 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 PHP and MYSQL Programming [Fourth Edition] Chapter 3 Essay - (2), MySQL Programming_PHP Tutorial
PHP and MYSQL Programming [Fourth Edition] Chapter 3 Essay - (2), MySQL Programming_PHP Tutorial
PHP and MYSQL Programming [Fourth Edition] Chapter 3 Essay - (2), MySQL Programming_PHP Tutorial
PHP and MYSQL Programming [Fourth Edition] Chapter 3 Essay - (2), MySQL Programming
Chapter 3 PHP Basics
(3.6——3.11)
3.6 Variables
Variable declaration
Variable assignment: assignment by value/assignment by reference
Variable scope:
Local variables: Variables declared in a function can only be referenced in the function
Function parameters: Any function that accepts parameters must declare these parameters at the beginning of the function. Although these parameters accept values from outside the function, they are no longer accessible after exiting the function
 Parameter instance
Parameter instanceGlobal variables: (use with caution)
When accessing within a function, just add the keyword global
in front of the variableAnother way is to use PHP’s $GLOBALS array. $GLOBALS[""];
Static variable:
Unlike variables declared as function parameters, function parameters will be revoked when the function exits, while static variables will not lose their value when the function exits, and can also save this value for use when calling this function again
You can declare a static variable by adding the keyword STATIC in front of the variable name
PHP super global variables:
You can obtain detailed information about the current user session, user operating environment and local operating environment through PHP's super global variables

"; } //For example, display the user IP address: printf("Your IP address is: %s",$_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR']); //You can also get information about the user's browser and operating system: printf("Your browser is: %s",$_SERVER['HTTP_USER-AGENT']); Gives all predefined variable codes related to the given web server and script execution environment
Use the GET method to obtain the passed variables
Use the POST method to get the passed variables
Get information stored in cookies:
The $_COOKIE super global variable stores the information passed to the script through the HTTP cookie
These cookies are generally set by a previously executed PHP script through the PHP function setcookie()
Use POST method to get information about uploaded files
The $_FILES super global variable includes information about the data uploaded to the server through the POST method
$_FILES is a two-dimensional array containing 5 elements:
$_FILES['upload-name']['name']. The file name of the file uploaded from the client to the server
$_FILES['upload-name']['type']. The MIME type of the uploaded file. Whether this variable is assigned a value depends on the browser's capabilities
$_FILES['upload-name']['size']. Size of uploaded file in bytes
$_FILES['upload-name']['tmp_name']. After uploading, give this file a temporary name before moving it to its final location
$_FILES['upload-name']['error']. Upload status code. 5 possible values:
UPLOAD_ERR_OK. File uploaded successfully
UPLOAD_ERR_INI_SIZE. The file size exceeds the maximum value set by the upload_max_filesize directive
UPLOAD_ERR_FORM_SIZE. File size exceeds the maximum value specified by the MAX_FILE_SIZE hidden form field parameter (optional)
UPLOAD_ERR_PARTIAL. Only part of the file was uploaded
UPLOAD_NO_FILES. No file specified in file form
More about the operating system environment:
The $_ENV super global variable provides information about the server environment where the PHP parser is located
$_ENV['HOSTNAME']. Server hostname
$_ENV['SHELL']. System shell
Get information stored in the session: $_SESSION super global variable contains information related to all session variables
Variable of variable: Add a dollar sign before the original variable name, and then assign another value to it
3.7 Constants
Constants refer to values that cannot be modified in the program
The define() function defines a constant by assigning a value to a variable name. Its form is as follows:
boolean define(string name,mixed value [,bol case_insensitive])
If the optional parameter case_insensitive is used and the value of this parameter is TRUE, then subsequent references to this constant will not be case sensitive
There is no need to use the dollar sign before constants
Once defined, a defined constant cannot be redefined or undefined.
3.8 Expression
Operand (operand): The operand is the input of the expression
Operator: An operator is a symbol that specifies an action in an expression
Operator list
Operator precedence
Operator associativity
Arithmetic operators: " ", "-", "*", "/", "%"
Assignment operators: "=", " =", "*=", "/=", ".="
String operators: "=", ".="
Self-increase and self-reduced operator: "", "-"
According to the placement position of the auto-increment and auto-decrement operators, they can be divided into front auto-increment operation, front auto-decrement operation, post-increment operation, and post-auto-decrement operation
Logical operators: "&&", "AND", "||", "OR", "!", "NOT", "XOR"
Equality operators: "==", "!=", "==="
Comparison operators: "<", ">", "<=", ">=", "($a == 12) ? 5 : -1" (if $a is equal to 12, Return value 5; otherwise return value -1)
Bit operators: "&", "|", "^" (XOR. Every bit contained in $a or $b is XORed), "~ $b" (not. Every bit in $b) Bit opposite), "$a<<$b" (shift left. Move $a's bit left by $b steps), ">>" (shift right)
3.9 String insertion
Double quotes
Escape sequence: Description
n Line break character
r
t Horizontal tabBackslash
single quote
Braces
heredoc syntax:
phpThe homepage of the blog park (i.e. the homepage of the website) can only publish original, high-quality content that readers can learn from.
