 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 JavaScript creates a cross-browser event handling mechanism [Produced by Blue-Dream]_javascript skills
JavaScript creates a cross-browser event handling mechanism [Produced by Blue-Dream]_javascript skills
JavaScript creates a cross-browser event handling mechanism [Produced by Blue-Dream]_javascript skills
It is easier to solve compatibility problems by using class libraries. But what is the mechanism behind it? Let’s explain it bit by bit.
First of all, DOM Level2 defines two functions addEventListener and removeEventListener for event processing, both of which come from the EventTarget interface.
element.addEventListener(eventName, listener, useCapture);
element .removeEventListener(eventName, listener, useCapture);
The EventTarget interface is usually implemented from the Node or Window interface. It is also the so-called DOM element.
For example, window can also add listeners through addEventListener .
function loadHandler() {
console.log ('the page is loaded!');
}
window.addEventListener('load', loadHandler, false);
Removing the listener is also easy to do through removeEventListener, Just note that the removed handle and the added handle refer to a function.
window.removeEventListener('load', loadHandler, false);
If we live in a perfect world. Then estimate the event The function ends here.
But this is not the case. Because IE is unique. The two functions attachEvent and detachEvent are defined through MSDHTML DOM to replace addEventListener and removeEventListener.
There are many differences between the functions, which makes the entire The event mechanism has become extremely complex.
So what we have to do is actually to deal with the differences in event processing between IE browsers and w3c standards.
Add monitoring and To remove the listener, you can write
function loadHandler() {
alert('the page is loaded!');
}
window.attachEvent('onload', loadHandler); // Add listener
window.detachEvent('onload', loadHandler); / / Remove monitoring
From the surface, we can see two differences between IE and w3c:
1. There is an "on" prefix in front of the event.
2. The third parameter of useCapture has been removed.
In fact, the real differences are far more than these. We will continue to analyze them later. So for these two differences, we can easily abstract a common function
function addListener(element, eventName, handler) {
if (element. addEventListener) {
element.addEventListener(eventName, handler, false);
}
else if (element.attachEvent) {
element.attachEvent('on' eventName, handler);
}
else {
element['on' eventName] = handler;
}
}
function removeListener(element, eventName, handler) {
if (element.addEventListener) {
element.removeEventListener(eventName, handler, false);
}
else if (element.detachEvent) {
element.detachEvent('on' eventName, handler);
}
else {
element['on' eventName] = null;
}
}
There are two things to note about the above function:
1. First It is best to measure the w3c standard for this branch first. Because IE is gradually getting closer to the standard. The second branch monitors IE.
2. The third branch is reserved for neither supporting (add/remove) EventListener nor (attach) /detach)Event browser.
Performance Optimization
For the above function, we use "runtime" monitoring. That is, each binding event requires branch monitoring. We can Change to "before running" to determine the compatible function. There is no need to monitor every time.
In this way, we need to use a DOM element to detect in advance. Here we choose document.documentElement. Why not use document.body? Because document .documentElement already exists when the document is not ready. And document.body does not exist before it is ready.
In this way, the function is optimized to
var addListener, removeListener,
/* test element */
docEl = document.documentElement;
// addListener
if (docEl.addEventListener) {
/* if `addEventListener` exists on test element, define function to use `addEventListener` */
addListener = function (element, eventName, handler) {
element.addEventListener(eventName, handler, false);
};
}
else if (docEl.attachEvent) {
/* if `attachEvent` exists on test element, define function to use `attachEvent` */
addListener = function (element, eventName, handler) {
element.attachEvent('on' eventName, handler);
};
}
else {
/* if neither methods exists on test element, define function to fallback strategy */
addListener = function (element, eventName, handler) {
element['on' eventName] = handler;
};
}
// removeListener
if (docEl.removeEventListener) {
removeListener = function (element, eventName, handler) {
element.removeEventListener(eventName, handler, false);
};
}
else if (docEl.detachEvent) {
removeListener = function (element, eventName, handler) {
element.detachEvent('on' eventName, handler);
};
}
else {
removeListener = function (element, eventName, handler) {
element['on' eventName] = null;
};
}
这样就避免了每次绑定都需要判断.
