 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 jQuery Learning Lesson 7 Extending the Functions of jQuery Plug-in Development_jquery
jQuery Learning Lesson 7 Extending the Functions of jQuery Plug-in Development_jquery
jQuery Learning Lesson 7 Extending the Functions of jQuery Plug-in Development_jquery
The main body of jQuery is as follows:
(function(){ ……})();
is strange for people who are not very good at Javascript. In effect, this expression declares an anonymous function (first bracket) and then executes it (second bracket). In this function, the definition of a series of jQuery methods and objects is completed. Line 24 is critical,
jQuery = window.jQuery = window.$ = function( selector, context ) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
return new jQuery.fn.init( selector, context );
}
Here, a very powerful $ function is defined. $ is actually an alias for jQuery. jQuery is the "authentic" jQuery function, and the definition of $ is just to reduce the amount of typing by programmers. $ can easily conflict with other libraries. For example, the famous prototype library also uses this name. However, there are much fewer chances for jQuery to conflict with other libraries, so using jQuery is much safer than $. Let’s talk about conflicts next. Look at the definition of return object fn, line 35
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
init: function( selector, context ) { … }, …
};
Obviously fn is just a prototype of jQuery Just an abbreviation. An init function is defined. In fact, init acts as jQuery's constructor. When we use code like var i=$('selector'), we can find that the variable i is wrapped by jQuery, that is, i brings the jQuery.fn method. Obviously, i's prototype is pointed to jQuery.fn. In the world of Javascript, it can be said that i is an instance of jQuery. If you try i instanceof jQuery, it will return true. However, i=new $(selector) is not used here; I estimate that $ is such a commonly used function. If you have to use new to construct an object every time, it would be too troublesome. This is the reason for the existence of init , $ itself is defined as a very simple function, with only one line of code inside, returning an init object. Every time we call the $(selector) method, a jQuery object is returned. It smells a bit like factory mode. Of course, if you are familiar with Javascript, you will know that this is not enough. We need to set the prototype of init to jQuery.fn, line 541 of code:
jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn ;
Up to line 540, they are all defined jQuery prototype objects. In OO language, they are equivalent to instance methods. Starting from line 540, a series of jQuery methods are defined, which are equivalent to static methods. At this point, regardless of the specific implementation of the methods (some of which are too difficult), the structure of jQuery is basically clear. Let’s start with the extensions.
The first thing to pay attention to when extending jQuery is to avoid naming conflicts, especially the popular $. jQuery thoughtfully designed a jQuery.noConflict() method, so that jQuery can give up the $ symbol to avoid conflicts with other libraries, and programmers can use the complete symbol jQuery to call the methods provided by jQuery. The implementation of noConflict() is simple and clever. By the way, first of all, in line 21,
// Map over the $ in case of overwrite
_$ = window.$, jQuery first records windows .$, note that this line of code runs very early and will be executed before any jQuery function is executed. Of course, there is a possibility of conflict here, but the probability is too small. Who would use such a weird name as a key variable? At this time, if $ has been occupied by other libraries, its value will remain in _$. At any time, just call the jQuery.noConflict method, line 619, with the following code:
noConflict: function( deep ) {
window.$ = _$;
if ( deep )
window.jQuery = _jQuery;
return jQuery;
},
In this way, $ is returned.
As plug-in developers, we cannot guarantee whether $ will be given away. The safest thing is to call the jQuery method. However, there is a trick to retain the simple $ without affecting other parts, that is:
(function($){
// plugin code goes here, you can use $ safely.
})(jQuery);
Regarding the naming of the plugin’s js file, it is usually jquery.pluginname.js.
It is easy to extend jQuery tool functions (static functions). The following example implements a function that expands a number into a string of fixed digits.
