 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 yii2 source code study notes (13), yii2 source code study notes_PHP tutorial
yii2 source code study notes (13), yii2 source code study notes_PHP tutorial
yii2 source code study notes (13), yii2 source code study notes_PHP tutorial
yii2 source code study notes (13), yii2 source code study notes
The model class DynamicModel is mainly used to implement data verification within the model yii2baseDynamicModel.php
<span> 1</span> <?<span>php
</span><span> 2</span> <span>/*</span><span>*
</span><span> 3</span> <span> * @link </span><span>http://www.yiiframework.com/</span>
<span> 4</span> <span> * @copyright Copyright (c) 2008 Yii Software LLC
</span><span> 5</span> <span> * @license </span><span>http://www.yiiframework.com/license/</span>
<span> 6</span> <span>*/</span>
<span> 7</span> <span>namespace</span> yii\<span>base</span><span>;
</span><span> 8</span>
<span> 9</span> <span>use yii\validators\Validator;
</span><span> 10</span>
<span> 11</span> <span>/*</span><span>*
</span><span> 12</span> <span> * DynamicModel is a model class primarily used to support ad hoc data validation.
</span><span> 13</span> <span> * DynamicModel是一种主要用于支持ad hoc数据验证模型类
</span><span> 14</span> <span> * The typical usage of DynamicModel is as follows,
</span><span> 15</span> <span> *
</span><span> 16</span> <span> * ```php
</span><span> 17</span> <span> * public function actionSearch($name, $email)
</span><span> 18</span> <span> * {
</span><span> 19</span> <span> * $model = DynamicModel::validateData(compact('name', 'email'), [
</span><span> 20</span> <span> * [['name', 'email'], 'string', 'max' => 128],
</span><span> 21</span> <span> * ['email', 'email'],
</span><span> 22</span> <span> * ]);
</span><span> 23</span> <span> * if ($model->hasErrors()) {
</span><span> 24</span> <span> * // validation fails
</span><span> 25</span> <span> * } else {
</span><span> 26</span> <span> * // validation succeeds
</span><span> 27</span> <span> * }
</span><span> 28</span> <span> * }
</span><span> 29</span> <span> * ```
</span><span> 30</span> <span> *
</span><span> 31</span> <span> * The above example shows how to validate `$name` and `$email` with the help of DynamicModel.
</span><span> 32</span> <span> * 上面的例子演示了如何用DynamicModel验证用户名`$name`和邮箱`$email`
</span><span> 33</span> <span> * The [[validateData()]] method creates an instance of DynamicModel, defines the attributes
</span><span> 34</span> <span> * using the given data (`name` and `email` in this example), and then calls [[Model::validate()]].
</span><span> 35</span> <span> * validateData() 方法会创建一个 DynamicModel 的实例对象。通过给定数据定义模型特性,之后调用Model::validate() 方法。
</span><span> 36</span> <span> * You can check the validation result by [[hasErrors()]], like you do with a normal model.
</span><span> 37</span> <span> * You may also access the dynamic attributes defined through the model instance, e.g.,
</span><span> 38</span> <span> * 可以通过[[hasErrors()]]方法获取验证结果
</span><span> 39</span> <span> * `$model->name` and `$model->email`.
</span><span> 40</span> <span> *
</span><span> 41</span> <span> * Alternatively, you may use the following more "classic" syntax to perform ad-hoc data validation:
</span><span> 42</span> <span> * 除此之外,你也可以用如下的更加“classic(传统)”的语法来执行临时数据验
</span><span> 43</span> <span> * ```php
</span><span> 44</span> <span> * $model = new DynamicModel(compact('name', 'email'));
</span><span> 45</span> <span> * $model->addRule(['name', 'email'], 'string', ['max' => 128])
</span><span> 46</span> <span> * ->addRule('email', 'email')
</span><span> 47</span> <span> * ->validate();
</span><span> 48</span> <span> * ```
</span><span> 49</span> <span> *
</span><span> 50</span> <span> * DynamicModel implements the above ad-hoc data validation feature by supporting the so-called
</span><span> 51</span> <span> * "dynamic attributes". It basically allows an attribute to be defined dynamically through its constructor
</span><span> 52</span> <span> * or [[defineAttribute()]].
