 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 Symfony data verification method example analysis, symfony example analysis_PHP tutorial
Symfony data verification method example analysis, symfony example analysis_PHP tutorial
Symfony data verification method example analysis, symfony example analysis_PHP tutorial
Symfony data verification method example analysis, symfony example analysis
The examples in this article describe the Symfony data verification method. Share it with everyone for your reference. The specific analysis is as follows:
Validation is a common task in web applications. Data entered into the form needs to be validated. Data also needs to be verified before being written to the database or when passed to a webservice.
Symfony2 is equipped with a Validator component, which makes the verification work simple and easy to understand. This component is based on the JSR303 Bean validation specification. A Java specification for use in PHP.
Basic Verification
The best way to understand validation is to see how it performs. First, assume that you have created a PHP object that is used somewhere in your application.
namespace AcmeBlogBundleEntity;
class Author
{
Public $name;
}
Up to now, it's just a normal class that serves some purpose in your application. The purpose of verification is to tell you whether the object's data is legal. For this purpose, you need to configure an object to follow a list of rules or constraints to make its data legal. These rules can be described in many different formats (eg, YAML, XML, class declarations or PHP). For example, we ensure that the attribute $name cannot be empty, so add the following rule:
YAML format:
AcmeBlogBundleEntityAuthor:
Properties:
name:
- NotBlank: ~
Class declaration format:
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraints as Assert;
class Author
{
/**
* @AssertNotBlank()
*/
Public $name;
}
XML format:
xsi:schemaLocation="http://symfony.com/schema/dic/constraint-mapping http://symfony.com/schema/dic/constraint-mapping/constraint-mapping-1.0.xsd">
PHP code format:
use SymfonyComponentValidatorMappingClassMetadata;
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraintsNotBlank;
class Author
{
Public $name;
Public static function loadValidatorMetadata(ClassMetadata $metadata)
{
$metadata->addPropertyConstraint('name', new NotBlank());
}
}
Protected and private attributes and getter methods can also be verified.
Use validator service:
Next, use the validate method of the validator service to actually verify the Author object. The validator's job is simple: read the constraint rules of a class to verify whether the data of an object conforms to these rule constraints. If validation fails, an error array will be returned. Now we execute it in a controller:
use AcmeBlogBundleEntityAuthor;
//...
public function indexAction()
{
$author = new Author();
//... What to do with the $auother object
$validator = $this->get('validator');
$errors = $validator->validate($author);
if(count($errors) >0){
Return new Response(print_r($errors, true));
}else{
Return new Response('The author is valid! Yes!');
}
}
If the $name attribute is empty, you will see the following error message:
AcmeBlogBundleAuthor.name:
This value should not be blank
If you insert a value for the $name attribute, you will get a happy success message.
Most of the time, you don't need to communicate directly with the validator service or worry about printing errors at all.
Most of the time, you will use validation indirectly when processing submitted form data.
You can also pass a collection of error messages to a template:
Return $this->render('AcmeBlogBundle:Author:validate.html.twig',array(
'errors' => $errors,
));
}else{
//...
}
In the template, you can output the error list as accurately as you need:
Twig format:
The author has the following errros
- {{ error.message }}
{% for error in errors %}
{% endfor %}
Checksum form
The validator service can be used to verify any object at any time. In fact, you will often use validators indirectly when processing forms. Symfony's form library indirectly uses the validator service to validate the underlying objects after the data has been submitted and bound. Object constraint violation information will be converted to a FieldError object, which can be easily displayed in your form. The traditional form submission process in a controller is as follows:
use AcmeBlogBundleFormAuthorType;
use AcmeComponentHttpFoundationRequest;
//...
public function updateAction(Request $request)
{
$author = new AcmeBlogBundleEntityAuthor();
$form = $this->createForm(new AuthorType(),$author);
if($request->getMethod() =='POST'){
$form->bindRequest($request);
If($form->isvalid()){
//Do some operations on $author
return $this->redirect($this->generateUrl('...'));
}
}
return $this->render('BlogBundle:Author:form.html.twig',array(
'form' => $form->createView(),
));
}
Configuration:
Symfony2 validator is available by default. But if you use the life method to specify your constraints, then you need to explicitly enable the declaration function:
YAML format:
framework:
Validation: {enable_annotations: true }
XML format:
PHP code format:
$contianer->loadFromExtension('framework',array('validation'=> array(
'enable_annotations'=>true,
)));
Constraint rules
Validator is designed to verify objects according to constraint rules. To validate an object, just map one or more constraints to the class it is validating and pass it to the validator service.
