 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 The most complete Chinese description of CURL function library_PHP tutorial
The most complete Chinese description of CURL function library_PHP tutorial
The most complete Chinese description of CURL function library_PHP tutorial
The Chinese explanation of CURL is currently the most comprehensive, and those who learn PHP should master it well. There are many parameters. Most of them are useful. If you truly master it and regular rules, you must be a collection master.
First write a simple page grabbing function
function GetSources($Url,$User_Agent='',$Referer_Url='') //Catch a specified page
{
//$Url The page address to be crawled
//$User_Agent needs to return the user_agent information such as "baiduspider" or "googlebot"
$ch = curl_init();
curl_setopt ($ch, CURLOPT_URL, $Url);
curl_setopt ($ch, CURLOPT_USERAGENT, $User_Agent);
curl_setopt ($ch, CURLOPT_REFERER, $Referer_Url);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_FOLLOWLOCATION,1);
curl_setopt ($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, 1);
$MySources = curl_exec ($ch);
curl_close($ch);
return $MySources;
}
Parameter value:
$Url = "http://www.baidu.com";
$User_Agent = "baiduspider+(+http://www.baidu.com/search/spider.htm)";
$Referer_Url = 'http://www.chinaz.com/';
The result after executing GetSources($Url,$User_Agent,$Referer_Url) is:
http://test.huangchao.org/curl/curl_test1.php
CURL function library (Client URL Library Function) in PHP
curl_close — close a curl session;
curl_copy_handle — Copy all contents and parameters of a curl connection resource;
curl_errno — Returns a numeric number containing error information for the current session;
curl_error — Returns a string containing error information for the current session;
curl_exec — execute a curl session;
curl_getinfo — Get information about a curl connection resource handle;
curl_init — Initialize a curl session;
curl_multi_add_handle — Add individual curl handle resources to a curl batch session;
curl_multi_close — Close a batch handle resource;
curl_multi_exec — parse a curl batch handle;
curl_multi_getcontent — Returns the text stream of the obtained output;
curl_multi_info_read — Get the relevant transmission information of the currently parsed curl;
curl_multi_init — Initialize a curl batch handle resource;
curl_multi_remove_handle — Remove a handle resource in the curl batch handle resource;
curl_multi_select — Get all the sockets associated with the cURL extension, which can then be "selected";
curl_setopt_array — Set session parameters for a curl as an array;
curl_setopt — Set session parameters for a curl;
curl_version — Get curl-related version information;
The function of curl_init() initializes a curl session. The only parameter of the curl_init() function is optional and represents a URL address;
The function of the curl_exec() function is to execute a curl session. The only parameter is the handle returned by the curl_init() function;
The curl_close() function is used to close a curl session. The only parameter is the handle returned by the curl_init() function;
PHP code
$ch = curl_init("http://www.BkJia.com/");
curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
?>
The curl_version() function is used to obtain curl-related version information. The curl_version() function has a parameter, and it is unclear what it does;
PHP code
print_r(curl_version())
?>
The curl_getinfo() function is used to obtain information about a curl connection resource handle. The curl_getinfo() function has two parameters. The first parameter is the curl resource handle, and the second parameter is the following constants:
PHP code
$ch = curl_init("http://www.BkJia.com/");
print_r(curl_getinfo($ch));
?>
Optional constants include:
CURLINFO_EFFECTIVE_URL: The last valid url address;
CURLINFO_HTTP_CODE: The last HTTP code received;
CURLINFO_FILETIME: The time to obtain the document remotely. If it cannot be obtained, the return value is "-1";
CURLINFO_TOTAL_TIME: The time consumed by the last transmission;
CURLINFO_NAMELOOKUP_TIME: Time spent on name resolution;
CURLINFO_CONNECT_TIME: The time it takes to establish a connection;
CURLINFO_PRETRANSFER_TIME: The time it takes from establishing the connection to preparing for transmission;