</span><span> 53</span> <span> * 实现了上述特殊数据模型验证功能支持的“动态属性”。允许通过它的构造函数或 [[defineAttribute()]]来定义一个属性
</span><span> 54</span> <span> * @author Qiang Xue <qiang.xue@gmail.com>
</span><span> 55</span> <span> * @since 2.0
</span><span> 56</span> <span>*/</span>
<span> 57</span> <span>class</span><span> DynamicModel extends Model
</span><span> 58</span> <span>{
</span><span> 59</span> <span>private</span> $_attributes = [];<span>//</span><span>动态模型内动态属性</span>
<span> 60</span>
<span> 61</span>
<span> 62</span> <span>/*</span><span>*
</span><span> 63</span> <span> * Constructors.构造函数,用于将传入的属性赋值给_attributes,便于使用
</span><span> 64</span> <span> * @param array $attributes the dynamic attributes (name-value pairs, or names) being defined被定义的动态属性
</span><span> 65</span> <span> * @param array $config the configuration array to be applied to this object.用于该对象的配置数组。
</span><span> 66</span> <span>*/</span>
<span> 67</span> <span>public</span> function __construct(array $attributes = [], $config =<span> [])
</span><span> 68</span> <span> {
</span><span> 69</span> <span>foreach</span> ($attributes <span>as</span> $name => $value) {<span>//</span><span>遍历传入的属性</span>
<span> 70</span> <span>if</span> (is_integer($name)) {<span>//</span><span>如果是整型,说明只传入了属性名,将属性名写入_attributes</span>
<span> 71</span> $<span>this</span>->_attributes[$value] = <span>null</span><span>;
</span><span> 72</span> } <span>else</span><span> {
</span><span> 73</span> $<span>this</span>->_attributes[$name] = $value;<span>//</span><span>按键值对的形式写入</span>
<span> 74</span> <span> }
</span><span> 75</span> <span> }
</span><span> 76</span> parent::__construct($config);<span>//</span><span>调用父类的配置</span>
<span> 77</span> <span> }
</span><span> 78</span>
<span> 79</span> <span>/*</span><span>*
</span><span> 80</span> <span> * @inheritdoc 重写__get方法,从_attributes中取值
</span><span> 81</span> <span>*/</span>
<span> 82</span> <span>public</span><span> function __get($name)
</span><span> 83</span> <span> {
</span><span> 84</span> <span>if</span> (array_key_exists($name, $<span>this</span>-><span>_attributes)) {
</span><span> 85</span> <span>//</span><span>如果传入的$name在数组_attributes中存在,则从_attributes中取值</span>
<span> 86</span> <span>return</span> $<span>this</span>-><span>_attributes[$name];
</span><span> 87</span> } <span>else</span> {<span>//</span><span>否则调用父类的__get方法取属性值</span>
<span> 88</span> <span>return</span><span> parent::__get($name);
</span><span> 89</span> <span> }
</span><span> 90</span> <span> }
</span><span> 91</span>
<span> 92</span> <span>/*</span><span>*
</span><span> 93</span> <span> * @inheritdoc 重写__set方法,给_attributes设置值
</span><span> 94</span> <span>*/</span>
<span> 95</span> <span>public</span><span> function __set($name, $value)
</span><span> 96</span> <span> {
</span><span> 97</span> <span>if</span> (array_key_exists($name, $<span>this</span>-><span>_attributes)) {
</span><span> 98</span> <span>//</span><span>如果传入的$name在数组_attributes中存在,则将动态属性$name的值设置为$value</span>
<span> 99</span> $<span>this</span>->_attributes[$name] =<span> $value;
</span><span>100</span> } <span>else</span><span> {
</span><span>101</span> parent::__set($name, $value);<span>//</span><span>调用父类的__set方法设置属性值</span>
