Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Learn jQuery from scratch (4) Attributes and styles of operating elements in jQuery_jquery
Learn jQuery from scratch (4) Attributes and styles of operating elements in jQuery_jquery
Learn jQuery from scratch (4) Attributes and styles of operating elements in jQuery_jquery
This article explains how to use jQuery to obtain and manipulate element attributes and CSS styles. The distinction between DOM attributes and element attributes is worth learning.
2. Preface
Through the previous chapters, we have been able to fully control the jQuery packaging set, whether it is selecting objects through selectors, or deleting or filtering elements from the packaging set. This chapter will explain how to use jQuery to obtain and modify elements. Attributes and styles.
3. Distinguish between DOM attributes and element attributes
An img tag:

Usually developers are used to calling id, src, alt, etc. the "attributes" of this element. I call it " Element attributes". However, when parsing into a DOM object, the actual browser will eventually parse the tag element into a "DOM object" and store the element's "element attributes" as "DOM attributes". There is a difference between the two.
Although we set the src of the element to be a relative path: images/image.1.jpg
But it will be converted into an absolute path in the "DOM Attributes": http://localhost/images/image.1.jpg.
Even some "element attributes" and "DOM attributes" have different names, such as the element attribute class above, which corresponds to className after being converted into a DOM attribute.
Keep in mind that in javascript we You can directly get or set "DOM attributes":
< script type="text/javascript">
$(function() {
var img1 = document.getElementById("hibiscus");
alert(img1.alt);
img1.alt = "Change the alt element attribute";
alert(img1.alt);
})
So if you want to set the CSS style class of the element , use the "DOM attribute "className" instead of the "element attribute" class:
img1.className = "classB";
4. Operation of "DOM attribute"
There is no wrapper function for operating "DOM attributes" in jQuery, because it is very simple to use javascript to get and set "DOM attributes". jQuery provides the each() function for traversing the jQuery wrapper set, where this The pointer is a DOM object, so we can apply this with native javascript to manipulate the DOM attributes of the element:
$("img").each(function(index) {
alert("index:" index ", id:" this.id ", alt:" this.alt );
this.alt = "changed";
alert("index:" index ", id:" this.id ", alt:" this.alt);
});
下面是each函数的说明:
each( callback ) Returns: jQuery包装集
对包装集中的每一个元素执行callback方法. 其中callback方法接受一个参数, 表示当前遍历的索引值,从0开始.
五. 操作"元素属性"
我们可以使用javascript中的getAttribute和setAttribute来操作元素的"元素属性".
在jQuery中给你提供了attr()包装集函数, 能够同时操作包装集中所有元素的属性:
| 名称 | 说明 | 举例 |
| 取得第一个匹配元素的属性值。通过这个方法可以方便地从第一个匹配元素中获取一个属性的值。如果元素没有相应属性,则返回 undefined 。 | 返回文档中第一个图像的src属性值: $("img").attr("src"); |
|
| attr( properties ) |
将一个“名/值”形式的对象设置为所有匹配元素的属性。 这是一种在所有匹配元素中批量设置很多属性的最佳方式。 注意,如果你要设置对象的class属性,你必须使用'className' 作为属性名。或者你可以直接使用.addClass( class ) 和 .removeClass( class ). |
为所有图像设置src和alt属性: $("img").attr({ src: "test.jpg", alt: "Test Image" }); |
| attr( key, value ) | 为所有匹配的元素设置一个属性值。 | 为所有图像设置src属性: $("img").attr("src","test.jpg"); |
| attr( key, fn ) |
为所有匹配的元素设置一个计算的属性值。 不提供值,而是提供一个函数,由这个函数计算的值作为属性值。 |
把src属性的值设置为title属性的值: $("img").attr("title", function() { return this.src }); |
| removeAttr( name ) | 从每一个匹配的元素中删除一个属性 | 将文档中图像的src属性删除: $("img").removeAttr("src"); |
function testAttr1(event) {
alert($("#hibiscus").attr("class"));
}
注意attr(name)函数只返回第一个匹配元素的特定元素属性值. 而attr(key, name)会设置所有包装集中的元素属性:
//修改所有img元素的alt属性
$("img").attr("alt", "修改后的alt属性");
而 attr( properties ) 可以一次修改多个元素属性:
$("img").attr({title:"修改后的title", alt: "同时修改alt属性"});
另外虽然我们可以使用 removeAttr( name ) 删除元素属性, 但是对应的DOM属性是不会被删除的, 只会影响DOM属性的值.