CURLINFO_STARTTRANSFER_TIME: The time elapsed from the establishment of the connection to the start of the transfer;
CURLINFO_REDIRECT_TIME: The time used for redirection before the transaction transfer begins;
CURLINFO_SIZE_UPLOAD: Total value of uploaded data;
CURLINFO_SIZE_DOWNLOAD: Total value of downloaded data;
CURLINFO_SPEED_DOWNLOAD: average download speed;
CURLINFO_SPEED_UPLOAD: average upload speed;
CURLINFO_HEADER_SIZE: The size of the header part;
CURLINFO_HEADER_OUT: The string to send the request;
CURLINFO_REQUEST_SIZE: The size of the request in question in the HTTP request;
CURLINFO_SSL_VERIFYRESULT:Result of SSL certification verification requested by setting CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER;
CURLINFO_CONTENT_LENGTH_DOWNLOAD: Download content length read from Content-Length: field;
CURLINFO_CONTENT_LENGTH_UPLOAD: Description of upload content size;
CURLINFO_CONTENT_TYPE: "Content-type" value of the downloaded content, NULL means that the server did not send a valid "Content-Type: header";
The curl_setopt() function is used to set session parameters for a curl. The curl_setopt_array() function is used to set session parameters for a curl in the form of an array;
PHP code
$ch = curl_init();
$fp = fopen("example_homepage.txt", "w");
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_FILE, $fp);
$options = array(
CURLOPT_URL => 'http://www.baidu.com/',
CURLOPT_HEADER => false
);
curl_setopt_array($ch, $options);
curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
fclose($fp);
?>
The parameters that can be set are:
CURLOPT_AUTOREFERER: Automatically set the referer information in the header;
CURLOPT_BINARYTRANSFER: Data will be retrieved and returned when CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER is enabled;
CURLOPT_COOKIESESSION: When enabled, curl will only pass one session cookie and ignore other cookies. By default, curl will return all cookies to the server. Session cookies refer to cookies that are used to determine whether the server-side session is valid;
CURLOPT_CRLF: When enabled, convert Unix line feeds into carriage returns and line feeds;
CURLOPT_DNS_USE_GLOBAL_CACHE: When enabled, a global DNS cache will be enabled. This item is thread-safe and defaults to true;
CURLOPT_FAILONERROR: Displays the HTTP status code. The default behavior is to ignore HTTP information with a number less than or equal to 400;
CURLOPT_FILETIME: When enabled, attempts to modify information in the remote document. The result information will be returned through the CURLINFO_FILETIME option of the curl_getinfo() function;
CURLOPT_FOLLOWLOCATION: When enabled, the "Location:" returned by the server will be placed in the header and returned to the server recursively. Use CURLOPT_MAXREDIRS to limit the number of recursive returns;
CURLOPT_FORBID_REUSE: Force the connection to be disconnected after completing the interaction and cannot be reused;
CURLOPT_FRESH_CONNECT: Force to obtain a new connection to replace the connection in the cache;
CURLOPT_FTP_USE_EPRT: TRUE to use EPRT (and LPRT) when doing active FTP downloads. Use FALSE to disable EPRT and LPRT and use PORT only; Added in PHP 5.0.0.
CURLOPT_FTP_USE_EPSV: TRUE to first try an EPSV command for FTP transfers before reverting back to PASV. Set to FALSE to disable EPSV;
CURLOPT_FTPAPPEND: TRUE to append to the remote file instead of overwriting it;
CURLOPT_FTPASCII: An alias of CURLOPT_TRANSFERTEXT. Use that instead;
CURLOPT_FTPLISTONLY: TRUE to only list the names of an FTP directory;
CURLOPT_HEADER: When enabled, the header file information will be output as a data stream;
CURLOPT_HTTPGET: When enabled, the HTTP method will be set to GET. Because GET is the default, it is only used when it is modified;
CURLOPT_HTTPPROXYTUNNEL: When enabled, it will be transmitted through HTTP proxy;
CURLOPT_MUTE: Restore all modified parameters in the curl function to their default values;
CURLOPT_NETRC: After the connection is established, access the ~/.netrc file to obtain the username and password information to connect to the remote site;
CURLOPT_NOBODY: When enabled, the body part in HTML will not be output;
CURLOPT_NOPROGRESS: Turn off the progress bar of curl transmission when enabled. The default setting of this item is true;
