Tree Algorithm_PHP Tutorial
//测试数据 $ar = array( array(id=>1,pid=>0), array(id=>2,pid=>0), array(id=>3,pid=>2), array(id=>4,pid=>0), array(id=>5,pid=>3), array(id=>6,pid=>1), array(id=>7,pid=>1), array(id=>8,pid=>6 ), array(id=>9,pid=>7), array(id=>10,pid=>9) ); //Sort function function cmd($a,$b) { if($a[pid] ==$b[pid]) return 0; return $a[pid]>$b[pid]?1:-1; } //Sort, in order to avoid the parent node appearing behind the child node in the data, this situation is It often happens after modifying data multiple times //The purpose of sorting is to prevent the confusion caused by this situation uasort($ar,cmd); //Define the target array $d = array(); //Define the index array for Record the position of the node in the target array $ind = array(); foreach($ar as $v) { $v[child] = array(); //Attach a child item to each node if($v[pid] == 0) { $i = count($d); $d[$i] = $v; $ind[$v[id]] =& $d[$i]; }else { $i = count( $ind[$v[pid]][child]); $ind[$v[pid]][child][$i] = $v; $ind[$v[id]] =& $ind[$v [pid]][child][$i]; } } //Check results print_r($d); ?> Algorithm features: Using the B+ tree concept, a tree array can be generated with only one cycle

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
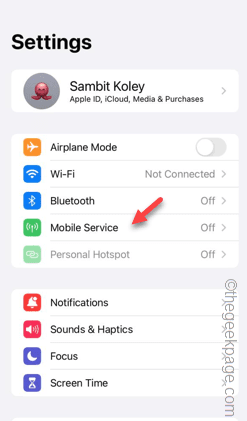 Slow Cellular Data Internet Speeds on iPhone: Fixes
May 03, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
Slow Cellular Data Internet Speeds on iPhone: Fixes
May 03, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
Facing lag, slow mobile data connection on iPhone? Typically, the strength of cellular internet on your phone depends on several factors such as region, cellular network type, roaming type, etc. There are some things you can do to get a faster, more reliable cellular Internet connection. Fix 1 – Force Restart iPhone Sometimes, force restarting your device just resets a lot of things, including the cellular connection. Step 1 – Just press the volume up key once and release. Next, press the Volume Down key and release it again. Step 2 – The next part of the process is to hold the button on the right side. Let the iPhone finish restarting. Enable cellular data and check network speed. Check again Fix 2 – Change data mode While 5G offers better network speeds, it works better when the signal is weaker
 The vitality of super intelligence awakens! But with the arrival of self-updating AI, mothers no longer have to worry about data bottlenecks
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:55 PM
The vitality of super intelligence awakens! But with the arrival of self-updating AI, mothers no longer have to worry about data bottlenecks
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:55 PM
I cry to death. The world is madly building big models. The data on the Internet is not enough. It is not enough at all. The training model looks like "The Hunger Games", and AI researchers around the world are worrying about how to feed these data voracious eaters. This problem is particularly prominent in multi-modal tasks. At a time when nothing could be done, a start-up team from the Department of Renmin University of China used its own new model to become the first in China to make "model-generated data feed itself" a reality. Moreover, it is a two-pronged approach on the understanding side and the generation side. Both sides can generate high-quality, multi-modal new data and provide data feedback to the model itself. What is a model? Awaker 1.0, a large multi-modal model that just appeared on the Zhongguancun Forum. Who is the team? Sophon engine. Founded by Gao Yizhao, a doctoral student at Renmin University’s Hillhouse School of Artificial Intelligence.
 The U.S. Air Force showcases its first AI fighter jet with high profile! The minister personally conducted the test drive without interfering during the whole process, and 100,000 lines of code were tested for 21 times.
May 07, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
The U.S. Air Force showcases its first AI fighter jet with high profile! The minister personally conducted the test drive without interfering during the whole process, and 100,000 lines of code were tested for 21 times.