EXCERPT; ?> //The start and end identifiers must be the same. The start and end identifiers here are EXCERPT, which can also be customized //The start and end identifiers can only consist of alphanumeric characters and underscores, and cannot start with numbers or underscores //There must be 3 angle brackets before the start identifier:<<< //The end identifier must be at the beginning of a line and cannot be preceded by any spaces or other extra characters. //Any spaces after the start and end identifiers will cause a syntax error heredoc example Nowdoc syntax3.10 Control Structure
Conditional statements (the syntax of each statement is omitted)
if statement
else statement
elseif statement
switch statement
Loop statements (the syntax of each statement is omitted)
while statement
do...while statement
for statement
foreach statement
Break statement and goto statement
continue statement
The file contains the statement
include()
include() or include ""
Format: include(/path/to/filename)
Make sure you only include the file once: include_once()
Request file: require()
When require() fails, the script will stop executing. include() will continue to execute in this case
Make sure you only request the file once: require_once()
3.11 Summary
To become a successful PHP programmer, the foundation laid in this chapter is of extraordinary significance!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Working with Flash Session Data in Laravel
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PM
Working with Flash Session Data in Laravel
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PM
Laravel simplifies handling temporary session data using its intuitive flash methods. This is perfect for displaying brief messages, alerts, or notifications within your application. Data persists only for the subsequent request by default: $request-
 cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIs
Mar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AM
cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIs
Mar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AM
The PHP Client URL (cURL) extension is a powerful tool for developers, enabling seamless interaction with remote servers and REST APIs. By leveraging libcurl, a well-respected multi-protocol file transfer library, PHP cURL facilitates efficient execution of various network protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP. This extension offers granular control over HTTP requests, supports multiple concurrent operations, and provides built-in security features.
 Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel Tests
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel Tests
Mar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Laravel provides concise HTTP response simulation syntax, simplifying HTTP interaction testing. This approach significantly reduces code redundancy while making your test simulation more intuitive. The basic implementation provides a variety of response type shortcuts: use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Http; Http::fake([ 'google.com' => 'Hello World', 'github.com' => ['foo' => 'bar'], 'forge.laravel.com' =>
 12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyon
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyon
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
Do you want to provide real-time, instant solutions to your customers' most pressing problems? Live chat lets you have real-time conversations with customers and resolve their problems instantly. It allows you to provide faster service to your custom
 PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log Analysis
Mar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PM
PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log Analysis
Mar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PM
PHP logging is essential for monitoring and debugging web applications, as well as capturing critical events, errors, and runtime behavior. It provides valuable insights into system performance, helps identify issues, and supports faster troubleshoot
 Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.
Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PM
Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.
Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PM
Article discusses late static binding (LSB) in PHP, introduced in PHP 5.3, allowing runtime resolution of static method calls for more flexible inheritance.Main issue: LSB vs. traditional polymorphism; LSB's practical applications and potential perfo
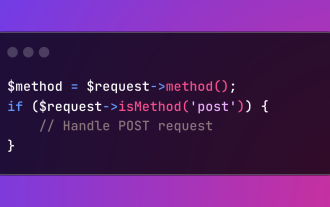 HTTP Method Verification in Laravel
Mar 05, 2025 pm 04:14 PM
HTTP Method Verification in Laravel
Mar 05, 2025 pm 04:14 PM
Laravel simplifies HTTP verb handling in incoming requests, streamlining diverse operation management within your applications. The method() and isMethod() methods efficiently identify and validate request types. This feature is crucial for building
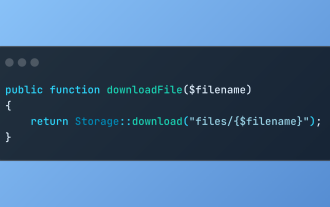 Discover File Downloads in Laravel with Storage::download
Mar 06, 2025 am 02:22 AM
Discover File Downloads in Laravel with Storage::download
Mar 06, 2025 am 02:22 AM
The Storage::download method of the Laravel framework provides a concise API for safely handling file downloads while managing abstractions of file storage. Here is an example of using Storage::download() in the example controller:





