Introduction to using JavaScript prototype
Students who have used JavaScript must be familiar with prototype, but beginners are confused about what it is. They only know that functions have a prototype attribute, and functions can be added for instance access. Others are not clear. Recently, I have seen some advanced JavaScript programming, and finally unveiled its mystery
Students who have used JavaScript must be familiar with prototype, but what exactly it is makes beginners confused. They only know Functions will have a prototype attribute, and functions can be added for instance access. The rest is not clear. I recently read some advanced JavaScript programming and finally unveiled its mystery.
Each function has a prototype attribute, which is a reference to an object. This object is called a prototype object. The prototype object contains methods and properties shared by function instances, which means that the function is used as a constructor. When a function is called (called using the new operator), the newly created object inherits properties and methods from the prototype object.
Private variables and functions
Let me talk about a few related things before talking about prototype in detail, so that you can better understand the design intention of prototype. A JavaScript namespace article I wrote before mentioned the function scope of JavaScript. If the variables and functions defined within the function do not provide an interface to the outside world, they will not be accessible from the outside, that is, they will become private variables and private functions.
The code is as follows:
function Obj(){
var a=0; //私有变量
var fn=function(){ //私有函数
}
}In this way, the variable a and function fn cannot be accessed outside the function object Obj, and they become private. When used inside Obj, even instances of function Obj still cannot access these variables and functions
The code is as follows:
var o=new Obj();
console.log(o.a); //undefined
console.log(o.fn); //undefinedStatic variables, functions
When a function is defined and the attributes and functions added to it through "." are still accessible through the object itself, but its instances are accessed No, such variables and functions are called static variables and static functions respectively. Students who have used Java and C# can easily understand the meaning of static.
The code is as follows:
function Obj(){
}
Obj.a=0; //静态变量
Obj.fn=function(){ //静态函数
}
console.log(Obj.a); //0
console.log(typeof Obj.fn); //function
var o=new Obj();
console.log(o.a); //undefined
console.log(typeof o.fn); //undefinedInstance variables, functions
In object-oriented programming, except for some For library functions, we still hope to define some properties and methods at the same time when the object is defined, which can be accessed after instantiation. JavaScript can also do this
The code is as follows:
function Obj(){
this.a=[]; //实例变量
this.fn=function(){ //实例方法
}
}
console.log(typeof Obj.a); //undefined
console.log(typeof Obj.fn); //undefined
var o=new Obj();
console.log(typeof o.a); //object
console.log(typeof o.fn); //functionThis can achieve the above purpose, however
The code is as follows:
function Obj(){
this.a=[]; //实例变量
this.fn=function(){ //实例方法
}
}
var o1=new Obj();
o1.a.push(1);
o1.fn={};
console.log(o1.a); //[1]
console.log(typeof o1.fn); //object
var o2=new Obj();
console.log(o2.a); //[]
console.log(typeof o2.fn); //functionThe above code running results are completely in line with expectations, but At the same time, it also illustrates a problem. A and fn are modified in o1, but not changed in o2. Since arrays and functions are both objects and reference types, this means that the properties and methods in o1 are different from the properties and methods in o2. Although it has the same name, it is not a reference, but a copy of the properties and methods defined by the Obj object.
This is not a problem for attributes, but it is a big problem for methods, because the methods are doing exactly the same function, but there are two copies. If a function object has If there are thousands of instance methods, then each instance of it must maintain a copy of thousands of methods. This is obviously unscientific. What can we do? Prototype came into being.
prototype
Whenever a new function is created, a prototype attribute is created for that function based on a specific set of rules. By default, prototype The attribute will get a constructor attribute by default. This attribute is a pointer to the function where the prototype attribute is located. It's a bit confusing. Write the code and see the picture above!
The code is as follows:
function Person(){
}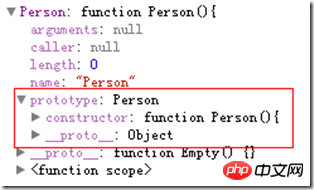
According to the above It can be seen from the figure that the Person object will automatically obtain the prototype attribute, and prototype is also an object and will automatically obtain a constructor attribute, which points to the Person object.
When a constructor is called to create an instance, the instance will contain an internal pointer (in many browsers this pointer is named __proto__) pointing to the prototype of the constructor. This connection exists between the prototype of the instance and the constructor. between the instance and the constructor.
The code is as follows:
function Person(name){
this.name=name;
}
Person.prototype.printName=function(){
alert(this.name);
}
var person1=new Person('Byron');
var person2=new Person('Frank');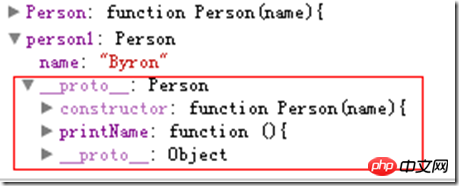
Person instance person1 contains the name attribute and automatically generates a The __proto__ attribute points to the prototype of the Person. You can access the printName method defined in the prototype, which probably looks like this
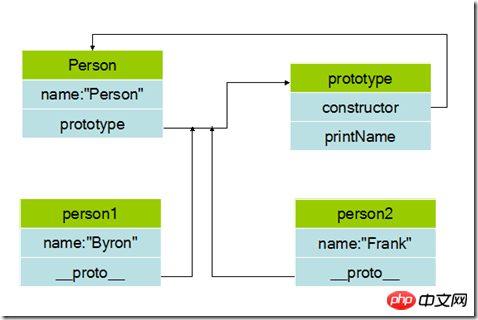
Write a program to test and see the prototype Internal attributes and methods can be shared
The code is as follows:
function Person(name){
this.name=name;
}
Person.prototype.share=[];
Person.prototype.printName=function(){
alert(this.name);
}
var person1=new Person('Byron');
var person2=new Person('Frank');
person1.share.push(1);
person2.share.push(2);
console.log(person2.share); //[1,2]果不其然!实际上当代码读取某个对象的某个属性的时候,都会执行一遍搜索,目标是具有给定名字的属性,搜索首先从对象实例开始,如果在实例中找到该属性则返回,如果没有则查找prototype,如果还是没有找到则继续递归prototype的prototype对象,直到找到为止,如果递归到object仍然没有则返回错误。同样道理如果在实例中定义如prototype同名的属性或函数,则会覆盖prototype的属性或函数。
代码如下:
function Person(name){
this.name=name;
}
Person.prototype.share=[];
var person=new Person('Byron');
person.share=0;
console.log(person.share); //0而不是prototype中的[]构造简单对象
当然prototype不是专门为解决上面问题而定义的,但是却解决了上面问题。了解了这些知识就可以构建一个科学些的、复用率高的对象,如果希望实例对象的属性或函数则定义到prototype中,如果希望每个实例单独拥有的属性或方法则定义到this中,可以通过构造函数传递实例化参数。
代码如下:
function Person(name){
this.name=name;
}
Person.prototype.share=[];
Person.prototype.printName=function(){
alert(this.name);
}
Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service




