Two ways to send php emails_php tips
The main content of this article is to use PHP to send emails, which is summarized in the following two methods:
1. Use PHP’s built-in mail() function
<?php $to = "test@163.com"; //收件人 $subject = "Test"; //主题 $message = "This is a test mail!"; //正文 mail($to,$subject,$message);
The result is an error, as follows:
Warning: mail() [function.mail]: Failed to connect to mailserver at "localhost" port 25, verify your "SMTP" and "smtp_port" setting in php.ini or use ini_set() inD: /www/Zend/email/email.php on line 10
Analysis of the reason: A local SMTP server is required, so I changed the code:
<?php
$to = "test@163.com";//收件人
$subject = "Test";//邮件主题
$message = "This is a test mail!";//邮件正文
ini_set('SMTP','smtp.163.com');//发件SMTP服务器
ini_set('smtp_port',25);//发件SMTP服务器端口
ini_set('sendmail_from',"admin@163.com");//发件人邮箱
mail($to,$subject,$message); The result is still wrong:
Warning: mail() [function.mail]: SMTP server response: 553 authentication is required,smtp2,DNGowKD7v5BTDo9NnplVBA--.1171S2 1301220947 inD:/www/Zend/email/email.php on line 9
Analysis reason: Verification information is needed. How to write verification information? Where to configure it? After referring to some technical articles with these questions, I came to the conclusion that using the mail() function to send emails requires a mail server that can send letters without SMTP authentication. But today's SMTP mail servers basically require authentication, so if you want to use it to send emails, you can only set up a local SMTP server that does not require authentication. Building method: Just use the IIS that comes with Windows, or download other SMTP server software from the Internet.
Conclusion: To use the mail() function to send emails, you must have an SMTP server that does not require authentication. In this case, the configuration work will be a little more, but it will be easier to use, just a few lines of code.
2. Use the email class that encapsulates the SMTP protocol
This method is relatively common, especially for the majority of students who do not have a server and purchase a virtual host online. The first method is not practical, so you should use the SMTP protocol to send emails yourself.
However, to complete this work, you need to have a certain understanding of the SMTP protocol. Students who like to do everything by themselves can write one by themselves, and students who like to use it as a tool can download it from the Internet. There are many.
However, I recommend using the Mail class in the PEAR extension. is powerful: can support emails in plain text and HTML formats; each field can Set the encoding, and the correct configuration will not cause Chinese garbled characters; attachments, etc. can be supported.
You can use the pear install Mail command on the server to quickly install it. Students who do not have sufficient server permissions can also directly download the PHP source code of the class and include it.
Note: Mail class depends on Net/SMTP.php and Mail/mime.php, which need to be downloaded together and included together when using them.
Let me give an example of how to send emails in the Mail class. The methods of using other SMTP mail classes on the Internet are similar. You can refer to:
<?php
// Pear Mail 扩展
require_once('Mail.php');
require_once('Mail/mime.php');
require_once('Net/SMTP.php');
$smtpinfo = array();
$smtpinfo["host"] = "smtp.163.com";//SMTP服务器
$smtpinfo["port"] = "25"; //SMTP服务器端口
$smtpinfo["username"] = "username@163.com"; //发件人邮箱
$smtpinfo["password"] = "password";//发件人邮箱密码
$smtpinfo["timeout"] = 10;//网络超时时间,秒
$smtpinfo["auth"] = true;//登录验证
//$smtpinfo["debug"] = true;//调试模式
// 收件人列表
$mailAddr = array('receiver@163.com');
// 发件人显示信息
$from = "Name <username@163.com>";
// 收件人显示信息
$to = implode(',',$mailAddr);
// 邮件标题
$subject = "这是一封测试邮件";
// 邮件正文
$content = "<h3>随便写点什么</h3>";
// 邮件正文类型,格式和编码
$contentType = "text/html; charset=utf-8";
//换行符号 Linux: \n Windows: \r\n
$crlf = "\n";
$mime = new Mail_mime($crlf);
$mime->setHTMLBody($content);
$param['text_charset'] = 'utf-8';
$param['html_charset'] = 'utf-8';
$param['head_charset'] = 'utf-8';
$body = $mime->get($param);
$headers = array();
$headers["From"] = $from;
$headers["To"] = $to;
$headers["Subject"] = $subject;
$headers["Content-Type"] = $contentType;
$headers = $mime->headers($headers);
$smtp =& Mail::factory("smtp", $smtpinfo);
$mail = $smtp->send($mailAddr, $headers, $body);
$smtp->disconnect();
if (PEAR::isError($mail)) {
//发送失败
echo 'Email sending failed: ' . $mail->getMessage()."\n";
}
else{
//发送成功
echo "success!\n";
} If you find the SMTP classes on the Internet, they are highly encapsulated, so they will be simpler to use than the above, but the usage methods are relatively similar.
