Today I will combine these two books and talk about closures in JavaScript in the simplest language and the most popular way. Since I am also a novice, please point out any mistakes. Thank you
1. Preparation Knowledge
1. Functions as parameters of functions
When learning JavaScript, you must always have a concept that is different from other languages : function (function) is not a special thing, it is also a kind of data, and bool, string, number are no different.
The parameters of the function can be string, number, bool, such as:
function(a, b) {return a b;}
But the function can also be passed in. You heard me right, the parameters of a function are functions! Join the following two functions:
//Place three Double the number
function multiplyByTwo(a, b, c) {
var i, ar = [];
for(i = 0; i < 3; i ) {
ar [i] = arguments[i] * 2;
}
return ar;
}
//Add the number by one
function addOne(a) {
return a 1;
}
Then use
var myarr = [] ;
//First multiply each number by two, using a loop
myarr = multiplyByTwo(10, 20, 30);
//Then add one to each number, using another Loop
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i ) {myarr[i] = addOne(myarr[i]);}
It should be noted that this process actually uses There is still room for improvement between the two loops, so why not do this:
function multiplyByTwo(a, b, c, addOne) {
var i, ar = [];
for(i = 0; i < 3; i ) {
ar[i] = addOne (arguments[i] * 2);
}
return ar;
}
In this way, the function is passed in as a parameter, and in the first loop call directly. Such a function is the famous callback function
2. Function as return value
There can be a return value in the function, but we are generally familiar with the return of numerical values, such as
function ex(){
return 12
}
But once you realize that functions are just a kind of data, you can think of returning functions as well. Pay attention to the following function:
function a() {
alert('A!');
return function(){
alert('B!');
};
}
it returns A function that pops "B!" Next use it:
var newFunc = a();
newFunc();
What’s the result? When a() is executed first, "A!" pops up. At this time, newFunc accepts the return value of a, a function - at this time, newFunc becomes the function returned by a. When newFunc is executed again, "B" pops up. !”
3. The scope of JavaScript
The scope of JavaScript is very special. It is based on functions, not blocks (such as a loop) like other languages. Look at the following example:
var a = 1; function f(){var b = 1; return a;}
If you try to get the value of b at this time: if you try to enter alert(b) in firebug, you will get an error Tip:
b is not defined
Why can you understand this: the programming environment or window you are in is a top-level function, like a universe, but b is just a variable in your internal function, in the universe A point on a small planet, it is difficult for you to find it, so you cannot call it in this environment; on the contrary, this internal function can call variable a, because it is exposed in the entire universe and has nowhere to hide, and it can also call b , because it's on its own planet, inside the function.
As for the above example:
Outside f(), a is visible, but b is invisible
Inside f(), a is visible, and b is also visible
A little more complicated:
var a = 1; //b,c are neither in this layer It can be seen that
function f(){
var b = 1;
function n() { //a, b, c can all call this n function, because a, b are exposed, and c is Own internal
var c = 3;
}
}
Ask you, can function b call variable c? No, remember that the scope of JavaScript is based on functions. c is inside n, so it is invisible to f.
Start formally talking about closures:
Look at this picture first:
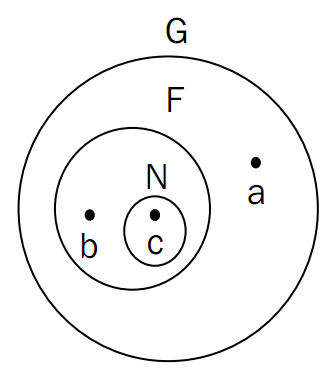
Assume that G, F, and N represent three levels of functions respectively. The levels are as shown in the figure, and a, b, and c are the variables respectively. Based on the scope mentioned above, we have the following conclusions:
- If you are at point a, you cannot reference b, because b is invisible to you
- Only c can reference b
The paradoxical thing about closures is that the following happens:
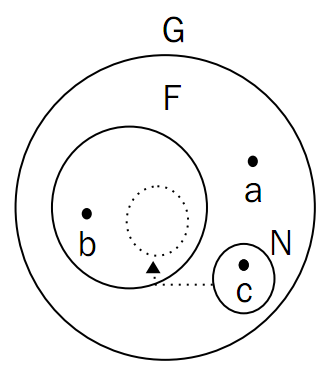
N breaks through the limit of F! We ran to the same floor as a! Because functions only recognize the environment they are in when they are defined ( not when executed, this is very important ), c in N can still access b! At this time, a is still Unable to access b!
