
AngularJs is a good framework for developing SPA applications (single page web applications). A single page web application (SPA) is an application with only one web page. The browser will load the necessary HTML, CSS and JavaScript at the beginning. All operations are completed on this page, and JavaScript controls the presentation of different views on this page. This article originates from a good introductory tutorial video on AngularJs on Youtube: AngularJS Fundamentals In 60-ish Minutes, which mainly explains the concepts and usage of Directive, Data Binding, Filter and Module in AngularJs. Personally, I think these four concepts are the core of AngularJs and support the skeleton of AngularJs. Mastering them is very helpful for understanding AngularJs overall. Advancement requires a lot of practice and reading of the official API documentation.
Look at the picture below to roughly understand what AngularJs is capable of.
First download angular.min.js and angular-route.min.js from the official website. Can be downloaded from the official website (https://angularjs.org/ or https://code.angularjs.org/)
Create an empty Empty Web project in VS.
Directive and Data Binding
The concept of Directive in AngularJs is not easy to understand. In the entry stage, it can be understood as a tag used to extend HTML. Angularjs will parse these tags to realize the Magic of Angularjs.
The following code uses two Directives: ng-app and ng-model.
ng-app: An AngularJs application for auto-bootstrap. This is a necessary Directive, usually added to the root object of HTML (as shown in the following code). For a more detailed explanation, please visit the official website: https://docs.angularjs.org/api/ng/directive/ngApp
ngModel: Used to establish a two-way Data Binding between the property and the HTML control (input, select, textarea), which means that the value change of the HTML control will be reflected on the property, and vice versa. Property is an object created through {{}}.
The following code shows the establishment of Data Binding between the text control and name.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html ng-app>
<head>
<title>Using Directives and Data Binding Syntax</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
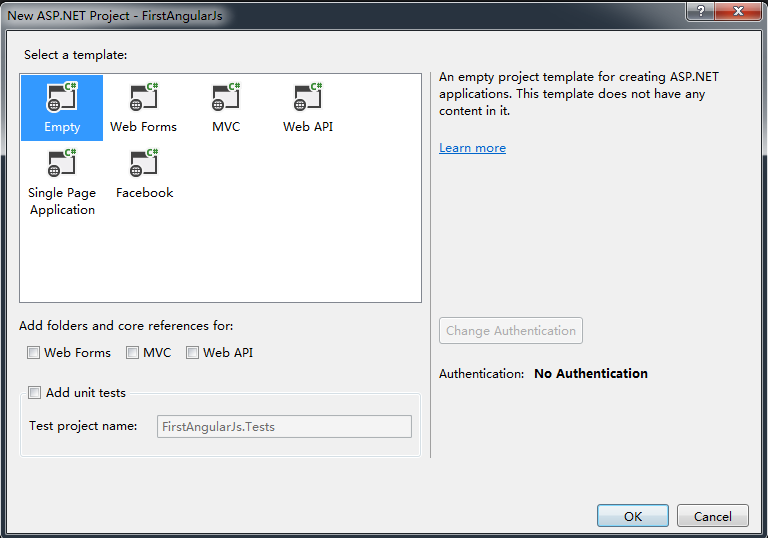
Name: <input type="text" ng-model="name" /> {{name}}
</div>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>Directive can be prefixed with "x-" or "data-". Directives can be placed in element names, attributes, classes, and comments.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html data-ng-app="">
<head>
<title>Using Directives and Data Binding Syntax</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
Name: <input type="text" data-ng-model="name" /> {{name}}
</div>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>The following is the result after running the HTML.
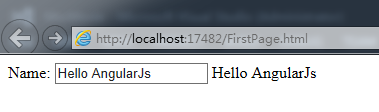
The following example shows the usage of traversing an array through ng-init and ng-repeat.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html data-ng-app="">
<head>
<title>Iterating with the ng-repeat Directive</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container" data-ng-init="names = ['Terry','William','Robert','Henry']">
<h3>Looping with the ng-repeat Directive</h3>
<ul>
<li data-ng-repeat="name in names">{{name}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>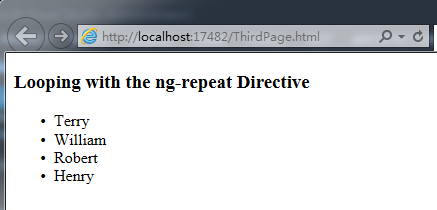
For more usage of directve, please refer to the official website https://docs.angularjs.org/api
Filter
The function is to receive an input, process it through a certain rule, and then return the processed result. It is mainly used to filter arrays, sort elements in arrays, format data, etc.
