DOM basic methods_basic knowledge
Direct reference to the node
1.document.getElementById(id);
--Find the node by id in the document
2.document.getElementByTagName(tagName);
--Return an array , including references to these nodes
--such as: document.getElementByTagName("span"); will return all nodes of span type
2. Indirect reference to nodes
3. element.childNodes
--Returns all child nodes of element. You can use element.childNodes[i] to call
--element.firstChild=element.childNodes[0];
--element .lastChild=element.childNodes[element.childNonts.length-1];
4.element.parentNode
--Reference the parent node
5.element.nextSibling; //Reference the next sibling node
element.previousSibling; //Refer to the previous sibling node
3. Obtain node information
6. The nodeName attribute obtains the node name
--for element nodes, the returned Tag name, such as: returns "a"
--for attribute nodes, returns the attribute name, such as: class="test" returns test
--for text The node returns the content of the text
7.nodeType returns the type of the node
--element node returns 1
--attribute node returns 2
--text node returns 3
8.nodeValue returns the value of the node
--element node returns null
--attribute node returns undefined
--text node returns text content
9.hasChildNodes() judgment Whether there are child nodes
10. The tagName attribute returns the tag name of the element
- this attribute is only available for element nodes, and is equivalent to the nodeName attribute of the element node
4. Process attribute structures Point
11. Each attribute node is an attribute of the element node and can be accessed through (element node.attribute name)
12. Use the setAttribute() method to add attributes to the element node
--elementNode.setAttribute(attributeName,attributeValue);
--attributeName is the name of the attribute, attributeValue is the value of the attribute
13. Use the getAttribute() method to obtain the attribute value
--elementNode.getAttribute(attributeName ; Spaces, newlines, tabs, etc. are treated as text nodes. All text nodes that are generally referenced through element.childNodes[i] generally need to be processed:
6. Change the hierarchy of the document
15.document.createElement() method Create element node
--such as: document.createElement("Span");
16.document.createTextNode() method creates text node
--such as: document.createTextNode(" "); //Note: It will not be encoded through html, which means that what is created here is not a space, but a string
17. Use the appendChild() method to add nodes
--parentElement.appendChild(childElement);
18. Use insertBefore() method to insert child nodes
--parentNode.insertBefore(newNode, referenceNode);
--newNode is the inserted node, referenceNode is the inserted node before this
19. Use the replaceChild method to replace the child node
--parentNode.replaceChild(newNode,oldNode);
--Note: oldNode must be a child node of parentNode,
20. Use the cloneNode method to copy the node
--node.cloneNode(includeChildren);
--includeChildren is bool, indicating whether to copy its child nodes
21. Use the removeChild method to delete child nodes
--parentNode.removeChild(childNode ; =document.createElement("table"); //Create table
table.insertRow(i); //Insert row in row i of table
row.insertCell(i); //Insert row in row i Insert cells at i positions
23. Reference cell objects
--table.rows[i].cells[i];
24. Delete rows and cells
--table.deleteRow (index);
--row.deleteCell(index);
25. Swap two rows to obtain the positions of two cells
node1.swapNode(node2);
--This method is available in firefox An error will occur in
General method:
function swapNode(node1,node2)
{
var _parent=node1.parentNode;
var _t1=node1.nextSubling;
var _t2=node2 .nextSubling;
if(_t1)parent.insertBefore(node2,_t1);
else _parent.appendChild(node2);
if(_t2)parent.insertBefore(node1,_t2);
else _parent.appendChild(node1);
}
Delete all blank nodes:
nodetype=3 node type is text s matches all blanks
Insert the node into the specified index position
function insertAt(parentNode,newNode,index)
{
if(!parentNode.hasChildNodes())
{
parentNode.appendChild(newNode);
return newNode;
}
//Use try to catch exceptions when the index does not exist
try{
parentNode.insertBefore(newNode,parentNode.childNodes[index]);
}
catch(e){
return null;
}
return newNode;

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What are the ways to obtain DOM nodes in Vue3
May 11, 2023 pm 04:55 PM
What are the ways to obtain DOM nodes in Vue3
May 11, 2023 pm 04:55 PM
1. Native js gets the DOM node: document.querySelector (selector) document.getElementById (id selector) document.getElementsByClassName (class selector).... 2. Get the instance object of the current component in vue2: because each vue Each component instance contains a $refs object, which stores references to the corresponding DOM elements or components. So by default, the component's $refs point to an empty object. You can first add ref="name" to the component, and then pass this.$refs.
