Application of JavaScript format string_javascript skills
After some design, this function was finally completed. After introducing this js, you can configure the format string yourself to output various customized date formats. 格式字符串 描述 示例 y 格式化年。年份由世纪+年代组成。 “y”输出8 “yy”输出08 “yyy”输出508 “yyyy”输出0508 “yyyyyy”输出000508 M 格式化月。 “M”输出1 “MM”输出01 “MMM”或更多输出一月 d 格式化日。 “d”输出9 “dd” 输出09 “ddd” 输出一 “dddd” 或更多输出星期一 H,h 格式化小时。其中H表示24小时制,h表示12小时制。 “H”输出14 “HH” 或更多输出14 “h”输出2 “hh” 或更多输出02 m 格式化分钟。 “m”输出3 “mm” 或更多输出03 s 格式化秒 “s”输出5 “ss” 或更多输出05 浏览器 快捷键 Chrome Ctrl + Shift + J IE8 F12 FireFox 忘了。FireFox中的控制台不是原生的,是一个叫FireBug的插件。
Flowchart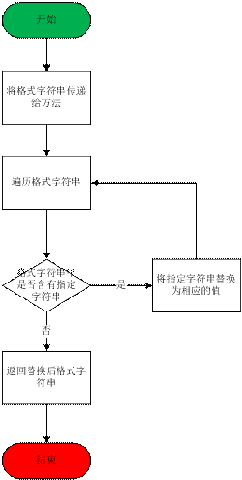
It can be seen that the so-called format string is actually a string containing specific characters, and then based on its actual The meaning is replaced with the specified value.
In this article, we only use the Date object as an example. In fact, the value of the format string goes beyond this. Under what circumstances can format strings be used? Hopefully you will find the answer by the end of this article.
Algorithm introduction
Below I will use an example to illustrate the format string algorithm. This example will format the "day" part of the date, such as 2008-8-8. If the format string is "d", it will output "8"; if the format string is "dd", it will output "08"; if If the format string is "dddd", "five" will be output; if the format string is "dddd", "friday" will be output. The parameter d is a Date object and format is a string:
//Format Day
function FormatDay(d, format){
while(format.indexOf("d") > -1){
var regex = /[d] /;
format = format.replace(regex,function(w){
switch(w.length){
case 0:break;
case 1:
return d.getDate();
case 2:
return d.getDate() < 10 ? "0" d.getDate() : d.getDate();
case 3:
switch(d.getDay()) {
case 0:
return "日";
case 1:
return "一";
case 2:
return "二";
case 3:
return "三";
case 4:
return "四";
case 5:
return "五";
case 6:
return "六";
}
default:
switch(d.getDay()){
case 0:
return "Sunday";
case 1:
return "Monday";
case 2:
return "Tuesday";
case 3:
return "Wednesday";
case 4:
return "Thursday";
case 5:
return "Friday";
case 6:
return "Saturday";
}
}
});
}
return format;
}
As you can see, the core part is:
while (format.indexOf("d") > -1) {
var regex = /[d] /;
format = format.replace(regex, function(w) {
switch (w.length) {
case 0: break;
case 1:
//todo
case 2:
//todo
case 3:
/ /todo
case x:
//todo
default:
//todo
}
});
}
解释:
1. 使用while循环,只要格式字符串format中含有特定字符就一直执行下去;
2. 声明一个正则表达式对象/[x]+/,其中x表示特定字符;
3. 使用string对象的replace方法替换特定字符;
4. 根据匹配到的特定字符串的长度,执行不同的操作(在本示例中,“d”、“dd”、“ddd”代表不同的含义)。
格式字符串说明
以508-1-9 14:3:5为例
更多的设置,大家可以自己动手做一下。
示例
引用此js后,在浏览器的控制台中测试结果如下: 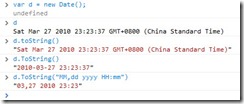
如何,有没有心动的感觉……
顺便说一下各浏览器的控制台呼出方式:
Source code
The following code can be downloaded from DateExtension.js
Date.prototype.ToString = function(format){
if(typeof(format) == "string"){
return FormatDateTime(this, format);
}
return FormatDateTime(this, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
}
//Format DateTime object
function FormatDateTime(d, format){
format = FormatYear( d, format);
format = FormatMonth(d, format);
format = FormatDay(d, format);
format = FormatHour(d, format);
format = FormatMinute(d, format);
format = FormatSecond(d, format);
return format;
}
//Format year
function FormatYear(d, format){
var fullYear = d.getFullYear(); //Full year
var century = Math.floor(fullYear / 100); //Century
var year = fullYear % 100; //Year
while(format.indexOf ("y") > -1){
var regex = /[y] /;
format = format.replace(regex,function(w){
//Format string if it is " y" or "yy", only the year is returned. Otherwise, the century year is returned.