AngualrJS has some built-in filters, they are: currency (currency), date (date), filter (substring matching), json (formatted json object), limitTo (limit number), lowercase (lowercase), uppercase (uppercase), number (number), orderBy (sort). Nine types in total. In addition, you can also customize filters, which is powerful and can meet any data processing requirements.
The following code shows the implementation of data filtering, sorting and case conversion. Each Filter follows the data and is separated by |.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html data-ng-app="">
<head>
<title>Using Filter</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container" data-ng-init="customers = [{name:'Terry Wu',city:'Phoenix'},
{name:'Terry Song',city:'NewYork'},{name:'Terry Dow',city:'NewYork'},
{name:'Henry Dow',city:'NewYork'}]">
Names:
<br />
<input type="text" data-ng-model="name" />
<br />
<ul>
<li data-ng-repeat="cust in customers | filter:name | orderBy:'city'">{{cust.name | uppercase}} - {{cust.city | lowercase}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>运行的结果:
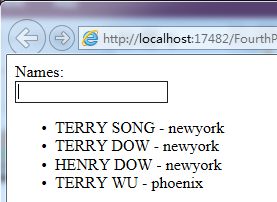
Module
Module就是一个容器,用于管理一个AngularJS应用的各个部分,是AngularJS中很重要的概念。一个AngularJS应用就是一个Module,其作用和C#应用程序中Assembly作用类似。C#中我们通过main函数来bootstrap应用程序。而AngularJS则通过na-app="moduleName"的方式来bootstrap一个AngularJS应用。moduleName就是Module对象的name.
下图是一个Module有哪些常见部分组成。
Config/Route:用于配置AngularJS应用的路由(AngularJS),作用类似于ASP.NET MVC应用中的Config/Route。
Filter:对数据起过滤作用,上文有解释。
Directive: 扩展HTML,AngularJS中最重要的概念。没有Directive就没有AngularJS。
Controller: 作用类似于ASP.NET MVC应用中的Controller。页面逻辑就在Controller中实现,通过controller可以对model进行操作。 AngularJS则通过内建的Data-Binding机制将model绑定到view(HTML控件)
Factory/Service/Provider/Value: 提供对数据源的访问。比如Restful API就是常见的数据源。 Controller通过Factory/Service/Provider/Value访问数据源完成数据的CRUD操作。

下面这段代码实现了上面实例的相同的功能,差异就在于这个实例通过创建一个module(angularJS应用),并在module下添加contorller来实现上面的功能。在SimpleController(Controller)中,我们创建了customers(Model)并进行数据初始化, View(Html控件)则直接绑定到customers(Model)。Scope是一个AngualrJS中所有viewModule的容器对象。Controller需要通过Scope是一个AngualrJS中所有viewModule的容器对象。Controller需要通过Scope来访问viewModule。
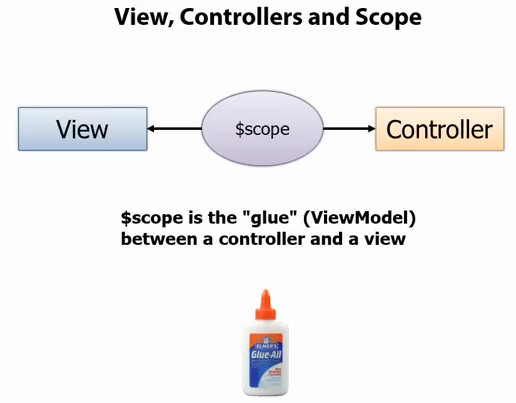
这个例子比上面例子更接近实际工程中的用法。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html data-ng-app="demoApp">
<head>
<title>Using module Controller</title>
</head>
<body>
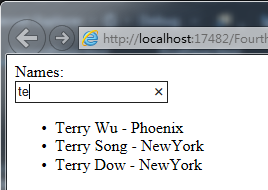
<div data-ng-controller="SimpleController">
Names:
<br />
<input type="text" data-ng-model="name" />
