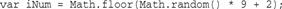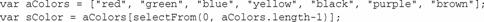Javascript Math Object_Basic Knowledge
Math对象
Math对象是在高中数学课就学过的内置对象。它知道解决最复杂的数学问题的所有公式,如果给它要处理的数字,即能计算出结果。
Math对象有几个属性,主要是数学界的专用值。下表类出了这些属性:
|
属 性 |
说 明 |
|
E |
值e,自然对数的底 |
|
LN10 |
10的自然对数 |
|
LN2 |
2的自然对数 |
|
LOG2E |
以2为底E的对数 |
|
LOG10E |
以10为底E的对数 |
|
PI |
值π |
|
SQRT1_2 |
1/2的平方根 |
|
SQRT2 |
2的平方根 |
虽然这些值的意义与用法不在本书讨论范围内,但如果清楚它们是什么,在需要时,即可使用它们。
Math对象还包括许多专门用于执行简单的及复杂的数学计算的方法。
方法min()和max()用于判断一组数中的最大值和最小值。这两个方法都可接受任意多个参数:

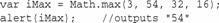
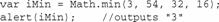
对于数字3、54、32和16,max()返回54,min()返回3。用这些方法,可免去用循环或if语句来判断一组数中的最大值。
另一个方法abs()返回数字的绝对值。绝对值是负数的正值版本(正数的绝对值就是它自身)。
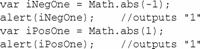
这个例子中,abs(-1)返回1,abs(1)也返回1。
下一组方法用于把小数舍入成整数。处理舍入操作的方法有三个,即ceil()、floor()和round(),它们的处理方法不同:
q 方法ceil()表示向上舍入函数,总是把数字向上舍入到最接近的值。
q 方法floor()表示向下舍入函数,总是把数字向下舍入到最接近的值。
q 方法round()表示标准的舍入函数,如果数字与下一个整数的差不超过0.5,则向上舍入,否则向下舍入。这是在初中学过的舍入规则。
为说明每种方法的处理方式,考虑使用值25.5:

对于ceil()和round(),传递25.5,返回的是26,而floor()返回的是25。注意不要交替使用这些方法,因为最后可能得到与预期不符的结果。
另一组方法与指数的用法有关。这些方法包括exp(),用于把Math.E升到指定的幂;log()用于返回特定数字的自然对数;pow()用于把指定的数字升到指定的幂;sqrt()用于返回指定数字的平方根。
方法exp()和log()本质上功能相反,exp()把Math.E升到特定的幂,log()则判断Math.E的多少次指数才等于指定的值。例如:

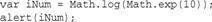
这里,首先用exp()把Math.E升到10次幂,然后log()返回10,即等于数字iNum必需的指数。很多人都对此感到迷茫。全世界的高中生和数学系的大学生都被此类问题难倒过。如果你对自然对数一无所知,那么有可能永远都不需要为它编写代码。
方法pow()用于把数字升到指定的幂,如把2升到10次幂(在数学中表示为210):
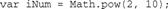
pow()的第一个参数是基数,此例子中是2。第二个参数是要升到的幂,此例子中是10。
不建议把Math.E作为pow()方法的基数。最好使用exp()对Math.E进行升幂运算,因为它是专用运算,计算出的值更精确。
The last method in this set of methods is sqrt(), which returns the square root of the specified number. It has only one parameter, the number whose square root is required. To ask for the square root of 4, you only need to use one line of code:
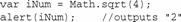
Of course, the square root of 4 is 2, which is the output of this line of code.
You may ask "Why does the square root have to use an exponent"? In fact, the square root of a number is its 1/2 power. For example, 21/2 is the square root of 2.
The Math object also has a complete set of trigonometric function methods. The following table lists these methods:
|
Fang method
|
Say Ming |
||||||||||||||||
|
acos(x) |
Returns the arc cosine of x |
||||||||||||||||
|
asin(x) |
Returns the arcsine of x | ||||||||||||||||
| atan(x) |
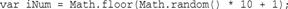 Returns the arctangent of x Returns the arctangent of x |
||||||||||||||||
|
atan2(y,x) |
Returns the inverse cosine of y/x |
||||||||||||||||
| cos(x) | Returns the cosine value of x | ||||||||||||||||
 sin(x) sin(x) |
Returns the sine value of x |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
Returns the tangent value of x |

