 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 PHP has detailed instructions on regular expressions_PHP tutorial
PHP has detailed instructions on regular expressions_PHP tutorial
PHP has detailed instructions on regular expressions_PHP tutorial
php(as the current mainstream development language) inherits the tradition of *NIX and fully supports the processing of regular expressions. Regular expressions provide an advanced, but non-intuitive, method of string matching and processing. Friends who have used PERL's regular expressions know that regular expressions are very powerful, but they are not easy to learn.
For example:
^.+@.+..+$
This effective but incomprehensible code is enough to give some programmers a headache (me) or make them give up using it Regular expression. I believe that after you finish reading this tutorial, you will understand the meaning of this code.
Basic Pattern Matching
Everything starts from the basics. Patterns are the most basic elements of regular expressions. They are a set of characters that describe the characteristics of a string. Patterns can be simple, consisting of ordinary strings, or very complex, often using special characters to represent a range of characters, recurrences, or to represent context. For example:
^once
This pattern contains a special character ^, which means that the pattern only matches those strings starting with once. For example, this pattern matches the string "once upon a time" but does not match "There once was a man from NewYork". Just like the ^ symbol indicates the beginning, the $ symbol is used to match strings that end with a given pattern.
bucket$
This pattern matches "Who kept all of this cash in a bucket" but does not match "buckets". When the characters ^ and $ are used together, they represent an exact match (strings are the same as patterns). For example:
^bucket$
only matches the string "bucket". If a pattern does not include ^ and $, then it matches any string that contains the pattern. For example: pattern
once
and string
There once was a man from NewYork
Who kept all of his cash in a bucket.
is a match.
The letters (o-n-c-e) in this pattern are literal characters, that is, they represent the letters themselves, as do numbers. Some other slightly more complex characters, such as punctuation marks and white characters (spaces, tabs, etc.), require escape sequences. All escape sequences begin with a backslash (). The escape sequence for the tab character is: . So if we want to detect whether a string starts with a tab character, we can use this pattern:
^
Similarly, use
It means "new line" and means carriage return. Other special symbols can be used with a backslash in front. For example, the backslash itself is represented by ., the period is represented by ., and so on.
Character cluster
In INTERNET programs, regular expressions are usually used to verify user input. When a user submits a FORM, it is not enough to use ordinary literal characters to determine whether the entered phone number, address, email address, credit card number, etc. are valid.
So we need to use a more free way to describe the pattern we want, which is character clusters. To create a cluster representing all vowel characters, place all vowel characters in square brackets:
[AaEeIiOoUu]
This pattern matches any vowel character, But it can only represent one character. Use hyphens to represent a range of characters, such as:
[a-z] // Match all lowercase letters
[A-Z] // Match all uppercase letters
[a-zA-Z ] //Match all letters
[0-9] //Match all numbers
[0-9.-] //Match all numbers, periods and minus signs
[ f
] //Match all white characters
Again, these only represent one character, which is very important. If you want to match a string consisting of a lowercase letter and a digit, such as "z2", "t6" or "g7", but not "ab2", "r2d3" or "b52", use this pattern:

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1371
1371
 52
52
 PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 brings several new features, security improvements, and performance improvements with healthy amounts of feature deprecations and removals. This guide explains how to install PHP 8.4 or upgrade to PHP 8.4 on Ubuntu, Debian, or their derivati
 CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work with date and time in cakephp4, we are going to make use of the available FrozenTime class.
 CakePHP Working with Database
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Working with Database
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
Working with database in CakePHP is very easy. We will understand the CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations in this chapter.
 CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work on file upload we are going to use the form helper. Here, is an example for file upload.
 Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
CakePHP is an open-source framework for PHP. It is intended to make developing, deploying and maintaining applications much easier. CakePHP is based on a MVC-like architecture that is both powerful and easy to grasp. Models, Views, and Controllers gu
 CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
Validator can be created by adding the following two lines in the controller.
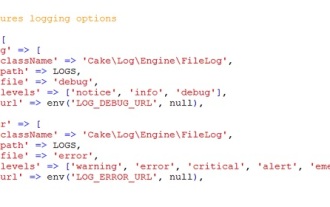 CakePHP Logging
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP Logging
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
Logging in CakePHP is a very easy task. You just have to use one function. You can log errors, exceptions, user activities, action taken by users, for any background process like cronjob. Logging data in CakePHP is easy. The log() function is provide
 How To Set Up Visual Studio Code (VS Code) for PHP Development
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
How To Set Up Visual Studio Code (VS Code) for PHP Development
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
Visual Studio Code, also known as VS Code, is a free source code editor — or integrated development environment (IDE) — available for all major operating systems. With a large collection of extensions for many programming languages, VS Code can be c