But how is this achieved? As follows:
Closure 1:
function f( ){
var b = "b";
return function(){ // Function without name, so it is an anonymous function
return b;
}
}
Note that the returned function can access the variable b in its parent function
If you want to get the value of b at this time, of course it is undefined
But if you do this:
var n = f();
n();
You can get the value of b! Although the n function is outside f at this time, and b is a variable inside f, there is an insider inside f, and the value of b is returned...
Now everyone has a feeling, right?
Closure 2:
var n;
function f(){
var b = "b";
n = function(){
return b;
}
}
What will happen if f is called at this time? Then a global scope function of n is generated, but it can access the inside of f and still return the value of b, which is similar to the above!
Closure 3:
You can also use closures to access the parameters of the function
function f(arg) {
var n = function(){
return arg;
};
arg;
return n;
}
If you use:
var m = f(123);
m();
The result is 124
Because the anonymous function returned in f has changed hands twice, first to n, and then to the outside m, but the essence has not changed. The parameters of the parent function when defined are returned
Closure 4:
var getValue, setValue;
function() {
var secret = 0;
getValue = function(){
return secret;
};
setValue = function(v){
secret = v ;
};
})
Run:
getValue()
0
setValue(123)
getValue()
123
No need to explain this, If you have a foundation in object-oriented languages (such as C#), getValue and setValue here are similar to the property accessors of an object. You can assign and get values through these two accessors, but not access the content
In fact, there are several examples of closures in the book, but the above four principles are enough. I hope it can serve as a starting point and give JavaScript advanced readers a deeper understanding of closures

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 Replace String Characters in JavaScript
Mar 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Replace String Characters in JavaScript
Mar 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Detailed explanation of JavaScript string replacement method and FAQ This article will explore two ways to replace string characters in JavaScript: internal JavaScript code and internal HTML for web pages. Replace string inside JavaScript code The most direct way is to use the replace() method: str = str.replace("find","replace"); This method replaces only the first match. To replace all matches, use a regular expression and add the global flag g: str = str.replace(/fi
 Build Your Own AJAX Web Applications
Mar 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Build Your Own AJAX Web Applications
Mar 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
So here you are, ready to learn all about this thing called AJAX. But, what exactly is it? The term AJAX refers to a loose grouping of technologies that are used to create dynamic, interactive web content. The term AJAX, originally coined by Jesse J
 10 jQuery Fun and Games Plugins
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:42 AM
10 jQuery Fun and Games Plugins
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:42 AM
10 fun jQuery game plugins to make your website more attractive and enhance user stickiness! While Flash is still the best software for developing casual web games, jQuery can also create surprising effects, and while not comparable to pure action Flash games, in some cases you can also have unexpected fun in your browser. jQuery tic toe game The "Hello world" of game programming now has a jQuery version. Source code jQuery Crazy Word Composition Game This is a fill-in-the-blank game, and it can produce some weird results due to not knowing the context of the word. Source code jQuery mine sweeping game
 jQuery Parallax Tutorial - Animated Header Background
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:39 AM
jQuery Parallax Tutorial - Animated Header Background
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:39 AM
This tutorial demonstrates how to create a captivating parallax background effect using jQuery. We'll build a header banner with layered images that create a stunning visual depth. The updated plugin works with jQuery 1.6.4 and later. Download the
 How do I create and publish my own JavaScript libraries?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How do I create and publish my own JavaScript libraries?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
Article discusses creating, publishing, and maintaining JavaScript libraries, focusing on planning, development, testing, documentation, and promotion strategies.
 How do I optimize JavaScript code for performance in the browser?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:14 PM
How do I optimize JavaScript code for performance in the browser?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:14 PM
The article discusses strategies for optimizing JavaScript performance in browsers, focusing on reducing execution time and minimizing impact on page load speed.
 Auto Refresh Div Content Using jQuery and AJAX
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:58 AM
Auto Refresh Div Content Using jQuery and AJAX
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:58 AM
This article demonstrates how to automatically refresh a div's content every 5 seconds using jQuery and AJAX. The example fetches and displays the latest blog posts from an RSS feed, along with the last refresh timestamp. A loading image is optiona
 Getting Started With Matter.js: Introduction
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:53 AM
Getting Started With Matter.js: Introduction
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:53 AM
Matter.js is a 2D rigid body physics engine written in JavaScript. This library can help you easily simulate 2D physics in your browser. It provides many features, such as the ability to create rigid bodies and assign physical properties such as mass, area, or density. You can also simulate different types of collisions and forces, such as gravity friction. Matter.js supports all mainstream browsers. Additionally, it is suitable for mobile devices as it detects touches and is responsive. All of these features make it worth your time to learn how to use the engine, as this makes it easy to create a physics-based 2D game or simulation. In this tutorial, I will cover the basics of this library, including its installation and usage, and provide a