<span>102</span> <span> }
</span><span>103</span> <span> }
</span><span>104</span>
<span>105</span> <span>/*</span><span>*
</span><span>106</span> <span> * @inheritdoc 同上 重写__isset方法,判断_attributes中是否设置$name值
</span><span>107</span> <span>*/</span>
<span>108</span> <span>public</span><span> function __isset($name)
</span><span>109</span> <span> {
</span><span>110</span> <span>if</span> (array_key_exists($name, $<span>this</span>-><span>_attributes)) {
</span><span>111</span> <span>return</span> isset($<span>this</span>-><span>_attributes[$name]);
</span><span>112</span> } <span>else</span><span> {
</span><span>113</span> <span>return</span><span> parent::__isset($name);
</span><span>114</span> <span> }
</span><span>115</span> <span> }
</span><span>116</span>
<span>117</span> <span>/*</span><span>*
</span><span>118</span> <span> * @inheritdoc 同上,重写__unset方法,删除_attributes中的$name属性值
</span><span>119</span> <span>*/</span>
<span>120</span> <span>public</span><span> function __unset($name)
</span><span>121</span> <span> {
</span><span>122</span> <span>if</span> (array_key_exists($name, $<span>this</span>-><span>_attributes)) {
</span><span>123</span> unset($<span>this</span>-><span>_attributes[$name]);
</span><span>124</span> } <span>else</span><span> {
</span><span>125</span> <span> parent::__unset($name);
</span><span>126</span> <span> }
</span><span>127</span> <span> }
</span><span>128</span>
<span>129</span> <span>/*</span><span>*
</span><span>130</span> <span> * Defines an attribute. 定义动态属性的方法
</span><span>131</span> <span> * @param string $name the attribute name 属性名
</span><span>132</span> <span> * @param mixed $value the attribute value 属性值
</span><span>133</span> <span>*/</span>
<span>134</span> <span>public</span> function defineAttribute($name, $value = <span>null</span><span>)
</span><span>135</span> <span> {
</span><span>136</span> $<span>this</span>->_attributes[$name] =<span> $value;
</span><span>137</span> <span> }
</span><span>138</span>
<span>139</span> <span>/*</span><span>*
</span><span>140</span> <span> * Undefines an attribute. 用于删除动态属性的方法
</span><span>141</span> <span> * @param string $name the attribute name 属性名
</span><span>142</span> <span>*/</span>
<span>143</span> <span>public</span><span> function undefineAttribute($name)
</span><span>144</span> <span> {
</span><span>145</span> unset($<span>this</span>-><span>_attributes[$name]);
</span><span>146</span> <span> }
</span><span>147</span>
<span>148</span> <span>/*</span><span>*
</span><span>149</span> <span> * Adds a validation rule to this model. 添加验证规则
</span><span>150</span> <span> * You can also directly manipulate [[validators]] to add or remove validation rules.
</span><span>151</span> <span> * This method provides a shortcut.
</span><span>152</span> <span> * 可以直接调用[[validators]]来添加或者删除验证规则,本方法提供了一个短方法
</span><span>153</span> <span> * @param string|array $attributes the attribute(s) to be validated by the rule 进行验证的属性
</span><span>154</span> <span> * @param mixed $validator the validator for the rule.This can be a built-in validator name,
</span><span>155</span> <span> * a method name of the model class, an anonymous function, or a validator class name.