比如将一个input元素的readonly元素属性去掉,会导致对应的DOM属性变成false(即input变成可编辑状态):
$("#inputTest").removeAttr("readonly");
六,修改CSS样式
修改元素的样式, 我们可以修改元素CSS类或者直接修改元素的样式.
一个元素可以应用多个css类, 但是不幸的是在DOM属性中是用一个以空格分割的字符串存储的, 而不是数组. 所以如果在原始javascript时代我们想对元素添加或者删除多个属性时, 都要自己操作字符串.
jQuery让这一切变得异常简单. 我们再也不用做那些无聊的工作了.
1. 修改CSS类
下表是修改CSS类相关的jQuery方法:
| 名称 | 说明 | 实例 |
| 为每个匹配的元素添加指定的类名。 | 为匹配的元素加上 'selected' 类: $("p").addClass("selected"); |
|
| hasClass( class ) | 判断包装集中是否至少有一个元素应用了指定的CSS类 |
$("p").hasClass("selected"); |
| removeClass( [classes] ) | 从所有匹配的元素中删除全部或者指定的类。 | 从匹配的元素中删除 'selected' 类: $("p").removeClass("selected"); |
| toggleClass( class ) | 如果存在(不存在)就删除(添加)一个类。 | 为匹配的元素切换 'selected' 类: $("p").toggleClass("selected"); |
| toggleClass( class, switch ) | 当switch是true时添加类, 当switch是false时删除类 |
每三次点击切换高亮样式: |
使用上面的方法, 我们可以将元素的CSS类像集合一样修改, 再也不必手工解析字符串.
注意 addClass( class ) 和removeClass( [classes] ) 的参数可以一次传入多个css类, 用空格分割,比如:
$(<SPAN class=str>"#btnAdd"</SPAN>).bind(<SPAN class=str>"click"</SPAN>, <SPAN class=kwrd>function</SPAN>(<SPAN class=kwrd>event</SPAN>) { $(<SPAN class=str>"p"</SPAN>).addClass(<SPAN class=str>"colorRed borderBlue"</SPAN>); });
removeClass方法的参数可选, 如果不传入参数则移除全部CSS类:
$(<SPAN class=str>"p"</SPAN>).removeClass()
2. 修改CSS样式
同样当我们想要修改元素的具体某一个CSS样式,即修改元素属性"style"时, jQuery也提供了相应的方法:
| 名称 | 说明 | 实例 |
| css( name ) | 访问第一个匹配元素的样式属性。 | 取得第一个段落的color样式属性的值: $("p").css("color"); |
| css( properties ) |
把一个“名/值对”对象设置为所有匹配元素的样式属性。 这是一种在所有匹配的元素上设置大量样式属性的最佳方式。 |
将所有段落的字体颜色设为红色并且背景为蓝色: $("p").css({ color: "#ff0011", background: "blue" }); |
| css( name, value ) |
在所有匹配的元素中,设置一个样式属性的值。 数字将自动转化为像素值 |
将所有段落字体设为红色: $("p").css("color","red"); |
七.获取常用属性
虽然我们可以通过获取属性,特性以及CSS样式来取得元素的几乎所有信息, 但是注意下面的实验:
<SPAN class=kwrd><!</SPAN><SPAN class=html>DOCTYPE</SPAN> <SPAN class=attr>html</SPAN> <SPAN class=attr>PUBLIC</SPAN> <SPAN class=kwrd>"-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"</SPAN> <SPAN class=kwrd>"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>></SPAN>
<SPAN class=kwrd><</SPAN><SPAN class=html>html</SPAN> <SPAN class=attr>xmlns</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>></SPAN>
<SPAN class=kwrd><</SPAN><SPAN class=html>head</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>></SPAN>
<SPAN class=kwrd><</SPAN><SPAN class=html>title</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>></SPAN>获取对象宽度<SPAN class=kwrd></</SPAN><SPAN class=html>title</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>></SPAN>
<SPAN class=kwrd><</SPAN><SPAN class=html>script</SPAN> <SPAN class=attr>type</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>="text/javascript"</SPAN> <SPAN class=attr>src</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>="scripts/jquery-1.3.2-vsdoc2.js"</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>></</SPAN><SPAN class=html>script</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>></SPAN>