值得一提的是.上面的代码其实也是有两处硬伤. 除了代码量增多外, 还有一点就是使用了硬性编码推测.上面代码我们基本的意思就是断定.如果document.documentElement具备了add/remove方法.那么element就一定具备(虽然大多数情况如此).但这显然是不够安全.
不安全的检测
下面两个例子说明.在某些情况下这种检测不是足够安全的.
// In Internet Explorer
var xhr = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.XMLHTTP');
if (xhr.open) { } // Error
var element = document.createElement('p');
if (element.offsetParent) { } // Error
如: 在IE7下 typeof xhr.open === 'unknown'. 详细可参考feature-detection
所以我们提倡的检测方式是
var isHostMethod = function (object, methodName) {
var t = typeof object[methodName];
return ((t === 'function' || t === 'object') && !!object[methodName]) || t === 'unknown';
};
这样我们上面的优化函数.再次改进成这样
var addListener, docEl = document.documentElement;
if (isHostMethod(docEl, 'addEventListener')) {
/* ... */
}
else if (isHostMethod(docEl, 'attachEvent')) {
/* ... */
}
else {
/* ... */
}
丢失的this指针
this指针的处理.IE与w3c又出现了差异.在w3c下函数的指针是指向绑定该句柄的DOM元素. 而IE下却总是指向window.
// IE
document.body.attachEvent('onclick', function () {
alert(this === window); // true
alert(this === document.body); // false
});
// W3C
document.body.addEventListener('onclick', function () {
alert(this === window); // false
alert(this === document.body); // true
});
这个问题修正起来也不算麻烦
if (isHostMethod(docEl, 'addEventListener')) {
/* ... */
}
else if (isHostMethod(docEl, 'attachEvent')) {
addListener = function (element, eventName, handler) {
element.attachEvent('on' eventName, function () {
handler.call(element, window.event);
});
};
}
else {
/* ... */
}
We only need to use a wrapper function. Then use call to re-correct the pointer of the handler internally. In fact, everyone should have noticed that there is also a problem that has been secretly corrected here. The event under IE is not passed through the first function. , but left in the global world. So we often write code like event = event || window.event. We have also made corrections here.
Corrected these major problems. Our function looks like It is much more robust. We can pause for a while and do a simple test. Three points of testing
1. Compatibility across browsers 2. Compatibility pointed by this pointer 3. Compatibility in event parameter passing.
The test code is as follows:

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 Python GUI programming: Get started quickly and easily create interactive interfaces
Feb 19, 2024 pm 01:24 PM
Python GUI programming: Get started quickly and easily create interactive interfaces
Feb 19, 2024 pm 01:24 PM
A brief introduction to python GUI programming GUI (Graphical User Interface, graphical user interface) is a way that allows users to interact with computers graphically. GUI programming refers to the use of programming languages to create graphical user interfaces. Python is a popular programming language that provides a rich GUI library, making Python GUI programming very simple. Introduction to Python GUI library There are many GUI libraries in Python, the most commonly used of which are: Tkinter: Tkinter is the GUI library that comes with the Python standard library. It is simple and easy to use, but has limited functions. PyQt: PyQt is a cross-platform GUI library with powerful functions.
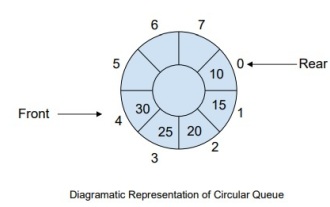 How to manage a complete circular queue of events in C++?
Sep 04, 2023 pm 06:41 PM
How to manage a complete circular queue of events in C++?
