 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Simulation code of jQuery's implementation principle -1 Core part_jquery
Simulation code of jQuery's implementation principle -1 Core part_jquery
Simulation code of jQuery's implementation principle -1 Core part_jquery
The core part implements two selectors, using id and tag name, and can also provide css settings and text settings.
// # Represents the corresponding in jQuery 1.4.2 Number of lines
// Define variable undefined for convenience
var undefined = undefined;
// jQuery is a function, in fact, jQuery.fn.init is called to create an object
var $ = jQuery = window.$ = window.jQuery // #19
= function (selector, context) {
return new jQuery.fn.init(selector, context);
};
// Used to check if it is An id
idExpr = /^#([w-] )$/;
// Set the prototype object of jQuery for sharing by all jQuery objects
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = { // #74
length: 0, // #190
jquery: "1.4.2", // # 187
// This is an example, only providing two selection methods: id and tag name
init: function (selector, context) { // #75
// Handle HTML strings
if (typeof selector === "string") {
// Are we dealing with HTML string or an ID?
match = idExpr.exec(selector);
// Verify a match, and that no context was specified for #id
if (match && match[1]) {
var elem = document.getElementById(match[1]);
if (elem) {
this.length = 1;
this[0] = elem;
}
}
else {
// Use tag name directly
var nodes = document.getElementsByTagName(selector);
for (var l = nodes.length, j = 0; j < l; j ) {
this[j] = nodes[j];
}
this.length = nodes.length;
}
this.context = document;
this.selector = selector;
return this;
}
},
//The number of represented DOM objects
size: function () { // #193
return this.length;
} ,
// Used to set css style
css: function (name, value) { // #4564
this.each(
function (name, value) {
this.style [name] = value;
},
arguments // The actual parameters are passed in the form of an array
);
return this;
},
// Used to set the text Content
text: function (val) { // #3995
if (val) {
this.each(function () {
this.innerHTML = val;
},
arguments // The actual parameters are passed in the form of array
)
}
return this;
},
// Used to operate on all DOM objects
// callback Customized callback function
// args Customized parameters
each: function (callback, args) { // #244
return jQuery.each(this, callback, args);
}
}
// The prototype of the init function is also the prototype of jQuery
jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.prototype; // #303
// Used to traverse the jQuery object contained Elements of
jQuery.each = function (object, callback, args) { // #550
var i = 0, length = object.length;
// No parameters provided
if (args === undefined) {
for (var value = object[0];
i < length && callback.call(value, i, value) !== false;
value = object[ i ])
{ }
}
else {
for (; i < length; ) {
if (callback.apply(object[i ], args) === false) {
break;
}
}
}
}
In jQuery, the jQuery object is actually an array-like object that represents the selector The obtained collection of all DOM objects has a length attribute like an array, indicating the number of DOM objects represented. It can also be traversed through subscripts.
The jQuery.each on line 95 is the basic method used in jQuery to traverse this imitation array and traverse each element in it. The callback represents the function that processes this DOM object. Normally, we do not use this method, but use the each method of the jQuery object to traverse. Internally, the jQuery object's css and text methods actually use the jQuery object's each method to process the selected element.
For the relationship between these functions and objects, see: jQuery prototype relationship diagram
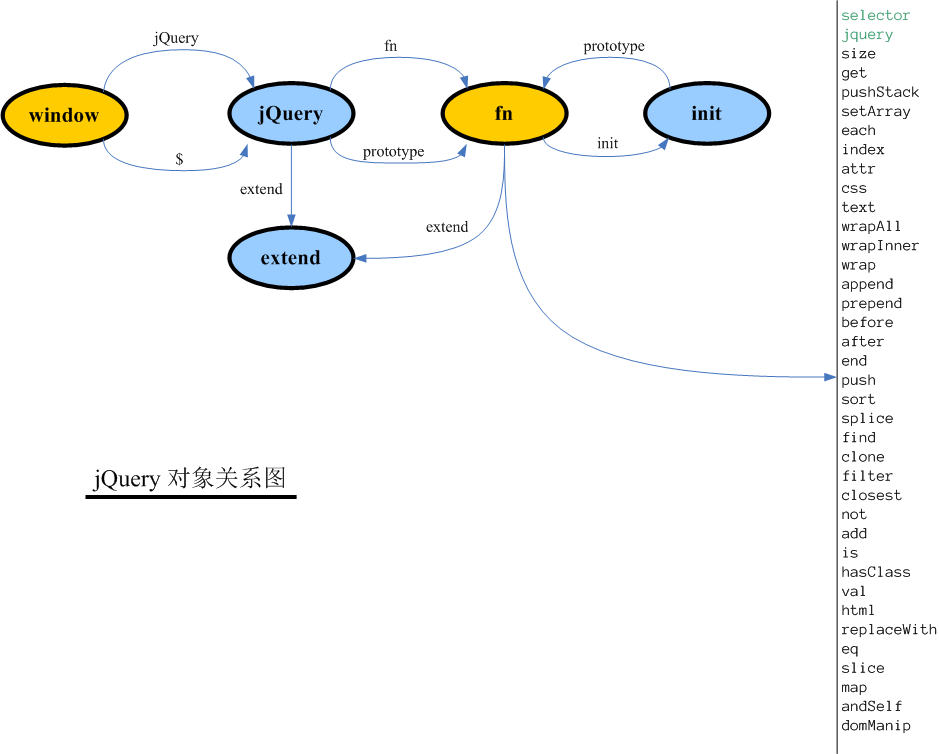
The following script uses this script library.
