跟老齐学Python之用while来循环
在python中,它也有这个含义,不过有点区别的是,“当...时候”这个条件成立在一段范围或者时间间隔内,从而在这段时间间隔内让python做好多事情。就好比这样一段情景:
while 年龄大于60岁:-------->当年龄大于60岁的时候
退休 -------->凡是符合上述条件就执行的动作
展开想象,如果制作一道门,这道门就是用上述的条件调控开关的,假设有很多人经过这个们,报上年龄,只要年龄大于60,就退休(门打开,人可以出去),一个接一个地这样循环下去,突然有一个人年龄是50,那么这个循环在他这里就停止,也就是这时候他不满足条件了。
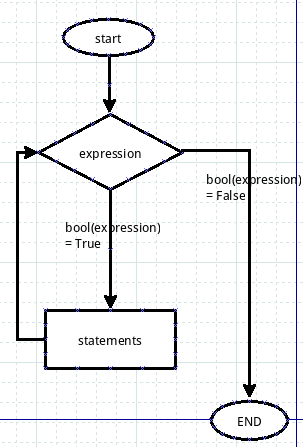
这就是while循环。写一个严肃点的流程,可以看下图:
再做猜数字游戏
本教程有一讲,是跟看官一同做一个小游戏,在里面做了一个猜数的游戏,当时遇到了一个问题,就是只能猜一两次,如果猜不到,程序就不能继续运行了。
前不久,有一个在校的大学生朋友(他叫李航),给我发邮件,让我看了他做的游戏,能够实现多次猜数,直到猜中为止。这是一个多么喜欢学习的大学生呀。
我在这里将他写的程序恭录于此,单元李航同学不要见怪,如果李航同学认为此举侵犯了自己的知识产权,可以告知我,我马上撤下此代码。
#! /usr/bin/env python
#coding:UTF-8
import random
i=0
while i
print'********************************'
num = input('请您输入0到9任一个数:') #李同学用的是python3
xnum = random.randint(0,9)
x = 3 - i
if num == xnum:
print'运气真好,您猜对了!'
break
elif num > xnum:
print'''您猜大了!\n哈哈,正确答案是:%s\n您还有%s次机会!''' %(xnum,x)
elif num
print'''您猜小了!\n哈哈,正确答案是:%s\n您还有%s次机会!''' %(xnum,x)
print'********************************'
i += 1
我们就用这段程序来分析一下,首先看while i
当bool(i
根据上述代码,看官看看是否可以修改?
为了让用户的体验更爽,不妨把输入的整数范围扩大,在1到100之间吧。
num_input = raw_input("please input one integer that is in 1 to 100:") #我用的是python2.7,在输入指令上区别于李同学
程序用num_input变量接收了输入的内容。但是,请列位看官一定要注意,看到这里想睡觉的要打起精神了,我要分享一个多年编程经验,请牢记:任何用户输入的内容都是不可靠的。这句话含义深刻,但是,这里不做过多的解释,需要各位在随后的编程生涯中体验了。为此,我们要检验用户输入的是否符合我们的要求,我们要求用户输入的是1到100之间的整数,那么就要做如下检验:
输入的是否是整数
如果是整数,是否在1到100之间。
为此,要做:
if not num_input.isdigit(): #str.isdigit()是用来判断字符串是否纯粹由数字组成
print "Please input interger."
elif int(num_input)=100:
print "The number should be in 1 to 100."
else:
pass #这里用pass,意思是暂时省略,如果满足了前面提出的要求,就该执行此处语句
再看看李航同学的程序,在循环体内产生一个随机的数字,这样用户每次输入,面对的都是一个新的随机数字。这样的猜数字游戏难度太大了。我希望是程序产生一个数字,直到猜中,都是这个数字。所以,要把产生随机数字这个指令移动到循环之前。
import random
number = random.randint(1,100)
while True: #不限制用户的次数了
...