switch(w.length){
case 0:break;
case 1:
return year;
case 2:
return year < 10 ? "0" year : year;
default:
var yearPart = year < 10 ? "0" year : year;
var centuryPart = "";
for(var i = 0; i < w.length - 2 - century.toString().length; i ){
centuryPart = "0";
}
centuryPart = century;
return centuryPart yearPart;
}
});
}
return format;
}
//Format month
function FormatMonth(d, format){
var month = d.getMonth() 1;
while(format.indexOf("M") > -1){
var regex = /[M] /;
format = format .replace(regex,function(w){
switch(w.length){
case 0:break;
case 1:
return month;
case 2:
return month < 10 ? "0" month : month;
default:
switch(month){
case 1:
return "January";
case 2:
return "February";
case 3:
return "March";
case 4:
return "April";
case 5:
return "May";
case 6:
return "June";
case 7:
return "July";
case 8:
return "August";
case 9 :
return "September";
case 10:
return "October";
case 11:
return "November";
case 12:
return "December";
}
}
});
}
return format;
}
//Format day
function FormatDay(d , format){
while(format.indexOf("d") > -1){
var regex = /[d] /;
format = format.replace(regex,function(w) {
switch(w.length){
case 0:break;
case 1:
return d.getDate();
case 2:
return d.getDate() < 10 ? "0" d.getDate() : d.getDate();
case 3:
switch(d.getDay()){
case 0:
return "Day" ;
case 1:
return "一";
case 2:
return "二";
case 3:
return "三";
case 4:
return "四";
case 5:
return "五";
case 6:
return "六";
}
default:
switch(d .getDay()){
case 0:
return "Sunday";
case 1:
return "Monday";
case 2:
return "Tuesday";
case 3:
return "Wednesday";
case 4:
return "Thursday";
case 5:
return "Friday";
case 6:
return "Saturday";
}
}
});
}
return format;
}
//Format hour
//H: 24 hours System
//h: 12-hour format
function FormatHour(d, format){
while(format.indexOf("H") > -1){
var regex = /[H ] /;
format = format.replace(regex,function(w){
switch(w.length){
case 0:break;
case 1:
return d.getHours ();
default:
return d.getHours() < 10 ? "0" d.getHours() : d.getHours();
}
});
}
while(format.indexOf("h") > -1){
var regex = /[h] /;
format = format.replace(regex,function(w){
switch(w.length){
case 0:break;
case 1:
return d.getHours() > 12 ? d.getHours() - 12 : d.getHours();
default:
var t = d.getHours() > 12 ? d.getHours() - 12 : d.getHours();
return t < 10 ? "0" t : t;
}
});
}
return format;
}
//Format minutes
function FormatMinute(d, format){
while(format.indexOf( "m") > -1){
var regex = /[m] /;
format = format.replace(regex,function(w){
switch(w.length){
case 0:break;
case 1:
return d.getMinutes();
default:
return d.getMinutes() < 10 ? "0" d.getMinutes() : d .getMinutes();
}
});
}
return format;
}
//Format seconds
function FormatSecond(d, format){
while(format.indexOf("s") > -1){
var regex = /[s] /;
format = format.replace(regex,function(w){
switch( w.length){
case 0:break;
case 1:
return d.getSeconds();
default:
return d.getSeconds() < 10 ? "0" d.getSeconds() : d.getSeconds();
}
});
}
return format;
}
Resources used in this article
DateExtension.js download
W3C School browsing
Browse for more support about Date objects
Date operation class DateTime function code implemented by js
pdf version download address

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service