Essentially, a constraint is a simple PHP object that generates a decision statement. In real life, a constraint can be a rule constraint such as "the cake cannot be burnt". In Symfony2, constraints are all the same: they determine whether a certain condition is true. Given a value, the constraint tells you whether the value obeys your constraint rules.
Constraint rules supported by Symfony2
First are the basic constraint rules: use them to decide very basic things, like the value of your object's properties or the return value of a method.
NotBlank, Blank, NotNull, Null, True, False, Type
String constraints: Email, MinLength, MaxLength, Url, Regex, Ip, etc.
Numerical constraints: Max, Min
Date constraints: Date, DateTime and Time
Collection constraints: Choice, Collection, UniqueEntity, Language, Locale and Country, etc.
File constraints: File,Image
Other constraints: Callback, All, Valid
You can also create your own custom constraints.
Constraint configuration:
Some constraints, such as NotBlank, are very simple, but others, such as Choice constraints, have many configuration items that need to be set. Assuming that the Author class has another attribute, gener can be set to "male" or "female":
YAML format:
AcmeBlogBundleEntityAuthor:
Properties:
gener:
- Choice: { choices: [male, female], message: Choos a valid gender. }
Class declaration format:
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraints as Assert;
class Author
{
/**
* @AssertChoice(
* choices = {"male","female"},
* message = "Choose a valid gender."
* )
*/
Public $gender;
}
XML format:
xsi:schemaLocation="http://symfony.com/schema/dic/constraint-mapping http://symfony.com/schema/dic/constraint-mapping/constraint-mapping-1.0.xsd">
in
& Lt; option name = "Message" & gt; Choose a valid gender. & Lt;/option & gt;
PHP code format:
Copy code
use SymfonyComponentValidatorMappingClassMetadata;
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraintsNotBlank;
class Author
{
Public $gender;
public static function loadValidatorMetadata(ClassMetadata $metadata)
{
$metadata->addPropertyConstraint('gender', new Choice(array(
'choices' => array('male', 'female'),
'message' => 'Choose a valid gender.',
)));
}
}
A constraint’s options are usually passed through an array. Some constraints also allow you to pass a value. "default" is optional in arrays. When using Choice constraints, the choices option can be specified in this way.
YAML format:
AcmeBlogBundleEntityAuthor:
Properties:
gender:
- Choice: [male, female]
Class declaration format:
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraints as Assert;
class Author
{
/**
* @AssertChoice({"male", "female"})
*/
protected $gender;
}
XML format:
xsi:schemaLocation="http://symfony.com/schema/dic/constraint-mapping http://symfony.com/schema/dic/constraint-mapping/constraint-mapping-1.0.xsd">
PHP format:
use SymfonyComponentValidatorMappingClassMetadata;
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraintsChoice;
class Author
{
protected $gender;
public static function loadValidatorMetadata(ClassMetadata $metadata)
{
$metadata->addPropertyConstraint('gender', new Choice(array('male', 'female')));
}
}
Constraint target
Constraints can be applied to a class property or a public getter method. Attribute constraints are the most commonly used and simplest, while public getter method constraints allow you to specify a complex constraint rule.
Attribute constraints:
The attributes of the verification class are one of the most common verification techniques. Symfony2 allows you to verify private, protected or public properties. The following code shows how to configure the $firstName property of the Author object to have at least 3 characters:
YAML format:
AcmeBlogBundleEntityAuthor:
Properties:
firstName:
- NotBlank: ~
- MinLength: 3
Class declaration format:
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraints as Assert;
class Author
{
/**
* @AssertNotBlank()
* @AssertMinLength(3)
*/
Private $firstName;
}
XML format:
PHP code format:
use SymfonyComponentValidatorMappingClassMetadata;
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraintsNotBlank;
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraintsMinLength;
class Author
{
Private $firstName;
public static function loadValidatorMetadata(ClassMetadata $metadata)
{
$metadata->addPropertyConstraint('firstName', new NotBlank());
$metadata->addPropertyConstraint('firstName', new MinLength(3));
}
}
Getters
Constraints can also be applied to the return value of a method. Symfony2 allows you to add a constraint to any public method that begins with "get" or "is". The benefit of this technique is that it allows you to dynamically validate your objects. For example, suppose you want to make sure that the password field does not match the user's first name (for security reasons). You can do this by creating an idPasswordLegal method and then determining that this method must return true:
YAML format:
AcmeBlogBundleEntityAuthor:
Getters:
passwordLegal:
- "True": { message: "The password cannot match your first name" }
Class declaration format:
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraints as Assert;
class Author
{
/**
* @AssertTrue(message = "The password cannot match your first name")
*/
Public function isPasswordLegal()
{
// return true or false
}
}
XML format:
use SymfonyComponentValidatorMappingClassMetadata;
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraintsTrue;
class Author
{
Public static function loadValidatorMetadata(ClassMetadata $metadata)
{
$metadata->addGetterConstraint('passwordLegal', new True(array(
'message' => 'The password cannot match your first name',
)));
}
}
Now we create an isPasswordLegal() method and include the logic you need:
{
Return ($this->firstName != $this->password);
}
The eagle-eyed may notice that the getter prefix ("get" or "is") is ignored when mapping. This allows you to move a constraint to a property with the same name, or vice versa, without changing the validation rules.
Category:
Some constraints apply to the entire class being verified. For example, the Callback constraint is a general constraint that can be applied to the class itself. When a class is validated, the methods described by the constraints are simply executed so that each can provide a more personalized validation.
Check grouping
So far, you have been able to add constraints to a class and ask if the class passes in all the defined constraint rules. In some cases, you only need to verify an object using some of the rules of the class. To do this, you organize each constraint into one or more validation groups, and then the application uses one of the validation groups. For example, suppose you have a User class that is used when users register and when users update their contact information.
YAML format:
AcmeBlogBundleEntityUser:
Properties:
email:
- Email: { groups: [registration] }
Password:
- NotBlank: { groups: [registration] }
- MinLength: { limit: 7, groups: [registration] }
city:
- MinLength: 2
Class declaration format:
namespace AcmeBlogBundleEntity;
use SymfonyComponentSecurityCoreUserUserInterface;
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraints as Assert;
class User implements UserInterface
{
/**
* @AssertEmail(groups={"registration"})
*/
private $email;
/**
* @AssertNotBlank(groups={"registration"})
* @AssertMinLength(limit=7, groups={"registration"})
*/
private $password;
/**
* @AssertMinLength(2)
*/
private $city;
}
XML format:
PHP代码格式:
namespace AcmeBlogBundleEntity;
use SymfonyComponentValidatorMappingClassMetadata;
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraintsEmail;
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraintsNotBlank;
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraintsMinLength;
class User
{
public static function loadValidatorMetadata(ClassMetadata $metadata)
{
$metadata->addPropertyConstraint('email', new Email(array(
'groups' => array('registration')
)));
$metadata->addPropertyConstraint('password', new NotBlank(array(
'groups' => array('registration')
)));
$metadata->addPropertyConstraint('password', new MinLength(array(
'limit' => 7,
'groups' => array('registration')
)));
$metadata->addPropertyConstraint('city', new MinLength(3));
}
}
这里我们配置了两个校验组:
default默认组: 包括所有没有分配到任何组的约束规则
registration: 只包含了email和password字段的校验规则
告诉validator使用指定的校验组,传一个或者多个组名作为validate()方法的第二个参数即可:
Value and array validation
So far, we have looked at how to validate an entire object. But sometimes, we may want to verify a single value, such as verifying whether a string is a valid email address. This is very simple and is done in the Controller class as follows:
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraintsEmail;
public function addEmailAction($email)
{
$emailConstraint = new Email();
// All verification options can be set like this
$emailConstraint->message = 'Invalid email address';
// Use validator to verify a value
$errorList = $this->get('validator')->validateValue($email, $emailConstraint);
if (count($errorList) == 0) {
// This is a legitimate email address, what can be done
} else {
// This is an illegal email address
$errorMessage = $errorList[0]->getMessage()
// Do some error handling
}
// ...