<br />
<ul>
<li data-ng-repeat="cust in customers | filter:name | orderBy:'city'">{{cust.name | uppercase}} - {{cust.city | lowercase}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
<script>
var demoApp = angular.module("demoApp", []);
demoApp.controller("SimpleController", function ($scope) {
$scope.customers = [
{ name: 'Terry Wu', city: 'Phoenix' },
{ name: 'Terry Song', city: 'NewYork' },
{ name: 'Terry Dow', city: 'NewYork' },
{ name: 'Henry Dow', city: 'NewYork' }
];
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html data-ng-app="demoApp">
<head>
<title>Using Controller</title>
</head>
<body>
<div data-ng-controller="SimpleController">
Names:
<br />
<input type="text" data-ng-model="name" />
<br />
<ul>
<li data-ng-repeat="cust in customers | filter:name | orderBy:'city'">{{cust.name | uppercase}} - {{cust.city | lowercase}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
<script>
var demoApp = angular.module("demoApp", []);
var controllers = {};
controllers.SimpleController = function ($scope) {
$scope.customers = [
{ name: 'Terry Wu', city: 'Phoenix' },
{ name: 'Terry Song', city: 'NewYork' },
{ name: 'Terry Dow', city: 'NewYork' },
{ name: 'Henry Dow', city: 'NewYork' }
];
}
demoApp.controller(controllers);
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html data-ng-app="demoApp">
<head>
<title>Using Controller</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div data-ng-view=""></div>
</div>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="angular-route.min.js"></script>
<script>
var demoApp = angular.module('demoApp', ['ngRoute']);
demoApp.config(function ($routeProvider) {
$routeProvider
.when('/',
{
controller: 'SimpleController',
templateUrl: 'Partials/View1.html'
})
.when('/view2',
{
controller: 'SimpleController',
templateUrl: 'Partials/View2.html'
})
.otherwise({redirectTo:'/'});
});
var controllers = {};
controllers.SimpleController = function ($scope) {
$scope.customers = [
{ name: 'Terry Wu', city: 'Phoenix' },
{ name: 'Terry Song', city: 'NewYork' },
{ name: 'Terry Dow', city: 'NewYork' },
{ name: 'Henry Dow', city: 'NewYork' }
];
$scope.addCustomer = function () {
$scope.customers.push({ name: $scope.newCustomer.name, city: $scope.newCustomer.city });
};
}
demoApp.controller(controllers);
</script>
</body>
</html>
下图展示了Module及其各个组成部分的关系。
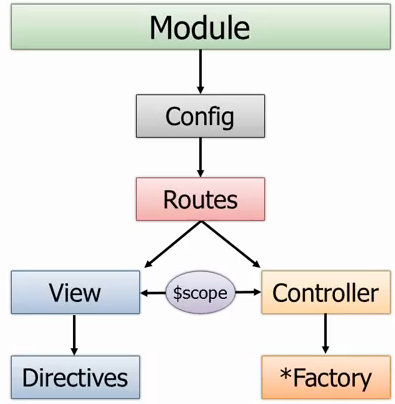
下面实例通过config配置module的route实现一个SPA实例。首先创建View1.html 和View2.html。 目录结构如下图.