</span><span>156</span> <span> * 规则的验证。这是一个内置验证器的名字, 一个模型类的方法名,一个匿名函数或一个验证器类的名称。
</span><span>157</span> <span> * @param array $options the options (name-value pairs) to be applied to the validator
</span><span>158</span> <span> * (name-value)被应用到验证器
</span><span>159</span> <span> * @return static the model itself 模型本身
</span><span>160</span> <span>*/</span>
<span>161</span> <span>public</span> function addRule($attributes, $validator, $options =<span> [])
</span><span>162</span> <span> {
</span><span>163</span> $validators = $<span>this</span>->getValidators();<span>//</span><span>所有的验证规则对象
</span><span>164</span> <span>//</span><span>生成Validator对象,并且插入 $validators中</span>
<span>165</span> $validators->append(Validator::createValidator($validator, $<span>this</span><span>, (array) $attributes, $options));
</span><span>166</span>
<span>167</span> <span>return</span> $<span>this</span><span>;
</span><span>168</span> <span> }
</span><span>169</span>
<span>170</span> <span>/*</span><span>*
</span><span>171</span> <span> * Validates the given data with the specified validation rules.通过指定的规则验证给定的数据
</span><span>172</span> <span> * This method will create a DynamicModel instance, populate it with the data to be validated,
</span><span>173</span> <span> * create the specified validation rules, and then validate the data using these rules.
</span><span>174</span> <span> * @param array $data the data (name-value pairs) to be validated
</span><span>175</span> <span> * @param array $rules the validation rules. Please refer to [[Model::rules()]] on the format of this parameter.
</span><span>176</span> <span> * @return static the model instance that contains the data being validated
</span><span>177</span> <span> * @throws InvalidConfigException if a validation rule is not specified correctly.
</span><span>178</span> <span>*/</span>
<span>179</span> <span>public</span> <span>static</span> function validateData(array $data, $rules =<span> [])
</span><span>180</span> <span> {
</span><span>181</span> <span>/*</span><span> @var $model DynamicModel </span><span>*/</span>
<span>182</span> $model = <span>new</span> <span>static</span>($data);<span>//</span><span>实例化调用类,将$data赋值给_attributes</span>
<span>183</span> <span>if</span> (!<span>empty($rules)) {
</span><span>184</span> $validators = $model->getValidators();<span>//</span><span>获取所有定义的验证规则</span>
<span>185</span> <span>foreach</span> ($rules <span>as</span><span> $rule) {
</span><span>186</span> <span>if</span><span> ($rule instanceof Validator) {
</span><span>187</span> $validators->append($rule);<span>//</span><span>如果$rule是Validator的实例,则添加到$validators中</span>
<span>188</span> } elseif (is_array($rule) && isset($rule[<span>0</span>], $rule[<span>1</span>])) { <span>//</span><span> attributes, validator type
</span><span>189</span> <span>//</span><span>如果$rule是数组,则判断动态属性和验证类型是否存在,创建Validator对象,添加到$validators中</span>
<span>190</span> $validator = Validator::createValidator($rule[<span>1</span>], $model, (array) $rule[<span>0</span>], array_slice($rule, <span>2</span><span>));
</span><span>191</span> $validators-><span>append($validator);
</span><span>192</span> } <span>else</span> {<span>//</span><span>抛出异常</span>
<span>193</span> <span>throw</span> <span>new</span> InvalidConfigException(<span>'</span><span>Invalid validation rule: a rule must specify both attribute names and validator type.</span><span>'</span><span>);
</span><span>194</span> <span> }
</span><span>195</span> <span> }
</span><span>196</span> <span> }
</span><span>197</span>
<span>198</span> $model->validate();<span>//</span><span>执行验证</span>
<span>199</span>
<span>200</span> <span>return</span><span> $model;
</span><span>201</span> <span> }
</span><span>202</span>
<span>203</span> <span>/*</span><span>*
</span><span>204</span> <span> * @inheritdoc 返回所有的动态属性
</span><span>205</span> <span>*/</span>
<span>206</span> <span>public</span><span> function attributes()
</span><span>207</span> <span> {
</span><span>208</span> <span>return</span> array_keys($<span>this</span>-><span>_attributes);