<script type=<SPAN class=str>"text/javascript"</SPAN>>
$(<SPAN class=kwrd>function</SPAN>()
{
alert(<SPAN class=str>"attr(\"width\"):"</SPAN> + $(<SPAN class=str>"#testDiv"</SPAN>).attr(<SPAN class=str>"width"</SPAN>)); <SPAN class=rem>//undifined</SPAN>
alert(<SPAN class=str>"css(\"width\"):"</SPAN> + $(<SPAN class=str>"#testDiv"</SPAN>).css(<SPAN class=str>"width"</SPAN>)); <SPAN class=rem>//auto(ie6) 或 1264px(ff)</SPAN>
alert(<SPAN class=str>"width():"</SPAN> + $(<SPAN class=str>"#testDiv"</SPAN>).width()); <SPAN class=rem>//正确的数值1264</SPAN>
alert(<SPAN class=str>"style.width:"</SPAN> + $(<SPAN class=str>"#testDiv"</SPAN>)[0].style.width ); <SPAN class=rem>//空值</SPAN>
})
<SPAN class=kwrd></</SPAN><SPAN class=html>script</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>></SPAN>
<SPAN class=kwrd></</SPAN><SPAN class=html>head</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>></SPAN>
<SPAN class=kwrd><</SPAN><SPAN class=html>body</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>></SPAN>
<SPAN class=kwrd><</SPAN><SPAN class=html>div</SPAN> <SPAN class=attr>id</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>="testDiv"</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>></SPAN>
测试文本<SPAN class=kwrd></</SPAN><SPAN class=html>div</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>></SPAN>
<SPAN class=kwrd></</SPAN><SPAN class=html>body</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>></SPAN>
<SPAN class=kwrd></</SPAN><SPAN class=html>html</SPAN><SPAN class=kwrd>></SPAN>
我们希望获取测试图层的宽度, 使用attr方法获取"元素特性"为undifined, 因为并没有为div添加width. 而使用css()方法虽然可以获取到style属性的值, 但是在不同浏览器里返回的结果不同, IE6下返回auto, 而FF下虽然返回了正确的数值但是后面带有"px". 所以jQuery提供了width()方法, 此方法返回的是正确的不带px的数值.
针对上面的问题, jQuery为常用的属性提供了获取和设置的方法, 比如width()用户获取元素的宽度, 而 width(val)用来设置元素宽度.
下面这些方法可以用来获取元素的常用属性值:
1.宽和高相关 Height and Width
| 名称 | 说明 | 举例 |
| height( ) | 取得第一个匹配元素当前计算的高度值(px)。 | 获取第一段的高: $("p").height(); |
| height( val ) | 为每个匹配的元素设置CSS高度(hidth)属性的值。如果没有明确指定单位(如:em或%),使用px。 | 把所有段落的高设为 20: $("p").height(20); |
| width( ) | 取得第一个匹配元素当前计算的宽度值(px)。 | 获取第一段的宽: $("p").width(); |
| width( val ) |
为每个匹配的元素设置CSS宽度(width)属性的值。 如果没有明确指定单位(如:em或%),使用px。 |
将所有段落的宽设为 20: $("p").width(20); |
| innerHeight( ) |
获取第一个匹配元素内部区域高度(包括补白、不包括边框)。 |
见最后示例 |
| innerWidth( ) |
获取第一个匹配元素内部区域宽度(包括补白、不包括边框)。 |
见最后示例 |
| outerHeight( [margin] ) |
获取第一个匹配元素外部高度(默认包括补白和边框)。 |
见最后示例 |
| outerWidth( [margin] ) |
获取第一个匹配元素外部宽度(默认包括补白和边框)。 |
见最后示例 |
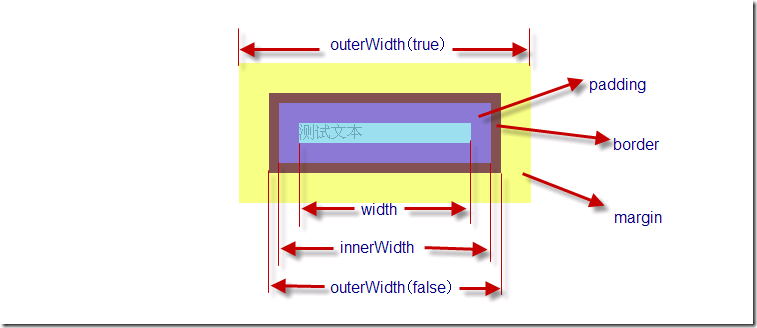
关于在获取长宽的函数中, 要区别"inner", "outer"和height/width这三种函数的区别:
outerWith可以接受一个bool值参数表示是否计算margin值.