<div>
<h2>View1</h2>
Names:
<br />
<input type="text" data-ng-model="filter.name" />
<br />
<ul>
<li data-ng-repeat="cust in customers | filter:filter.name | orderBy:'city'">{{cust.name | uppercase}} - {{cust.city | lowercase}}</li>
</ul>
<br />
Customer Names:<br />
<input type="text" data-ng-model="newCustomer.name" />
<br />
Customer City:<br />
<input type="text" data-ng-model="newCustomer.city" />
<br />
<button data-ng-click="addCustomer()">Add Customer </button>
<br />
<a href="#/view2">View 2</a>
</div>
<div>
<h2>View2</h2>
City:
<br />
<input type="text" data-ng-model="city" />
<br />
<ul>
<li data-ng-repeat="cust in customers | filter:city | orderBy:'city'">{{cust.name | uppercase}} - {{cust.city | lowercase}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
通过$routeProvider来配置当前页面中view1 和view2 的路由,已经每个view所对应的controller。 view1和view2会显示在当前页面标注了ng-view的位置。
同时通过config我们解耦了controller和HTML标签。 上面的例子,我们需要给html标签添加ng-controller tag来使用controller。这边直接通过config完成这样的配置。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html data-ng-app="demoApp">
<head>
<title>View</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div data-ng-view=""></div>
</div>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="angular-route.min.js"></script>
<script>
var demoApp = angular.module('demoApp', ['ngRoute']);
demoApp.config(function ($routeProvider) {
$routeProvider
.when('/',
{
controller: 'SimpleController',
templateUrl: 'Partials/View1.html'
})
.when('/view2',
{
controller: 'SimpleController',
templateUrl: 'Partials/View2.html'
})
.otherwise({redirectTo:'/'});
});
var controllers = {};
controllers.SimpleController = function ($scope) {
$scope.customers = [
{ name: 'Terry Wu', city: 'Phoenix' },
{ name: 'Terry Song', city: 'NewYork' },
{ name: 'Terry Dow', city: 'NewYork' },
{ name: 'Henry Dow', city: 'NewYork' }
];
$scope.addCustomer = function () {
$scope.customers.push({ name: $scope.newCustomer.name, city: $scope.newCustomer.city });
};
}
demoApp.controller(controllers);
</script>
</body>
</html>效果如下图。


最后一个实例更接近实际工程中的用法,我们引入了Factory来初始化数据(实际工程中,在这里可访问webAPI获取数据完成初始化),Controller中则通过Factory获得数据。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html data-ng-app="demoApp">
<head>
<title>Using Factory</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div data-ng-view=""></div>
</div>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="angular-route.min.js"></script>
<script>
var demoApp = angular.module('demoApp', ['ngRoute']);
demoApp.config(function ($routeProvider) {
$routeProvider
.when('/',
{
controller: 'SimpleController',
templateUrl: 'Partials/View1.html'
})
.when('/view2',
{
controller: 'SimpleController',
templateUrl: 'Partials/View2.html'
})
.otherwise({ redirectTo: '/' });
});
demoApp.factory('simpleFactory', function () {
var customers = [
{ name: 'Terry Wu', city: 'Phoenix' },
{ name: 'Terry Song', city: 'NewYork' },
{ name: 'Terry Dow', city: 'NewYork' },
{ name: 'Henry Dow', city: 'NewYork' }
];
var factory = {};
factory.getCustomers = function ()
{
return customers;
}
return factory;
});
var controllers = {};
controllers.SimpleController = function ($scope, simpleFactory) {
$scope.customers = [];
init();
function init() {
$scope.customers = simpleFactory.getCustomers();
}
$scope.addCustomer = function () {
$scope.customers.push({ name: $scope.newCustomer.name, city: $scope.newCustomer.city });
};
}
demoApp.controller(controllers);
</script>
</body>
</html>以上内容是小编给大家介绍的AngularJs 60分钟入门基础教程,希望对大家以上帮助!
 Ouyi trading platform app
Ouyi trading platform app
 Python online playback function implementation method
Python online playback function implementation method
 What does data encryption storage include?
What does data encryption storage include?
 The role of validate function
The role of validate function
 Solid state drive data recovery
Solid state drive data recovery
 What is the difference between webstorm and idea?
What is the difference between webstorm and idea?
 Second-level domain name query method
Second-level domain name query method
 What is the transfer limit of Alipay?
What is the transfer limit of Alipay?
 What should I do if eDonkey Search cannot connect to the server?
What should I do if eDonkey Search cannot connect to the server?