May 07, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
Recently, the military circle has been overwhelmed by the news: US military fighter jets can now complete fully automatic air combat using AI. Yes, just recently, the US military’s AI fighter jet was made public for the first time and the mystery was unveiled. The full name of this fighter is the Variable Stability Simulator Test Aircraft (VISTA). It was personally flown by the Secretary of the US Air Force to simulate a one-on-one air battle. On May 2, U.S. Air Force Secretary Frank Kendall took off in an X-62AVISTA at Edwards Air Force Base. Note that during the one-hour flight, all flight actions were completed autonomously by AI! Kendall said - "For the past few decades, we have been thinking about the unlimited potential of autonomous air-to-air combat, but it has always seemed out of reach." However now,
 Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Common challenges faced by machine learning algorithms in C++ include memory management, multi-threading, performance optimization, and maintainability. Solutions include using smart pointers, modern threading libraries, SIMD instructions and third-party libraries, as well as following coding style guidelines and using automation tools. Practical cases show how to use the Eigen library to implement linear regression algorithms, effectively manage memory and use high-performance matrix operations.
 How to turn off Bitlocker encryption using CMD at the command prompt
Jun 19, 2024 am 11:33 AM
How to turn off Bitlocker encryption using CMD at the command prompt
Jun 19, 2024 am 11:33 AM
Enter the following command in the administrator command prompt to turn off manage-bde-offC: But sometimes the following prompt appears: Error - This volume stores one or more external keys that can automatically unlock other volumes. This type of key must first be deleted before this volume can be unlocked. At this time, you need to execute the following command first: (If the system partition is not C, change the drive letter below) manage-bde-autounlock-ClearAllKeysc: Error 2: This operation cannot be performed because the volume is locked. manage-bde-unlockc:-rp123456789012345678901234567890123456789012345678 Note:
 Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The latest video of Tesla's robot Optimus is released, and it can already work in the factory. At normal speed, it sorts batteries (Tesla's 4680 batteries) like this: The official also released what it looks like at 20x speed - on a small "workstation", picking and picking and picking: This time it is released One of the highlights of the video is that Optimus completes this work in the factory, completely autonomously, without human intervention throughout the process. And from the perspective of Optimus, it can also pick up and place the crooked battery, focusing on automatic error correction: Regarding Optimus's hand, NVIDIA scientist Jim Fan gave a high evaluation: Optimus's hand is the world's five-fingered robot. One of the most dexterous. Its hands are not only tactile
 Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
01 Outlook Summary Currently, it is difficult to achieve an appropriate balance between detection efficiency and detection results. We have developed an enhanced YOLOv5 algorithm for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images, using multi-layer feature pyramids, multi-detection head strategies and hybrid attention modules to improve the effect of the target detection network in optical remote sensing images. According to the SIMD data set, the mAP of the new algorithm is 2.2% better than YOLOv5 and 8.48% better than YOLOX, achieving a better balance between detection results and speed. 02 Background & Motivation With the rapid development of remote sensing technology, high-resolution optical remote sensing images have been used to describe many objects on the earth’s surface, including aircraft, cars, buildings, etc. Object detection in the interpretation of remote sensing images
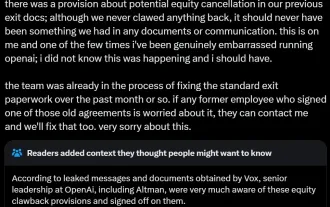 AI startups collectively switched jobs to OpenAI, and the security team regrouped after Ilya left!
Jun 08, 2024 pm 01:00 PM
AI startups collectively switched jobs to OpenAI, and the security team regrouped after Ilya left!
Jun 08, 2024 pm 01:00 PM
Last week, amid the internal wave of resignations and external criticism, OpenAI was plagued by internal and external troubles: - The infringement of the widow sister sparked global heated discussions - Employees signing "overlord clauses" were exposed one after another - Netizens listed Ultraman's "seven deadly sins" Rumors refuting: According to leaked information and documents obtained by Vox, OpenAI’s senior leadership, including Altman, was well aware of these equity recovery provisions and signed off on them. In addition, there is a serious and urgent issue facing OpenAI - AI safety. The recent departures of five security-related employees, including two of its most prominent employees, and the dissolution of the "Super Alignment" team have once again put OpenAI's security issues in the spotlight. Fortune magazine reported that OpenA




