php mysql implements infinite classification_php skills
Project idea analysis: A PHP project needs to use classification, but I am not sure how many levels it will be divided into, so I want to make it into infinite classification.
At first I thought I would create 4 values in the database as before, as follows:
id: auto-increment | pid: parent class ID | xid: sorting ID | classname: category name
Later, I thought that this would be inconvenient when reading data and modifying it, and it was especially inconvenient when reading products, so I changed it to the following solution:
A new field has been added to the Mysql table. The database is now as follows:
Table name w_faqclass: id: auto-increment | pid: parent class ID | xid: sort ID | classname: category name | rank: level
Definition:
Level 1 classification, pid is 0, rank is "/"
Second-level classification, pid is the id of the first-level classification, rank is "/the id of the first-level classification/"
Three-level classification, pid is the id of the second-level classification, rank is "/the id of the first-level classification/the id of the second-level classification/"
And so on...
1. Basic functions
/*
利于递归返回已经进行了排序的无限级分类的数组
不想用递归的话也可以用 like 来获取后再进行排序,我比较懒,就不写那种获取方式了,其实用 like 更好,推荐用那种方式
$datatable : 数据表名
$startid : 开始父类ID
$wheretColumns :父类列名
$xColumns : 排序列名
$xtype : 排序方式
$returnArr : 返回数组
*/
function ReadClass($datatable,$startid,$xtype,$returnArr){
$db = $datatable;
$sid = $startid;
$xtype = $xtype;
$lu = $returnArr;
$sql = "select * from `".$db."` where `pid`='".$sid."' order by xid ".$xtype.";";
$cresult= mysql_query($sql);
if(mysql_num_rows($cresult)>0){
while($rs = mysql_fetch_array($cresult)){
$lunum = count($lu);
$lu[$lunum]['id'] = $rs['id'];
$lu[$lunum]['pid'] = $rs['pid'];
$lu[$lunum]['rank'] = $rs['rank'];
$lu[$lunum]['classname']= $rs['classname'];
$lu[$lunum]['xid'] = $rs['xid'];
$lu = ReadClass($db,$rs['id'],$xtype,$lu);
}
}
return $lu;
}
/*
查询某表中的某个值,只会返回一个值
$datatable : 数据表名
$wherevalue : 条件值
$selectColumns : 查询列名
$whereColumns : 条件列
*/
function SelectValue($datatable,$wherevalue,$selectColumns,$whereColumns){
$sql = "select `".$selectColumns."` from `".$datatable."` where `".$whereColumns."`='".$wherevalue."';";
$result = mysql_query($sql);
while($rs = mysql_fetch_array($result)){
return $rs[$selectColumns];
}
}
2. Add categories (directly used for selection in select)
<?php
$classArr = ReadClass('w_faqclass','0','asc',array());
$canum = count($classArr);
echo "<select name='pid'>";
echo "<option value='0'>主分类</option>";
for($i=0; $i<$canum; $i++){
$rankArr = split("/",$classArr[$i]['rank']);
$ranknum = count($rankArr);
$t = "";
for($j=1; $j<$ranknum; $j++){ //用于格式化显示子类
$t .= "├┄┄";
}
echo "<option value='".$classArr[$i]['id']."'>".$t.$classArr[$i]['classname']."</option>";
}
echo "</select>"
?>
//保存时的操作,需要判断是否为主分类,当为主类时, rank 值设为 /
//查询父类的 rank 值,用父类的 rank 加上 父类的 id 值
if($pid != 0){
$pidrank = SelectValue('w_faqclass',$pid,'rank','id');
$rank = $pidrank.$pid."/";
}else{
$rank = "/";
}
3. Modify classification
<?php
/*
注意,因为是修改,在此页面加载时已将当前分类的所有值读出来了,对应是:$pid,$rank
*/
$classArr = ReadClass('w_faqclass','0','asc',array());
$canum = count($classArr);
echo "<select name='pid'>";
echo "<option value='0'>主分类</option>";
for($i=0; $i<$canum; $i++){
// 因为是修改,所以当前分类不能选择自身或自身以下的分类,多加个 rank 值的优势啊,哈哈,以前做单pid值的时候这里还得用次递归查询
while($ids == $classArr[$i]['id'] || strstr($classArr[$i]['rank'],$rank.$ids."/")){
$i++;
}
$rankArr = split("/",$classArr[$i]['rank']);
$ranknum = count($rankArr);
$t = "";
for($j=1; $j<$ranknum; $j++){
$t .= "├┄┄";
}
if($pid == $classArr[$i]['id']){
$selected = "selected";
}else{
$selected = "";
}
echo "<option value='".$classArr[$i]['id']."' ".$selected.">".$t.$classArr[$i]['classname']."</option>";
}
echo "</select>"
?>
// 保存时的操作
// 要做到改动时该分类的所有子分类rank值都需要变动,选取得原来子分类通用到的 rank 值,也就是该分类的 rank值加上它的ID值
// 利于 mysql 的REPLACE语句进行替换
if($pid != 0){
$pidrank = SelectValue('w_faqclass',$pid,'rank','id');
$rank = $pidrank.$pid."/";
}else{
$rank = "/";
}
$orank = SelectValue('w_faqclass',$ids,'rank','id').$ids."/";
$nrank = $rank.$ids."/";
mysql_query("UPDATE `w_faqclass` SET rank = REPLACE(rank,'".$orank."','".$nrank."');");
mysql_query("UPDATE `w_faqclass` SET `classname`='".$classname."',`xid`='".$xid."',`pid`='".$pid."',`rank`='".$rank."' where `id`='".$ids."';");
4. Deletion and query are simple. I won’t go into details on this. Just remember to confirm whether there are subclasses under the class before deleting.