相信此图一目了然各个函数所索取的范围. 图片以width为例说明的, height的各个函数同理.
2.位置相关 Positioning
另外在一些设计套弹出对象的脚本中,常常需要动态获取弹出坐标并且设置元素的位置.
但是很多的计算位置的方法存在着浏览器兼容性问题, jQuery中为我们提供了位置相关的各个函数:
| 名称 | 说明 | 举例 |
| offset( ) |
获取匹配元素在当前窗口的相对偏移。 返回的对象包含两个整形属性:top 和 left。此方法只对可见元素有效。 |
获取第二段的偏移: var p = $("p:last"); <br>var offset = p.offset(); <br>p.html( "left: " + offset.left + ", top: " + offset.top );
|
| position( ) |
获取匹配元素相对父元素的偏移。 返回的对象包含两个整形属性:top 和 left。为精确计算结果,请在补白、边框和填充属性上使用像素单位。此方法只对可见元素有效。 |
获取第一段的偏移: var p = $("p:first"); <br>var position = p.position(); <br>$("p:last").html( "left: " + position.left + ", top: " + position.top );
|
| scrollTop( ) |
获取匹配元素相对滚动条顶部的偏移。 此方法对可见和隐藏元素均有效。 |
获取第一段相对滚动条顶部的偏移: var p = $("p:first"); <br>$("p:last").text( "scrollTop:" + p.scrollTop() );
|
| scrollTop( val ) |
传递参数值时,设置垂直滚动条顶部偏移为该值。 此方法对可见和隐藏元素均有效。 |
设定垂直滚动条值: <code>$("div.demo").scrollTop(300);</code>Copy after login |
| scrollLeft( ) |
获取匹配元素相对滚动条左侧的偏移。 此方法对可见和隐藏元素均有效。 |
获取第一段相对滚动条左侧的偏移: var p = $("p:first"); <br>$("p:last").text( "scrollLeft:" + p.scrollLeft() );
|
| scrollLeft( val ) |
传递参数值时,设置水平滚动条左侧偏移为该值。 此方法对可见和隐藏元素均有效。 |
设置相对滚动条左侧的偏移: <code>$("div.demo").scrollLeft(300);</code>Copy after login |
八.总结
本篇文章主要讲解如何使用jQuery操作元素的属性和修改样式. 请大家主要注意元素属性和DOM属性的区别. 下一篇文章将讲解最重要的事件, 介绍如何绑定事件, 操作事件对象等.