Sep 04, 2023 pm 06:41 PM
Introduction CircularQueue is an improvement on linear queues, which was introduced to solve the problem of memory waste in linear queues. Circular queues use the FIFO principle to insert and delete elements from it. In this tutorial, we will discuss the operation of a circular queue and how to manage it. What is a circular queue? Circular queue is another type of queue in data structure where the front end and back end are connected to each other. It is also known as circular buffer. It operates similarly to a linear queue, so why do we need to introduce a new queue in the data structure? When using a linear queue, when the queue reaches its maximum limit, there may be some memory space before the tail pointer. This results in memory loss, and a good algorithm should be able to make full use of resources. In order to solve the waste of memory
 Event processing library in PHP8.0: Event
May 14, 2023 pm 05:40 PM
Event processing library in PHP8.0: Event
May 14, 2023 pm 05:40 PM
Event processing library in PHP8.0: Event With the continuous development of the Internet, PHP, as a popular back-end programming language, is widely used in the development of various Web applications. In this process, the event-driven mechanism has become a very important part. The event processing library Event in PHP8.0 will provide us with a more efficient and flexible event processing method. What is event handling? Event handling is a very important concept in the development of web applications. Events can be any kind of user row
 What is the meaning of bubbling events
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:53 AM
What is the meaning of bubbling events
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:53 AM
Bubbling events mean that in web development, when an event is triggered on an element, the event will propagate to upper elements until it reaches the document root element. This propagation method is like a bubble gradually rising from the bottom, so it is called a bubbling event. In actual development, knowing and understanding how bubbling events work is very important to handle events correctly. The following will introduce the concept and usage of bubbling events in detail through specific code examples. First, we create a simple HTML page with a parent element and three children
 Analysis of v-on directive in Vue: how to handle form submission events
Sep 15, 2023 am 09:12 AM
Analysis of v-on directive in Vue: how to handle form submission events
Sep 15, 2023 am 09:12 AM
Analysis of the v-on directive in Vue: How to handle form submission events In Vue.js, the v-on directive is used to bind event listeners and can capture and process various DOM events. Among them, processing form submission events is one of the common operations in Vue. This article will introduce how to use the v-on directive to handle form submission events and provide specific code examples. First of all, it is necessary to clarify that the form submission event in Vue refers to the event triggered when the user clicks the submit button or presses the Enter key. In Vue, you can pass
 Using $listeners to pass event handling functions in Vue
Jun 11, 2023 pm 03:09 PM
Using $listeners to pass event handling functions in Vue
Jun 11, 2023 pm 03:09 PM
In Vue, there are often some nested components, and events need to be passed between these nested components. In Vue, the $emit event is used for event communication between components. However, in some cases, we need to pass the event handler of a parent component to a nested child component. In this case, using the $emit event is not appropriate. At this time, you can use the $listeners provided by Vue to pass the event processing function. So, what are $listeners?
 Practical applications of event bubbling and applicable event types
Feb 18, 2024 pm 04:19 PM
Practical applications of event bubbling and applicable event types
Feb 18, 2024 pm 04:19 PM
Application scenarios of event bubbling and the types of events it supports. Event bubbling means that when an event on an element is triggered, the event will be passed to the parent element of the element, and then to the ancestor element of the element until it is passed to the root node of the document. It is an important mechanism of the event model and has a wide range of application scenarios. This article will introduce the application scenarios of event bubbling and explore the types of events it supports. 1. Application scenarios Event bubbling has a wide range of application scenarios in web development. Here are several common application scenarios. form validation in form
 In-depth study of the key code implementation of PHP and Vue in the brain map function
Aug 27, 2023 pm 12:15 PM
In-depth study of the key code implementation of PHP and Vue in the brain map function
Aug 27, 2023 pm 12:15 PM
In-depth study of the key code implementation of PHP and Vue in the brain map function Summary: This article will delve into the key code implementation of PHP and Vue in the realization of the mind map function. Brain mapping is a graphical tool commonly used to display thinking structures and relationships. It is widely used in fields such as project planning, knowledge management, and information organization. By learning the relevant knowledge of PHP and Vue, we can implement a simple yet powerful brain mapping application. Understand PHPPHP is a commonly used server-side scripting language. It is easy to learn and highly scalable