</span><span>209</span> <span> }
</span><span>210</span> }

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Imagine an artificial intelligence model that not only has the ability to surpass traditional computing, but also achieves more efficient performance at a lower cost. This is not science fiction, DeepSeek-V2[1], the world’s most powerful open source MoE model is here. DeepSeek-V2 is a powerful mixture of experts (MoE) language model with the characteristics of economical training and efficient inference. It consists of 236B parameters, 21B of which are used to activate each marker. Compared with DeepSeek67B, DeepSeek-V2 has stronger performance, while saving 42.5% of training costs, reducing KV cache by 93.3%, and increasing the maximum generation throughput to 5.76 times. DeepSeek is a company exploring general artificial intelligence
 AI subverts mathematical research! Fields Medal winner and Chinese-American mathematician led 11 top-ranked papers | Liked by Terence Tao
Apr 09, 2024 am 11:52 AM
AI subverts mathematical research! Fields Medal winner and Chinese-American mathematician led 11 top-ranked papers | Liked by Terence Tao
Apr 09, 2024 am 11:52 AM
AI is indeed changing mathematics. Recently, Tao Zhexuan, who has been paying close attention to this issue, forwarded the latest issue of "Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society" (Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society). Focusing on the topic "Will machines change mathematics?", many mathematicians expressed their opinions. The whole process was full of sparks, hardcore and exciting. The author has a strong lineup, including Fields Medal winner Akshay Venkatesh, Chinese mathematician Zheng Lejun, NYU computer scientist Ernest Davis and many other well-known scholars in the industry. The world of AI has changed dramatically. You know, many of these articles were submitted a year ago.
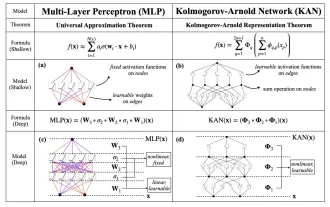 KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
Earlier this month, researchers from MIT and other institutions proposed a very promising alternative to MLP - KAN. KAN outperforms MLP in terms of accuracy and interpretability. And it can outperform MLP running with a larger number of parameters with a very small number of parameters. For example, the authors stated that they used KAN to reproduce DeepMind's results with a smaller network and a higher degree of automation. Specifically, DeepMind's MLP has about 300,000 parameters, while KAN only has about 200 parameters. KAN has a strong mathematical foundation like MLP. MLP is based on the universal approximation theorem, while KAN is based on the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem. As shown in the figure below, KAN has
 Google is ecstatic: JAX performance surpasses Pytorch and TensorFlow! It may become the fastest choice for GPU inference training
Apr 01, 2024 pm 07:46 PM
Google is ecstatic: JAX performance surpasses Pytorch and TensorFlow! It may become the fastest choice for GPU inference training
Apr 01, 2024 pm 07:46 PM
The performance of JAX, promoted by Google, has surpassed that of Pytorch and TensorFlow in recent benchmark tests, ranking first in 7 indicators. And the test was not done on the TPU with the best JAX performance. Although among developers, Pytorch is still more popular than Tensorflow. But in the future, perhaps more large models will be trained and run based on the JAX platform. Models Recently, the Keras team benchmarked three backends (TensorFlow, JAX, PyTorch) with the native PyTorch implementation and Keras2 with TensorFlow. First, they select a set of mainstream
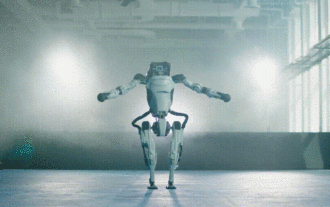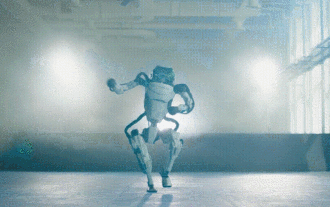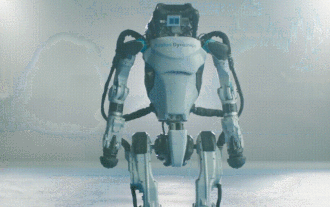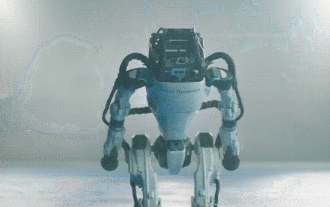 Hello, electric Atlas! Boston Dynamics robot comes back to life, 180-degree weird moves scare Musk
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:58 PM