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Calculate the natural logarithm using Java's Math.log() function
Jul 24, 2023 am 11:10 AM
Calculate the natural logarithm using Java's Math.log() function
Jul 24, 2023 am 11:10 AM
Calculate the natural logarithm using Java's Math.log() function Natural logarithm (Naturallogarithm) is one of the common logarithm types in mathematics. In the Java programming language, you can use the Math.log() function to calculate the natural logarithm. The usage of this function is introduced below and some code examples are given. The Math.log() function is a static method in Java that is used to calculate the logarithm with base e. This function accepts a parameter x and returns the natural logarithm of x
 Use the math.Log2 function to calculate the base 2 logarithm of a specified number
Jul 24, 2023 pm 12:14 PM
Use the math.Log2 function to calculate the base 2 logarithm of a specified number
Jul 24, 2023 pm 12:14 PM
Use the math.Log2 function to calculate the base 2 logarithm of a specified number. In mathematics, the logarithm is an important concept that describes the exponential relationship of one number to another number (the so-called base). Among them, the base 2 logarithm is particularly common and is frequently used in the fields of computer science and information technology. In the Python programming language, we can calculate the base 2 logarithm of a number using the log2 function from the math library. Here is a simple code example: importmathdef
 Python's Math library: usage and introduction to common functions
Apr 24, 2023 pm 11:10 PM
Python's Math library: usage and introduction to common functions
Apr 24, 2023 pm 11:10 PM
Overview of the Math library The math library is a built-in mathematical function library provided by Python. Because complex number types are often used in scientific calculations and not in general calculations, the math library does not support complex number types and only supports integer and floating point number operations. The math library provides a total of 4 mathematical constants and 44 functions. The 44 functions are divided into 4 categories, including 16 numerical representation functions, 8 power logarithmic functions, 16 trigonometric logarithmic functions and 4 advanced special functions. There are a large number of functions in the math library. During the learning process, we only need to understand the function functions one by one and remember some commonly used functions. In actual programming, if you need to use the math library, you can check the math library quick reference at any time. The functions in the math library cannot be used directly and need to be first
 Convert radians to degrees using java's Math.toDegrees() function
Jul 27, 2023 pm 10:51 PM
Convert radians to degrees using java's Math.toDegrees() function
Jul 27, 2023 pm 10:51 PM
Title: Convert radians to angles using Java's Math.toDegrees() function Abstract: In mathematics and computer programming, it is often necessary to convert radians to degrees. Java provides the toDegrees() function in the Math class to facilitate this conversion. This article will introduce how to use Java's Math.toDegrees() function to convert radians to angles and give code examples. Definition of radians and angles In mathematics, angles are measured in degrees (°), while arcs
 How to compare the size of two numbers using the Math.max() method in Java?
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:29 PM
How to compare the size of two numbers using the Math.max() method in Java?
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:29 PM
How to compare the size of two numbers using the Math.max() method in Java? In the Java programming language, the Math class is a very commonly used class and provides many mathematics-related methods. Among them, the Math.max() method can be used to compare the sizes of two numbers and return the larger number. The signature of the Math.max() method is as follows: publicstaticintmax(inta,intb) This method accepts two parameters a and b and returns the larger one.
 Use the math.Log10 function to calculate the base 10 logarithm of a specified number
Jul 25, 2023 pm 06:33 PM
Use the math.Log10 function to calculate the base 10 logarithm of a specified number
Jul 25, 2023 pm 06:33 PM
Use the math.Log10 function to calculate the base 10 logarithm of a specified number. Logarithms are a common concept in mathematics and computer science. We often use logarithms to describe the size or proportion of numbers. In computer programming, the commonly used logarithmic function is the logarithmic function with base 10. In the Python language, you can use the log10 function in the math library to calculate the base 10 logarithm of a specified number. Below we will demonstrate the use of this function through a simple code example. First, we need
 Calculate exponential functions using Java's Math.exp() function
Jul 26, 2023 pm 04:28 PM
Calculate exponential functions using Java's Math.exp() function
Jul 26, 2023 pm 04:28 PM
Use Java's Math.exp() function to calculate the exponential function. The exponential function is a common type of function in mathematics. It has the form y=a^x, where a is the base and x is the exponent. Exponential functions are widely used in mathematics, physics, engineering and other fields. In Java programming, we can use the exp() function of the Math class to calculate the value of the exponential function. The Math class is a mathematical calculation class provided in the Java language, which contains many commonly used mathematical functions. The exp() function is Ma
 Math.abs function in JavaScript: Returns the absolute value of a number
Nov 18, 2023 pm 12:01 PM
Math.abs function in JavaScript: Returns the absolute value of a number
Nov 18, 2023 pm 12:01 PM
JavaScript language is a scripting language commonly used for web page interaction and dynamic effects. The Math.abs function is one of the very useful functions, which is used to find the absolute value of a number. This article will introduce the usage and examples of the Math.abs function in detail, hoping to be helpful to beginners. Basic usage of the Math.abs function The Math.abs function is a built-in function in the JavaScript language, used to obtain the absolute value of a number. Its syntax format is: Mat




 tan(x)
tan(x)