}
By calling the validateValue method of the validator, you can pass in a raw value and a verification object you want to use. This method returns a ConstraintViolationList object, which only plays the role of an array of error messages. Each error in the collection is a ConstraintViolation object, and the error information can be obtained using the object's getMessage method.
Summary:
Symfony2’s validator is a powerful tool that can be used to ensure the validity of any object data. Its power comes from the constraint rules you can apply to your object's properties and getter methods. In fact, most of the time you use the validation framework indirectly when using forms. Remember that it can be applied to validate any object anywhere.
I hope this article will be helpful to everyone’s Symfony framework programming.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How to delete WeChat friends? How to delete WeChat friends
Mar 04, 2024 am 11:10 AM
How to delete WeChat friends? How to delete WeChat friends
Mar 04, 2024 am 11:10 AM
WeChat is one of the mainstream chat tools. We can meet new friends, contact old friends and maintain the friendship between friends through WeChat. Just as there is no such thing as a banquet that never ends, disagreements will inevitably occur when people get along with each other. When a person extremely affects your mood, or you find that your views are inconsistent when you get along, and you can no longer communicate, then we may need to delete WeChat friends. How to delete WeChat friends? The first step to delete WeChat friends: tap [Address Book] on the main WeChat interface; the second step: click on the friend you want to delete and enter [Details]; the third step: click [...] in the upper right corner; Step 4: Click [Delete] below; Step 5: After understanding the page prompts, click [Delete Contact]; Warm
 How to write a novel in the Tomato Free Novel app. Share the tutorial on how to write a novel in Tomato Novel.
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
How to write a novel in the Tomato Free Novel app. Share the tutorial on how to write a novel in Tomato Novel.
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
Tomato Novel is a very popular novel reading software. We often have new novels and comics to read in Tomato Novel. Every novel and comic is very interesting. Many friends also want to write novels. Earn pocket money and edit the content of the novel you want to write into text. So how do we write the novel in it? My friends don’t know, so let’s go to this site together. Let’s take some time to look at an introduction to how to write a novel. Share the Tomato novel tutorial on how to write a novel. 1. First open the Tomato free novel app on your mobile phone and click on Personal Center - Writer Center. 2. Jump to the Tomato Writer Assistant page - click on Create a new book at the end of the novel.
 How to enter bios on Colorful motherboard? Teach you two methods
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
How to enter bios on Colorful motherboard? Teach you two methods
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
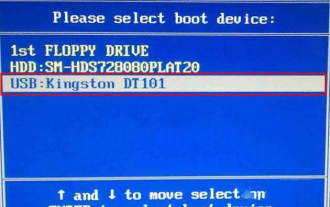
Colorful motherboards enjoy high popularity and market share in the Chinese domestic market, but some users of Colorful motherboards still don’t know how to enter the bios for settings? In response to this situation, the editor has specially brought you two methods to enter the colorful motherboard bios. Come and try it! Method 1: Use the U disk startup shortcut key to directly enter the U disk installation system. The shortcut key for the Colorful motherboard to start the U disk with one click is ESC or F11. First, use Black Shark Installation Master to create a Black Shark U disk boot disk, and then turn on the computer. When you see the startup screen, continuously press the ESC or F11 key on the keyboard to enter a window for sequential selection of startup items. Move the cursor to the place where "USB" is displayed, and then
 How to recover deleted contacts on WeChat (simple tutorial tells you how to recover deleted contacts)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
How to recover deleted contacts on WeChat (simple tutorial tells you how to recover deleted contacts)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
Unfortunately, people often delete certain contacts accidentally for some reasons. WeChat is a widely used social software. To help users solve this problem, this article will introduce how to retrieve deleted contacts in a simple way. 1. Understand the WeChat contact deletion mechanism. This provides us with the possibility to retrieve deleted contacts. The contact deletion mechanism in WeChat removes them from the address book, but does not delete them completely. 2. Use WeChat’s built-in “Contact Book Recovery” function. WeChat provides “Contact Book Recovery” to save time and energy. Users can quickly retrieve previously deleted contacts through this function. 3. Enter the WeChat settings page and click the lower right corner, open the WeChat application "Me" and click the settings icon in the upper right corner to enter the settings page.