Hello, electric Atlas! Boston Dynamics robot comes back to life, 180-degree weird moves scare Musk
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:58 PM
Boston Dynamics Atlas officially enters the era of electric robots! Yesterday, the hydraulic Atlas just "tearfully" withdrew from the stage of history. Today, Boston Dynamics announced that the electric Atlas is on the job. It seems that in the field of commercial humanoid robots, Boston Dynamics is determined to compete with Tesla. After the new video was released, it had already been viewed by more than one million people in just ten hours. The old people leave and new roles appear. This is a historical necessity. There is no doubt that this year is the explosive year of humanoid robots. Netizens commented: The advancement of robots has made this year's opening ceremony look like a human, and the degree of freedom is far greater than that of humans. But is this really not a horror movie? At the beginning of the video, Atlas is lying calmly on the ground, seemingly on his back. What follows is jaw-dropping
 FisheyeDetNet: the first target detection algorithm based on fisheye camera
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:37 AM
FisheyeDetNet: the first target detection algorithm based on fisheye camera
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:37 AM
Target detection is a relatively mature problem in autonomous driving systems, among which pedestrian detection is one of the earliest algorithms to be deployed. Very comprehensive research has been carried out in most papers. However, distance perception using fisheye cameras for surround view is relatively less studied. Due to large radial distortion, standard bounding box representation is difficult to implement in fisheye cameras. To alleviate the above description, we explore extended bounding box, ellipse, and general polygon designs into polar/angular representations and define an instance segmentation mIOU metric to analyze these representations. The proposed model fisheyeDetNet with polygonal shape outperforms other models and simultaneously achieves 49.5% mAP on the Valeo fisheye camera dataset for autonomous driving
 Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The latest video of Tesla's robot Optimus is released, and it can already work in the factory. At normal speed, it sorts batteries (Tesla's 4680 batteries) like this: The official also released what it looks like at 20x speed - on a small "workstation", picking and picking and picking: This time it is released One of the highlights of the video is that Optimus completes this work in the factory, completely autonomously, without human intervention throughout the process. And from the perspective of Optimus, it can also pick up and place the crooked battery, focusing on automatic error correction: Regarding Optimus's hand, NVIDIA scientist Jim Fan gave a high evaluation: Optimus's hand is the world's five-fingered robot. One of the most dexterous. Its hands are not only tactile
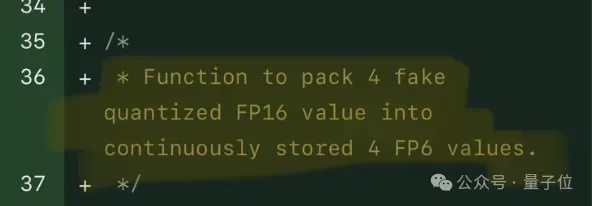 Single card running Llama 70B is faster than dual card, Microsoft forced FP6 into A100 | Open source
Apr 29, 2024 pm 04:55 PM
Single card running Llama 70B is faster than dual card, Microsoft forced FP6 into A100 | Open source
Apr 29, 2024 pm 04:55 PM
FP8 and lower floating point quantification precision are no longer the "patent" of H100! Lao Huang wanted everyone to use INT8/INT4, and the Microsoft DeepSpeed team started running FP6 on A100 without official support from NVIDIA. Test results show that the new method TC-FPx's FP6 quantization on A100 is close to or occasionally faster than INT4, and has higher accuracy than the latter. On top of this, there is also end-to-end large model support, which has been open sourced and integrated into deep learning inference frameworks such as DeepSpeed. This result also has an immediate effect on accelerating large models - under this framework, using a single card to run Llama, the throughput is 2.65 times higher than that of dual cards. one