观察李同学的程序,还有一点需要向列位显明的,那就是在条件表达式中,两边最好是同种类型数据,上面的程序中有:num>xnum样式的条件表达式,而一边是程序生成的int类型数据,一边是通过输入函数得到的str类型数据。在某些情况下可以运行,为什么?看官能理解吗?都是数字的时候,是可以的。但是,这样不好。
那么,按照这种思路,把这个猜数字程序重写一下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding:utf-8
import random
number = random.randint(1,100)
guess = 0
while True:
num_input = raw_input("please input one integer that is in 1 to 100:")
guess +=1
if not num_input.isdigit():
print "Please input interger."
elif int(num_input)=100:
print "The number should be in 1 to 100."
else:
if number==int(num_input):
print "OK, you are good.It is only %d, then you successed."%guess
break
elif number>int(num_input):
print "your number is more less."
elif number
else:
print "There is something bad, I will not work"
以上供参考,看官还可改进。
break和continue
break,在上面的例子中已经出现了,其含义就是要在这个地方中断循环,跳出循环体。下面这个简要的例子更明显:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding:utf-8
a = 8
while a:
if a%2==0:
break
else:
print "%d is odd number"%a
a = 0
print "%d is even number"%a
a=8的时候,执行循环体中的break,跳出玄幻,执行最后的打印语句,得到结果:
8 is even number
如果a=9,则要执行else里面的的print,然后a=0,循环就在执行一次,又break了,得到结果:
9 is odd number
0 is even number
而continue则是要从当前位置(即continue所在的位置)跳到循环体的最后一行的后面(不执行最后一行),对一个循环体来讲,就如同首尾衔接一样,最后一行的后面是哪里呢?当然是开始了。
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding:utf-8
a = 9
while a:
if a%2==0:
a -=1
continue #如果是偶数,就返回循环的开始
else:
print "%d is odd number"%a #如果是奇数,就打印出来
a -=1
其实,对于这两东西,我个人在编程中很少用到。我有一个固执的观念,尽量将条件在循环之前做足,不要在循环中跳来跳去,不仅可读性下降,有时候自己也糊涂了。
while...else
这两个的配合有点类似if ... else,只需要一个例子列为就理解了,当然,一遇到else了,就意味着已经不在while循环内了。
#!/usr/bin/env python
count = 0
while count
print count, " is less than 5"
count = count + 1
else:
print count, " is not less than 5"
执行结果:
0 is less than 5
1 is less than 5
2 is less than 5
3 is less than 5
4 is less than 5
5 is not less than 5

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 In C language, what is the difference between while(1) and while(0)?
Aug 31, 2023 am 10:45 AM
In C language, what is the difference between while(1) and while(0)?
Aug 31, 2023 am 10:45 AM
We know that in C language, 'while' keyword is used to define a loop that works based on the condition passed to the loop. Now, since the condition can have two values, true or false, the code inside the while block will be executed repeatedly if the condition is true and will not be executed if the condition is false. Now, by passing parameters to the while loop, we can differentiate between while(1) and while(0) because while(1) is a loop where the condition is always considered true and hence the code inside the block will start executing repeatedly. Furthermore, we can state that it is not 1 that is passed to the loop that makes the condition true, but if any non-zero integer is passed to the while loop, then it will be considered as the true condition, so
 Lambda expression breaks out of loop
Feb 20, 2024 am 08:47 AM
Lambda expression breaks out of loop
Feb 20, 2024 am 08:47 AM
Lambda expression breaks out of the loop, specific code examples are needed. In programming, the loop structure is an important syntax that is often used. However, in certain circumstances, we may want to break out of the entire loop when a certain condition is met within the loop body, rather than just terminating the current loop iteration. At this time, the characteristics of lambda expressions can help us achieve the goal of jumping out of the loop. Lambda expression is a way to declare an anonymous function, which can define simple function logic internally. It is different from an ordinary function declaration,
 A comparative study of loops and recursion in Go language
Jun 01, 2023 am 09:23 AM
A comparative study of loops and recursion in Go language
Jun 01, 2023 am 09:23 AM
Note: This article compares loops and recursion from the perspective of Go language. When writing programs, you often encounter situations where a series of data or operations need to be processed repeatedly. To achieve this we need to use loops or recursion. Loops and recursions are both commonly used processing methods, but in practical applications, they each have advantages and disadvantages, so the actual situation needs to be considered when choosing which method to use. This article will conduct a comparative study of loops and recursion in the Go language. 1. Loops A loop is a mechanism that repeatedly executes a certain piece of code. There are three main types of Go language
