跟老齐学Python之for循环语句
废话少说,上干活。
for的基本操作
for是用来循环的,是从某个对象那里依次将元素读取出来。看下面的例子,将已经学习过的数据对象用for循环一下,看看哪些能够使用,哪些不能使用。同时也是复习一下过往的内容。
>>> name_str = "qiwsir"
>>> for i in name_str: #可以对str使用for循环
... print i,
...
q i w s i r
>>> name_list = list(name_str)
>>> name_list
['q', 'i', 'w', 's', 'i', 'r']
>>> for i in name_list: #对list也能用
... print i,
...
q i w s i r
>>> name_set = set(name_str) #set还可以用
>>> name_set
set(['q', 'i', 's', 'r', 'w'])
>>> for i in name_set:
... print i,
...
q i s r w
>>> name_tuple = tuple(name_str)
>>> name_tuple
('q', 'i', 'w', 's', 'i', 'r')
>>> for i in name_tuple: #tuple也能呀
... print i,
...
q i w s i r
>>> name_dict={"name":"qiwsir","lang":"python","website":"qiwsir.github.io"}
>>> for i in name_dict: #dict也不例外
... print i,"-->",name_dict[i]
...
lang --> python
website --> qiwsir.github.io
name --> qiwsir
除了上面的数据类型之外,对文件也能够用for,这在前面有专门的《不要红头文件》两篇文章讲解有关如何用for来读取文件对象的内容。看官若忘记了,可去浏览。
for在list解析中,用途也不可小觑,这在讲解list解析的时候,业已说明,不过,还是再复习一下为好,所谓学而时常复习之,不亦哈哈乎。
>>> one = range(1,9)
>>> one
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
>>> [ x for x in one if x%2==0 ]
[2, 4, 6, 8]
什么也不说了,list解析的强悍,在以后的学习中会越来越体会到的,佩服佩服呀。
列位如果用python3,会发现字典解析、元组解析也是奇妙的呀。
要上升一个档次,就得进行概括。将上面所说的for循环,概括一下,就是下图所示:
请输入图片描述
用一个文字表述:
for iterating_var in sequence:
statements
iterating_var是对象sequence的迭代变量,也就是sequence必须是一个能够有某种序列的对象,特别注意没某种序列,就是说能够按照一定的脚标获取元素。当然,文件对象属于序列,我们没有用脚标去获取每行,如果把它读取出来,因为也是一个str,所以依然可以用脚标读取其内容。
zip
zip是什么东西?在交互模式下用help(zip),得到官方文档是:
zip(...)
zip(seq1 [, seq2 [...]]) -> [(seq1[0], seq2[0] ...), (...)]
Return a list of tuples, where each tuple contains the i-th element from each of the argument sequences. The returned list is truncated in length to the length of the shortest argument sequence.
通过实验来理解上面的文档:
>>> a = "qiwsir"
>>> b = "github"
>>> zip(a,b)
[('q', 'g'), ('i', 'i'), ('w', 't'), ('s', 'h'), ('i', 'u'), ('r', 'b')]
>>> c = [1,2,3]
>>> d = [9,8,7,6]
>>> zip(c,d)
[(1, 9), (2, 8), (3, 7)]
>>> e = (1,2,3)
>>> f = (9,8)
>>> zip(e,f)
[(1, 9), (2, 8)]
>>> m = {"name","lang"}
>>> n = {"qiwsir","python"}
>>> zip(m,n)
[('lang', 'python'), ('name', 'qiwsir')]
>>> s = {"name":"qiwsir"}
>>> t = {"lang":"python"}
>>> zip(s,t)
[('name', 'lang')]
zip是一个内置函数,它的参数必须是某种序列数据类型,如果是字典,那么键视为序列。然后将序列对应的元素依次组成元组,做为一个list的元素。
下面是比较特殊的情况,参数是一个序列数据的时候,生成的结果样子:
>>> a
'qiwsir'
>>> c
[1, 2, 3]
>>> zip(c)
[(1,), (2,), (3,)]
>>> zip(a)
[('q',), ('i',), ('w',), ('s',), ('i',), ('r',)]
这个函数和for连用,就是实现了:
>>> c
[1, 2, 3]
>>> d
[9, 8, 7, 6]
>>> for x,y in zip(c,d): #实现一对一对地打印
... print x,y
...
1 9
2 8
3 7
>>> for x,y in zip(c,d): #把两个list中的对应量上下相加。
... print x+y
...
10
10
10
上面这个相加的功能,如果不用zip,还可以这么写:
>>> length = len(c) if len(c)
... print c[i]+d[i]
...
10
10
10
以上两种写法那个更好呢?前者?后者?哈哈。我看差不多了。还可以这么做呢:
>>> [ x+y for x,y in zip(c,d) ]
[10, 10, 10]
前面多次说了,list解析强悍呀。当然,还可以这样的:
>>> [ c[i]+d[i] for i in range(length) ]
[10, 10, 10]
for循环语句在后面还会经常用到,其实前面已经用了很多了。所以,看官应该不感到太陌生。

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 17 ways to solve the kernel_security_check_failure blue screen
Feb 12, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
17 ways to solve the kernel_security_check_failure blue screen
Feb 12, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Kernelsecuritycheckfailure (kernel check failure) is a relatively common type of stop code. However, no matter what the reason is, the blue screen error causes many users to be very distressed. Let this site carefully introduce 17 types to users. Solution. 17 solutions to kernel_security_check_failure blue screen Method 1: Remove all external devices When any external device you are using is incompatible with your version of Windows, the Kernelsecuritycheckfailure blue screen error may occur. To do this, you need to unplug all external devices before trying to restart your computer.