(function($) {
$.toFixedWidth = function(value, length, fill) {
var res = value.toString();
if (!fill) fill = 0;
var padding = length - res.length;
if (padding < 0) {
res = res.substr(-padding);
} else {
for (var n = 0; n < padding; n )
res = fill res ;
}
return res;
}
})(jQuery);
It is equally easy to write a wrapper set. Here is a way to make the form elements only Reading method:
$.fn.setReadOnly = function( readonly) {
return this.find('input:text').attr('readonly', readonly).css('opacity', readonly ? 0.5 : 1.0);
}
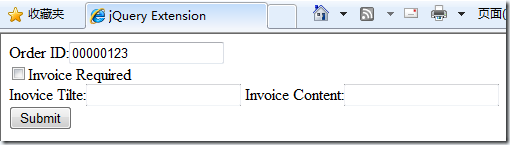
Write a small page for testing below. This page simulates the order submission page. If the user needs an invoice, he or she needs to fill in the invoice information, otherwise the invoice information cannot be filled in.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1374
1374
 52
52
 Extensions and third-party modules for PHP functions
Apr 13, 2024 pm 02:12 PM
Extensions and third-party modules for PHP functions
Apr 13, 2024 pm 02:12 PM
To extend PHP function functionality, you can use extensions and third-party modules. Extensions provide additional functions and classes that can be installed and enabled through the pecl package manager. Third-party modules provide specific functionality and can be installed through the Composer package manager. Practical examples include using extensions to parse complex JSON data and using modules to validate data.
 How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 am 08:39 AM
How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 am 08:39 AM
How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery? In front-end development, we often encounter the need to manipulate the height attributes of elements. Sometimes, we may need to dynamically change the height of an element, and sometimes we need to remove the height attribute of an element. This article will introduce how to use jQuery to remove the height attribute of an element and provide specific code examples. Before using jQuery to operate the height attribute, we first need to understand the height attribute in CSS. The height attribute is used to set the height of an element
 How to use PUT request method in jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to use PUT request method in jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to use PUT request method in jQuery? In jQuery, the method of sending a PUT request is similar to sending other types of requests, but you need to pay attention to some details and parameter settings. PUT requests are typically used to update resources, such as updating data in a database or updating files on the server. The following is a specific code example using the PUT request method in jQuery. First, make sure you include the jQuery library file, then you can send a PUT request via: $.ajax({u
 jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page
Feb 28, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page
Feb 28, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Title: jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page In web development, we often need to modify and operate elements on the page. When using jQuery, sometimes you need to modify the text content of all a tags in the page at once, which can save time and energy. The following will introduce how to use jQuery to quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page, and give specific code examples. First, we need to introduce the jQuery library file and ensure that the following code is introduced into the page: <
 Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags
Feb 28, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags
Feb 28, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Title: Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags. jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used to handle DOM operations. In web development, we often encounter the need to modify the text content of the link tag (a tag) on the page. This article will explain how to use jQuery to achieve this goal, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to introduce the jQuery library into the page. Add the following code in the HTML file:
 How do the types of PHP function return values relate to the interoperability of PHP extensions?
Apr 15, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
How do the types of PHP function return values relate to the interoperability of PHP extensions?
Apr 15, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
PHP function return value types can be expressed as type description syntax, which clearly specifies the return value type of each function. Understanding return value types is critical to creating extensions that are compatible with the PHP core engine, avoiding unexpected conversions, improving efficiency, and enhancing code readability. Specifically, extension functions can define a return value type so that the PHP engine can optimize code execution based on that type and allow developers to explicitly handle the return value. In practice, extension functions can return PHP objects, and PHP code can handle the returned results according to the return value type.
 Learn more about how to use the Laravel Redis extension
Mar 09, 2024 pm 02:03 PM
Learn more about how to use the Laravel Redis extension
Mar 09, 2024 pm 02:03 PM
Laravel is a popular PHP development framework with rich functions and flexible scalability. The Redis extension is a commonly used database caching tool. This article will deeply explore the use of Redis extensions in Laravel, introduce its basic concepts, configuration methods and specific code examples in detail to help developers better use Redis extensions to improve system performance. 1. What is RedisRedis is an open source memory data storage system, also known as
 How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute? When using jQuery to operate DOM elements, you often encounter situations where you need to determine whether an element has a specific attribute. In this case, we can easily implement this function with the help of the methods provided by jQuery. The following will introduce two commonly used methods to determine whether a jQuery element has specific attributes, and attach specific code examples. Method 1: Use the attr() method and typeof operator // to determine whether the element has a specific attribute