// Prototype operation
$("h1" ).text("Hello, world.").css("color", "green");

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 Analysis of the function and principle of nohup
Mar 25, 2024 pm 03:24 PM
Analysis of the function and principle of nohup
Mar 25, 2024 pm 03:24 PM
Analysis of the role and principle of nohup In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, nohup is a commonly used command that is used to run commands in the background. Even if the user exits the current session or closes the terminal window, the command can still continue to be executed. In this article, we will analyze the function and principle of the nohup command in detail. 1. The role of nohup: Running commands in the background: Through the nohup command, we can let long-running commands continue to execute in the background without being affected by the user exiting the terminal session. This needs to be run
 How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 am 08:39 AM
How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 am 08:39 AM
How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery? In front-end development, we often encounter the need to manipulate the height attributes of elements. Sometimes, we may need to dynamically change the height of an element, and sometimes we need to remove the height attribute of an element. This article will introduce how to use jQuery to remove the height attribute of an element and provide specific code examples. Before using jQuery to operate the height attribute, we first need to understand the height attribute in CSS. The height attribute is used to set the height of an element
 How to use PUT request method in jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to use PUT request method in jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to use PUT request method in jQuery? In jQuery, the method of sending a PUT request is similar to sending other types of requests, but you need to pay attention to some details and parameter settings. PUT requests are typically used to update resources, such as updating data in a database or updating files on the server. The following is a specific code example using the PUT request method in jQuery. First, make sure you include the jQuery library file, then you can send a PUT request via: $.ajax({u
 jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page
Feb 28, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page
Feb 28, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Title: jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page In web development, we often need to modify and operate elements on the page. When using jQuery, sometimes you need to modify the text content of all a tags in the page at once, which can save time and energy. The following will introduce how to use jQuery to quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page, and give specific code examples. First, we need to introduce the jQuery library file and ensure that the following code is introduced into the page: <
 Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags
Feb 28, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags
Feb 28, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Title: Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags. jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used to handle DOM operations. In web development, we often encounter the need to modify the text content of the link tag (a tag) on the page. This article will explain how to use jQuery to achieve this goal, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to introduce the jQuery library into the page. Add the following code in the HTML file:
 Astar staking principle, income dismantling, airdrop projects and strategies & operation nanny-level strategy
Jun 25, 2024 pm 07:09 PM
Astar staking principle, income dismantling, airdrop projects and strategies & operation nanny-level strategy
Jun 25, 2024 pm 07:09 PM
Table of Contents Astar Dapp Staking Principle Staking Revenue Dismantling of Potential Airdrop Projects: AlgemNeurolancheHealthreeAstar Degens DAOVeryLongSwap Staking Strategy & Operation "AstarDapp Staking" has been upgraded to the V3 version at the beginning of this year, and many adjustments have been made to the staking revenue rules. At present, the first staking cycle has ended, and the "voting" sub-cycle of the second staking cycle has just begun. To obtain the "extra reward" benefits, you need to grasp this critical stage (expected to last until June 26, with less than 5 days remaining). I will break down the Astar staking income in detail,
 How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute? When using jQuery to operate DOM elements, you often encounter situations where you need to determine whether an element has a specific attribute. In this case, we can easily implement this function with the help of the methods provided by jQuery. The following will introduce two commonly used methods to determine whether a jQuery element has specific attributes, and attach specific code examples. Method 1: Use the attr() method and typeof operator // to determine whether the element has a specific attribute
 Understand the role and application scenarios of eq in jQuery
Feb 28, 2024 pm 01:15 PM
Understand the role and application scenarios of eq in jQuery
Feb 28, 2024 pm 01:15 PM
jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used to handle DOM manipulation and event handling in web pages. In jQuery, the eq() method is used to select elements at a specified index position. The specific usage and application scenarios are as follows. In jQuery, the eq() method selects the element at a specified index position. Index positions start counting from 0, i.e. the index of the first element is 0, the index of the second element is 1, and so on. The syntax of the eq() method is as follows: $("s