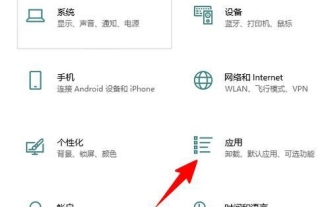 How to uninstall Skype for Business on Win10? How to completely uninstall Skype on your computer
Feb 13, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
How to uninstall Skype for Business on Win10? How to completely uninstall Skype on your computer
Feb 13, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
Can Win10 skype be uninstalled? This is a question that many users want to know, because many users find that this application is included in the default program on their computers, and they are worried that deleting it will affect the operation of the system. Let this website help users Let’s take a closer look at how to uninstall Skype for Business in Win10. How to uninstall Skype for Business in Win10 1. Click the Windows icon on the computer desktop, and then click the settings icon to enter. 2. Click "Apply". 3. Enter "Skype" in the search box and click to select the found result. 4. Click "Uninstall". 5
 Lambda expression breaks out of loop
Feb 20, 2024 am 08:47 AM
Lambda expression breaks out of loop
Feb 20, 2024 am 08:47 AM
Lambda expression breaks out of the loop, specific code examples are needed. In programming, the loop structure is an important syntax that is often used. However, in certain circumstances, we may want to break out of the entire loop when a certain condition is met within the loop body, rather than just terminating the current loop iteration. At this time, the characteristics of lambda expressions can help us achieve the goal of jumping out of the loop. Lambda expression is a way to declare an anonymous function, which can define simple function logic internally. It is different from an ordinary function declaration,
 A comparative study of loops and recursion in Go language
Jun 01, 2023 am 09:23 AM
A comparative study of loops and recursion in Go language
Jun 01, 2023 am 09:23 AM
Note: This article compares loops and recursion from the perspective of Go language. When writing programs, you often encounter situations where a series of data or operations need to be processed repeatedly. To achieve this we need to use loops or recursion. Loops and recursions are both commonly used processing methods, but in practical applications, they each have advantages and disadvantages, so the actual situation needs to be considered when choosing which method to use. This article will conduct a comparative study of loops and recursion in the Go language. 1. Loops A loop is a mechanism that repeatedly executes a certain piece of code. There are three main types of Go language
 PHP returns all the values in the array to form an array
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:06 AM
PHP returns all the values in the array to form an array
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:06 AM
This article will explain in detail how PHP returns all the values of an array to form an array. The editor thinks it is quite practical, so I share it with you as a reference. I hope you can gain something after reading this article. Using the array_values() function The array_values() function returns an array of all the values in an array. It does not preserve the keys of the original array. $array=["foo"=>"bar","baz"=>"qux"];$values=array_values($array);//$values will be ["bar","qux"]Using a loop can Use a loop to manually get all the values of the array and add them to a new
 How to use for to find the factorial of n in JavaScript
Dec 08, 2021 pm 06:04 PM
How to use for to find the factorial of n in JavaScript
Dec 08, 2021 pm 06:04 PM
How to use for to find n factorial: 1. Use the "for (var i=1;i<=n;i++){}" statement to control the loop traversal range to "1~n"; 2. In the loop body, use "cj *=i" Multiply the numbers from 1 to n, and assign the product to the variable cj; 3. After the loop ends, the value of the variable cj is the factorial of n, and then output it.
 Java Iterator vs. Iterable: A step into writing elegant code
Feb 19, 2024 pm 02:54 PM
Java Iterator vs. Iterable: A step into writing elegant code
Feb 19, 2024 pm 02:54 PM
Iterator interface The Iterator interface is an interface used to traverse collections. It provides several methods, including hasNext(), next() and remove(). The hasNext() method returns a Boolean value indicating whether there is a next element in the collection. The next() method returns the next element in the collection and removes it from the collection. The remove() method removes the current element from the collection. The following code example demonstrates how to use the Iterator interface to iterate over a collection: Listnames=Arrays.asList("John","Mary","Bob");Iterator
 What are the alternatives to recursive calls in Java functions?
May 05, 2024 am 10:42 AM
What are the alternatives to recursive calls in Java functions?
May 05, 2024 am 10:42 AM
Replacement of recursive calls in Java functions with iteration In Java, recursion is a powerful tool used to solve various problems. However, in some cases, using iteration may be a better option because it is more efficient and less prone to stack overflows. Here are the advantages of iteration: More efficient since it does not require the creation of a new stack frame for each recursive call. Stack overflows are less likely to occur because stack space usage is limited. Iterative methods as an alternative to recursive calls: There are several methods in Java to convert recursive functions into iterative functions. 1. Use the stack Using the stack is the easiest way to convert a recursive function into an iterative function. The stack is a last-in-first-out (LIFO) data structure, similar to a function call stack. publicintfa




