 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 PHP variable reference (&), function reference and object reference_PHP tutorial
PHP variable reference (&), function reference and object reference_PHP tutorial
PHP variable reference (&), function reference and object reference_PHP tutorial
PHP variable reference (&), function reference and object reference
1. Variable reference
PHP reference pointers of two variables point to the same memory address
$a="ABC"; $b =&$a; echo $a;//这里输出:ABC echo $b;//这里输出:ABC $b="EFG"; echo $a;//这里$a的值变为EFG 所以输出EFG echo $b;//这里输出EFG
2. Function reference transfer (call by address)
function test(&$a)
{
$a=$a+100;
}
$b=1;
echo $b;//输出1
test($b); //这里$b传递给函数的其实是$b的变量内容所处的内存地址,通过在函数里改变$a的值 就可以改变$b的值了
echo "<br>";
echo $b;//输出101
?>
3. Function reference return
function &test()
{
static $b=0;//申明一个静态变量
$b=$b+1;
echo $b;
return $b;
}
$a=test();//这条语句会输出 $b的值 为1
$a=5;
$a=test();//这条语句会输出 $b的值 为2
$a=&test();//这条语句会输出 $b的值 为3
$a=5;
$a=test();//这条语句会输出 $b的值 为6
Explanation below:
In this way, $a=test(); actually does not get a reference return from the function. It is no different from an ordinary function call. As for the reason: This is a rule of PHP
When calling a function through $a=&test(), its function is to point the memory address of the $b variable in return $b and the memory address of the $a variable to the same place
That is to say, the effect equivalent to this is produced ($a=&$b;), so changing the value of $a also changes the value of $b, so after executing
4. Object reference (PHP5)
class foo {
public $bar = 1;
}
$a = new foo; //$a其实也是一个引用
$b = $a; //拷贝引用 ($a)=($b)={id1}
$a->bar = 2;
echo "b->bar = $b->bar\n";
$b->bar = 3;
echo "a->bar = $a->bar\n";
//修改了b,但实际上是修改了a和b所引用的同一个对象
//并不会引发 Copy On Write 创建一个新对象b
$a = new foo; //$a被修改为一个新的引用,$b没有改变
//($a)={id2} ($b)={id1}
$a->bar = 4;
echo "b->bar = $b->bar\n";
$b = &$a; //显式地使用引用,b成为“对象的引用”的引用
$a = new foo; //($a)={id3} ($b)=&($a)=&{id3}
$a->bar = 5;
echo "b->bar = $b->bar\n"
//==output====
b->bar = 2
a->bar = 3
b->bar = 3
b->bar = 5

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 CakePHP Project Configuration
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Project Configuration
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
In this chapter, we will understand the Environment Variables, General Configuration, Database Configuration and Email Configuration in CakePHP.
 PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 brings several new features, security improvements, and performance improvements with healthy amounts of feature deprecations and removals. This guide explains how to install PHP 8.4 or upgrade to PHP 8.4 on Ubuntu, Debian, or their derivati
 CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work with date and time in cakephp4, we are going to make use of the available FrozenTime class.
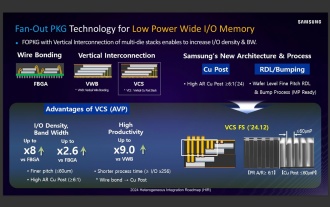 Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
According to news from this website on September 3, Korean media etnews reported yesterday (local time) that Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix’s “HBM-like” stacked structure mobile memory products will be commercialized after 2026. Sources said that the two Korean memory giants regard stacked mobile memory as an important source of future revenue and plan to expand "HBM-like memory" to smartphones, tablets and laptops to provide power for end-side AI. According to previous reports on this site, Samsung Electronics’ product is called LPWide I/O memory, and SK Hynix calls this technology VFO. The two companies have used roughly the same technical route, which is to combine fan-out packaging and vertical channels. Samsung Electronics’ LPWide I/O memory has a bit width of 512
 CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work on file upload we are going to use the form helper. Here, is an example for file upload.
 CakePHP Routing
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Routing
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
In this chapter, we are going to learn the following topics related to routing ?
 Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
CakePHP is an open-source framework for PHP. It is intended to make developing, deploying and maintaining applications much easier. CakePHP is based on a MVC-like architecture that is both powerful and easy to grasp. Models, Views, and Controllers gu
 CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
Validator can be created by adding the following two lines in the controller.