作者:张子秋
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhangziqiu/

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Guide to solving misalignment of WordPress web pages
Mar 05, 2024 pm 01:12 PM
Guide to solving misalignment of WordPress web pages
Mar 05, 2024 pm 01:12 PM
Guide to solving misaligned WordPress web pages In WordPress website development, sometimes we encounter web page elements that are misaligned. This may be due to screen sizes on different devices, browser compatibility, or improper CSS style settings. To solve this misalignment, we need to carefully analyze the problem, find possible causes, and debug and repair it step by step. This article will share some common WordPress web page misalignment problems and corresponding solutions, and provide specific code examples to help develop
 bottom attribute syntax in CSS
Feb 21, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
bottom attribute syntax in CSS
Feb 21, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
Bottom attribute syntax and code examples in CSS In CSS, the bottom attribute is used to specify the distance between an element and the bottom of the container. It controls the position of an element relative to the bottom of its parent element. The syntax of the bottom attribute is as follows: element{bottom:value;} where element represents the element to which the style is to be applied, and value represents the bottom value to be set. value can be a specific length value, such as pixels
 CSS transition effect: how to achieve the sliding effect of elements
Nov 21, 2023 pm 01:16 PM
CSS transition effect: how to achieve the sliding effect of elements
Nov 21, 2023 pm 01:16 PM
CSS transition effect: How to achieve the sliding effect of elements Introduction: In web design, the dynamic effect of elements can improve the user experience, among which the sliding effect is a common and popular transition effect. Through the transition property of CSS, we can easily achieve the sliding animation effect of elements. This article will introduce how to use CSS transition properties to achieve the sliding effect of elements, and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand and apply. 1. Introduction to CSS transition attribute transition CSS transition attribute tra
 CSS transformation: how to achieve the rotation effect of elements
Nov 21, 2023 pm 06:36 PM
CSS transformation: how to achieve the rotation effect of elements
Nov 21, 2023 pm 06:36 PM
CSS transformation: How to achieve the rotation effect of elements requires specific code examples. In web design, animation effects are one of the important ways to improve user experience and attract user attention, and rotation animation is one of the more classic ones. In CSS, you can use the "transform" attribute to achieve various deformation effects of elements, including rotation. This article will introduce in detail how to use CSS "transform" to achieve the rotation effect of elements, and provide specific code examples. 1. How to use CSS’s “transf
 Introduction to the attributes of Hearthstone's Despair Thread
Mar 20, 2024 pm 10:36 PM
Introduction to the attributes of Hearthstone's Despair Thread
Mar 20, 2024 pm 10:36 PM
Thread of Despair is a rare card in Blizzard Entertainment's masterpiece "Hearthstone" and has a chance to be obtained in the "Wizbane's Workshop" card pack. Can consume 100/400 arcane dust points to synthesize the normal/gold version. Introduction to the attributes of Hearthstone's Thread of Despair: It can be obtained in Wizbane's workshop card pack with a chance, or it can also be synthesized through arcane dust. Rarity: Rare Type: Spell Class: Death Knight Mana: 1 Effect: Gives all minions a Deathrattle: Deals 1 damage to all minions
 How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute? When using jQuery to operate DOM elements, you often encounter situations where you need to determine whether an element has a specific attribute. In this case, we can easily implement this function with the help of the methods provided by jQuery. The following will introduce two commonly used methods to determine whether a jQuery element has specific attributes, and attach specific code examples. Method 1: Use the attr() method and typeof operator // to determine whether the element has a specific attribute
 How to use CSS to achieve an element's transparency gradient effect
Nov 21, 2023 pm 01:38 PM
How to use CSS to achieve an element's transparency gradient effect
Nov 21, 2023 pm 01:38 PM
How to use CSS to achieve the transparency gradient effect of elements In web development, adding transition effects to web page elements is one of the important means to improve user experience. The gradient effect of transparency can not only make the page smoother, but also highlight the key content of the element. This article will introduce how to use CSS to achieve the transparency gradient effect of elements and provide specific code examples. Using the CSS transition attribute To achieve the transparency gradient effect of an element, we need to use the CSS transition attribute. t
 'Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming in PHP: From Concept to Practice'
Feb 25, 2024 pm 09:04 PM
'Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming in PHP: From Concept to Practice'
Feb 25, 2024 pm 09:04 PM
What is object-oriented programming? Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that abstracts real-world entities into classes and uses objects to represent these entities. Classes define the properties and behavior of objects, and objects instantiate classes. The main advantage of OOP is that it makes code easier to understand, maintain and reuse. Basic Concepts of OOP The main concepts of OOP include classes, objects, properties and methods. A class is the blueprint of an object, which defines its properties and behavior. An object is an instance of a class and has all the properties and behaviors of the class. Properties are characteristics of an object that can store data. Methods are functions of an object that can operate on the object's data. Advantages of OOP The main advantages of OOP include: Reusability: OOP can make the code more