Conclusion: You don’t need to install any software to send emails in this way. You only need to include a PHP class and write a few more lines of configuration code. That’s it. And there are many example codes on the Internet. In many cases, you only need to copy them and modify a few parameters to use them, so it is very convenient and it is recommended to use this method.
The above are two methods of sending emails using PHP. I have my own thinking process. I hope it will be helpful to everyone's learning.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Working with Flash Session Data in Laravel
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PM
Working with Flash Session Data in Laravel
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PM
Laravel simplifies handling temporary session data using its intuitive flash methods. This is perfect for displaying brief messages, alerts, or notifications within your application. Data persists only for the subsequent request by default: $request-
 cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIs
Mar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AM
cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIs
Mar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AM
The PHP Client URL (cURL) extension is a powerful tool for developers, enabling seamless interaction with remote servers and REST APIs. By leveraging libcurl, a well-respected multi-protocol file transfer library, PHP cURL facilitates efficient execution of various network protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP. This extension offers granular control over HTTP requests, supports multiple concurrent operations, and provides built-in security features.
 Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel Tests
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel Tests
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Laravel provides concise HTTP response simulation syntax, simplifying HTTP interaction testing. This approach significantly reduces code redundancy while making your test simulation more intuitive. The basic implementation provides a variety of response type shortcuts: use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Http; Http::fake([ 'google.com' => 'Hello World', 'github.com' => ['foo' => 'bar'], 'forge.laravel.com' =>
 12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyon
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyon
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
Do you want to provide real-time, instant solutions to your customers' most pressing problems? Live chat lets you have real-time conversations with customers and resolve their problems instantly. It allows you to provide faster service to your custom
 Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.
Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PM
Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.
Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PM
Article discusses late static binding (LSB) in PHP, introduced in PHP 5.3, allowing runtime resolution of static method calls for more flexible inheritance.Main issue: LSB vs. traditional polymorphism; LSB's practical applications and potential perfo
 PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log Analysis
Mar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PM
PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log Analysis
Mar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PM
PHP logging is essential for monitoring and debugging web applications, as well as capturing critical events, errors, and runtime behavior. It provides valuable insights into system performance, helps identify issues, and supports faster troubleshoot
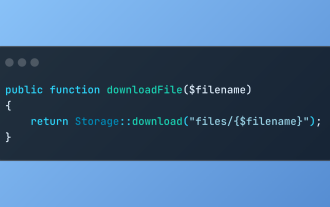 Discover File Downloads in Laravel with Storage::download
Mar 06, 2025 am 02:22 AM
Discover File Downloads in Laravel with Storage::download
Mar 06, 2025 am 02:22 AM
The Storage::download method of the Laravel framework provides a concise API for safely handling file downloads while managing abstractions of file storage. Here is an example of using Storage::download() in the example controller:
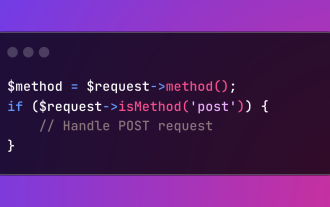 HTTP Method Verification in Laravel
Mar 05, 2025 pm 04:14 PM
HTTP Method Verification in Laravel
Mar 05, 2025 pm 04:14 PM
Laravel simplifies HTTP verb handling in incoming requests, streamlining diverse operation management within your applications. The method() and isMethod() methods efficiently identify and validate request types. This feature is crucial for building