 Summary of methods to obtain administrator rights in Win11
Mar 09, 2024 am 08:45 AM
Summary of methods to obtain administrator rights in Win11
Mar 09, 2024 am 08:45 AM
A summary of how to obtain Win11 administrator rights. In the Windows 11 operating system, administrator rights are one of the very important permissions that allow users to perform various operations on the system. Sometimes, we may need to obtain administrator rights to complete some operations, such as installing software, modifying system settings, etc. The following summarizes some methods for obtaining Win11 administrator rights, I hope it can help you. 1. Use shortcut keys. In Windows 11 system, you can quickly open the command prompt through shortcut keys.
 The secret of hatching mobile dragon eggs is revealed (step by step to teach you how to successfully hatch mobile dragon eggs)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
The secret of hatching mobile dragon eggs is revealed (step by step to teach you how to successfully hatch mobile dragon eggs)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
Mobile games have become an integral part of people's lives with the development of technology. It has attracted the attention of many players with its cute dragon egg image and interesting hatching process, and one of the games that has attracted much attention is the mobile version of Dragon Egg. To help players better cultivate and grow their own dragons in the game, this article will introduce to you how to hatch dragon eggs in the mobile version. 1. Choose the appropriate type of dragon egg. Players need to carefully choose the type of dragon egg that they like and suit themselves, based on the different types of dragon egg attributes and abilities provided in the game. 2. Upgrade the level of the incubation machine. Players need to improve the level of the incubation machine by completing tasks and collecting props. The level of the incubation machine determines the hatching speed and hatching success rate. 3. Collect the resources required for hatching. Players need to be in the game
 Quickly master: How to open two WeChat accounts on Huawei mobile phones revealed!
Mar 23, 2024 am 10:42 AM
Quickly master: How to open two WeChat accounts on Huawei mobile phones revealed!
Mar 23, 2024 am 10:42 AM
In today's society, mobile phones have become an indispensable part of our lives. As an important tool for our daily communication, work, and life, WeChat is often used. However, it may be necessary to separate two WeChat accounts when handling different transactions, which requires the mobile phone to support logging in to two WeChat accounts at the same time. As a well-known domestic brand, Huawei mobile phones are used by many people. So what is the method to open two WeChat accounts on Huawei mobile phones? Let’s reveal the secret of this method. First of all, you need to use two WeChat accounts at the same time on your Huawei mobile phone. The easiest way is to
 How to set font size on mobile phone (easily adjust font size on mobile phone)
May 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
How to set font size on mobile phone (easily adjust font size on mobile phone)
May 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Setting font size has become an important personalization requirement as mobile phones become an important tool in people's daily lives. In order to meet the needs of different users, this article will introduce how to improve the mobile phone use experience and adjust the font size of the mobile phone through simple operations. Why do you need to adjust the font size of your mobile phone - Adjusting the font size can make the text clearer and easier to read - Suitable for the reading needs of users of different ages - Convenient for users with poor vision to use the font size setting function of the mobile phone system - How to enter the system settings interface - In Find and enter the "Display" option in the settings interface - find the "Font Size" option and adjust it. Adjust the font size with a third-party application - download and install an application that supports font size adjustment - open the application and enter the relevant settings interface - according to the individual