$zid = SelectValue('w_faqclass',$ids,'id','pid');
if($zid>0){
...
}The above is the method of implementing Infinitus classification in php mysql. I hope it will be helpful to everyone's learning.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Working with Flash Session Data in Laravel
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PM
Working with Flash Session Data in Laravel
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PM
Laravel simplifies handling temporary session data using its intuitive flash methods. This is perfect for displaying brief messages, alerts, or notifications within your application. Data persists only for the subsequent request by default: $request-
 cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIs
Mar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AM
cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIs
Mar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AM
The PHP Client URL (cURL) extension is a powerful tool for developers, enabling seamless interaction with remote servers and REST APIs. By leveraging libcurl, a well-respected multi-protocol file transfer library, PHP cURL facilitates efficient execution of various network protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP. This extension offers granular control over HTTP requests, supports multiple concurrent operations, and provides built-in security features.
 Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel Tests
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel Tests
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Laravel provides concise HTTP response simulation syntax, simplifying HTTP interaction testing. This approach significantly reduces code redundancy while making your test simulation more intuitive. The basic implementation provides a variety of response type shortcuts: use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Http; Http::fake([ 'google.com' => 'Hello World', 'github.com' => ['foo' => 'bar'], 'forge.laravel.com' =>
 12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyon
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyon
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
Do you want to provide real-time, instant solutions to your customers' most pressing problems? Live chat lets you have real-time conversations with customers and resolve their problems instantly. It allows you to provide faster service to your custom
 Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.
Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PM
Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.
Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PM
Article discusses late static binding (LSB) in PHP, introduced in PHP 5.3, allowing runtime resolution of static method calls for more flexible inheritance.Main issue: LSB vs. traditional polymorphism; LSB's practical applications and potential perfo
 PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log Analysis
Mar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PM
PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log Analysis
Mar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PM
PHP logging is essential for monitoring and debugging web applications, as well as capturing critical events, errors, and runtime behavior. It provides valuable insights into system performance, helps identify issues, and supports faster troubleshoot
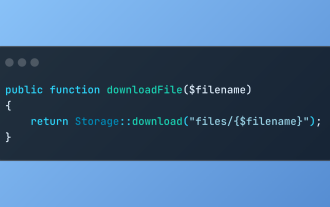 Discover File Downloads in Laravel with Storage::download
Mar 06, 2025 am 02:22 AM
Discover File Downloads in Laravel with Storage::download
Mar 06, 2025 am 02:22 AM
The Storage::download method of the Laravel framework provides a concise API for safely handling file downloads while managing abstractions of file storage. Here is an example of using Storage::download() in the example controller:
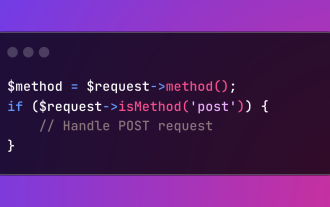 HTTP Method Verification in Laravel
Mar 05, 2025 pm 04:14 PM
HTTP Method Verification in Laravel
Mar 05, 2025 pm 04:14 PM
Laravel simplifies HTTP verb handling in incoming requests, streamlining diverse operation management within your applications. The method() and isMethod() methods efficiently identify and validate request types. This feature is crucial for building