 DOM manipulation guide in PHP
May 21, 2023 pm 04:01 PM
DOM manipulation guide in PHP
May 21, 2023 pm 04:01 PM
In web development, DOM (DocumentObjectModel) is a very important concept. It allows developers to easily modify and operate the HTML or XML document of a web page, such as adding, deleting, modifying elements, etc. The built-in DOM operation library in PHP also provides developers with rich functions. This article will introduce the DOM operation guide in PHP, hoping to help everyone. The basic concept of DOM DOM is a cross-platform, language-independent API that can
 What does vue dom mean?
Dec 20, 2022 pm 08:41 PM
What does vue dom mean?
Dec 20, 2022 pm 08:41 PM
DOM is a document object model and an interface for HTML programming. Elements in the page are manipulated through DOM. The DOM is an in-memory object representation of an HTML document, and it provides a way to interact with web pages using JavaScript. The DOM is a hierarchy (or tree) of nodes with the document node as the root.
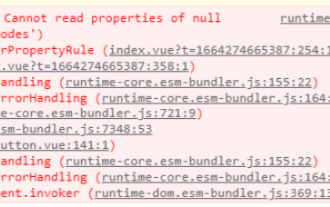 What is the reason why ref binding to dom or component fails in vue3 and how to solve it
May 12, 2023 pm 01:28 PM
What is the reason why ref binding to dom or component fails in vue3 and how to solve it
May 12, 2023 pm 01:28 PM
Vue3ref binding DOM or component failure reason analysis scenario description In Vue3, it is often used to use ref to bind components or DOM elements. Many times, ref is clearly used to bind related components, but ref binding often fails. Examples of ref binding failure situations The vast majority of cases where ref binding fails is that when the ref is bound to the component, the component has not yet been rendered, so the binding fails. Or the component is not rendered at the beginning and the ref is not bound. When the component starts to render, the ref also starts to be bound, but the binding between ref and the component is not completed. At this time, problems will occur when using component-related methods. The component bound to ref uses v-if, or its parent component uses v-if to cause the page to
 What are the dom and bom objects?
Nov 13, 2023 am 10:52 AM
What are the dom and bom objects?
Nov 13, 2023 am 10:52 AM
There are 5 DOM objects including "document", "element", "Node", "Event" and "Window"; 2. "window", "navigator", "location" and "history" and "screen" and other 5 BOM objects.
 What is the difference between bom and dom
Nov 13, 2023 pm 03:23 PM
What is the difference between bom and dom
Nov 13, 2023 pm 03:23 PM
BOM and DOM are different in terms of role and function, relationship with JavaScript, interdependence, compatibility of different browsers, and security considerations. Detailed introduction: 1. Role and function. The main function of BOM is to operate the browser window. It provides direct access and control of the browser window. The main function of DOM is to convert the web document into an object tree, allowing developers to Use this object tree to obtain and modify the elements and content of the web page; 2. Relationship with JavaScript, etc.
 What are the built-in objects of DOM?
Dec 19, 2023 pm 03:45 PM
What are the built-in objects of DOM?
Dec 19, 2023 pm 03:45 PM
dom内置对象有:1、document;2、window;3、navigator;4、location;5、history;6、screen;7、document.documentElement;8、document.body;9、document.head;10、document.title;11、document.cookie。
 Examples to explain how js implements horizontal and vertical scrolling animation of dom elements
Aug 07, 2022 am 09:36 AM
Examples to explain how js implements horizontal and vertical scrolling animation of dom elements
Aug 07, 2022 am 09:36 AM
This article will introduce to you how to implement horizontal and vertical scrolling animation of DOM elements in js. I hope it will be helpful to friends in need!