 PHP returns all the values in the array to form an array
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:06 AM
PHP returns all the values in the array to form an array
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:06 AM
This article will explain in detail how PHP returns all the values of an array to form an array. The editor thinks it is quite practical, so I share it with you as a reference. I hope you can gain something after reading this article. Using the array_values() function The array_values() function returns an array of all the values in an array. It does not preserve the keys of the original array. $array=["foo"=>"bar","baz"=>"qux"];$values=array_values($array);//$values will be ["bar","qux"]Using a loop can Use a loop to manually get all the values of the array and add them to a new
 Java Iterator vs. Iterable: A step into writing elegant code
Feb 19, 2024 pm 02:54 PM
Java Iterator vs. Iterable: A step into writing elegant code
Feb 19, 2024 pm 02:54 PM
Iterator interface The Iterator interface is an interface used to traverse collections. It provides several methods, including hasNext(), next() and remove(). The hasNext() method returns a Boolean value indicating whether there is a next element in the collection. The next() method returns the next element in the collection and removes it from the collection. The remove() method removes the current element from the collection. The following code example demonstrates how to use the Iterator interface to iterate over a collection: Listnames=Arrays.asList("John","Mary","Bob");Iterator
 What are the alternatives to recursive calls in Java functions?
May 05, 2024 am 10:42 AM
What are the alternatives to recursive calls in Java functions?
May 05, 2024 am 10:42 AM
Replacement of recursive calls in Java functions with iteration In Java, recursion is a powerful tool used to solve various problems. However, in some cases, using iteration may be a better option because it is more efficient and less prone to stack overflows. Here are the advantages of iteration: More efficient since it does not require the creation of a new stack frame for each recursive call. Stack overflows are less likely to occur because stack space usage is limited. Iterative methods as an alternative to recursive calls: There are several methods in Java to convert recursive functions into iterative functions. 1. Use the stack Using the stack is the easiest way to convert a recursive function into an iterative function. The stack is a last-in-first-out (LIFO) data structure, similar to a function call stack. publicintfa
 Using vectorization to replace loops in python
Apr 14, 2023 pm 07:07 PM
Using vectorization to replace loops in python
Apr 14, 2023 pm 07:07 PM
All programming languages are inseparable from loops. So, by default, we start executing a loop whenever there is a repeating operation. But when we are dealing with large number of iterations (millions/billions of rows), using loops is a crime. You might be stuck for a few hours, only to realize later that it doesn't work. This is where implementing vectorization in python becomes very critical. What is vectorization? Vectorization is a technique for implementing (NumPy) array operations on data sets. Behind the scenes, it applies the operation to all elements of the array or series at once (unlike a "for" loop that operates one row at a time). Next we use some use cases to demonstrate what vectorization is. Find the sum of numbers##Use the loop importtimestart
 How to handle PHP loop nesting errors and generate corresponding error messages
Aug 07, 2023 pm 01:33 PM
How to handle PHP loop nesting errors and generate corresponding error messages
Aug 07, 2023 pm 01:33 PM
How to handle PHP loop nesting errors and generate corresponding error messages. During development, we often use loop statements to handle repeated tasks, such as traversing arrays and processing database query results. However, when using loop nesting, you sometimes encounter errors, such as infinite loops or too many nesting levels. This problem can cause server performance to degrade or even crash. In order to better handle such errors and generate corresponding error messages, this article will introduce some common processing methods and give corresponding code examples. 1. Use counters to