CURLOPT_NOSIGNAL: When enabled, ignore all signals passed by curl to php. This item is turned on by default during SAPI multi-thread transmission;
CURLOPT_POST: When enabled, a regular POST request will be sent, type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded, just like form submission;
CURLOPT_PUT: Allow HTTP to send files when enabled. CURLOPT_INFILE and CURLOPT_INFILESIZE must be set at the same time
CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER: Return the information obtained by curl_exec() in the form of a file stream instead of outputting it directly;
CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER: FALSE to stop cURL from verifying the peer's certificate. Alternate certificates to verify against can be specified with the CURLOPT_CAINFO option or a certificate directory can be specified with the CURLOPT_CAPATH option. CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER may also need to be TRUE or FALSE if CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER is disabled ( it defaults to 2). TRUE by default as of cURL 7.10. Default bundle installed as of cURL 7.10;
CURLOPT_TRANSFERTEXT: TRUE to use ASCII mode for FTP transfers. For LDAP, it retrieves data in plain text instead of HTML. On Windows systems, it will not set STDOUT to binary mode;
CURLOPT_UNRESTRICTED_AUTH: Continuously append username and password information to multiple locations in the header generated using CURLOPT_FOLLOWLOCATION, even if the domain name has changed;
CURLOPT_UPLOAD: Allow file transfer when enabled;
CURLOPT_VERBOSE: When enabled, all information will be reported and stored in STDERR or the specified CURLOPT_STDERR;
CURLOPT_BUFFERSIZE: The size of the cache read into the data obtained each time. This value will be filled every time;
CURLOPT_CLOSEPOLICY: Either CURLCLOSEPOLICY_LEAST_RECENTLY_USED or CURLCLOSEPOLICY_OLDEST, there are three others, but curl does not support it yet;
CURLOPT_CONNECTTIMEOUT: The time to wait before initiating a connection. If set to 0, there will be no waiting;
CURLOPT_DNS_CACHE_TIMEOUT: Set the time to save DNS information in memory, the default is 120 seconds;
CURLOPT_FTPSSLAUTH: The FTP authentication method (when is activated): CURLFTPAUTH_SSL (try SSL first), CURLFTPAUTH_TLS (try TLS first), or CURLFTPAUTH_DEFAULT (let cURL decide);
CURLOPT_HTTP_VERSION: Set the HTTP protocol used by curl, CURL_HTTP_VERSION_NONE (let curl decide by itself), CURL_HTTP_VERSION_1_0 (HTTP/1.0), CURL_HTTP_VERSION_1_1 (HTTP/1.1);
CURLOPT_HTTPAUTH: The HTTP authentication method used. Optional values are: CURLAUTH_BASIC, CURLAUTH_DIGEST, CURLAUTH_GSSNEGOTIATE, CURLAUTH_NTLM, CURLAUTH_ANY, CURLAUTH_ANYSAFE. You can use the "|" operator to separate multiple values. curl lets the server choose the one with the best support, CURLAUTH_ANY. Equivalent to CURLAUTH_BASIC | CURLAUTH_DIGEST | CURLAUTH_GSSNEGOTIATE | CURLAUTH_NTLM, CURLAUTH_ANYSAFE is equivalent to CURLAUTH_DIGEST | CURLAUTH_GSSNEGOTIATE | CURLAUTH_NTLM
CURLOPT_INFILESIZE: Set the size of the uploaded file;
CURLOPT_LOW_SPEED_LIMIT: When the transmission speed is less than CURLOPT_LOW_SPEED_LIMIT, PHP will use CURLOPT_LOW_SPEED_TIME to determine whether to cancel the transmission because it is too slow;
CURLOPT_LOW_SPEED_TIME: The number of seconds the transfer should be below CURLOPT_LOW_SPEED_LIMIT for PHP to consider the transfer too slow and abort;
When the transmission speed is less than CURLOPT_LOW_SPEED_LIMIT, PHP will use CURLOPT_LOW_SPEED_TIME to determine whether to cancel the transmission because it is too slow;
CURLOPT_MAXCONNECTS: The maximum number of connections allowed. If it is exceeded, CURLOPT_CLOSEPOLICY will be used to determine which connections should be stopped;
CURLOPT_MAXREDIRS: Specify the maximum number of HTTP redirects. This option is used together with CURLOPT_FOLLOWLOCATION;
CURLOPT_PORT: An optional quantity used to specify the connection port;
CURLOPT_PROXYAUTH: The HTTP authentication method(s) to use for the proxy connection. Use the same bitmasks as described in CURLOPT_HTTPAUTH. For proxy authentication, only CURLAUTH_BASIC and CURLAUTH_NTLM are currently supported.
CURLOPT_PROXYPORT: The port number of the proxy to connect to. This port number can also be set in CURLOPT_PROXY.
CURLOPT_PROXYTYPE: Either CURLPROXY_HTTP (default) or CURLPROXY_SOCKS5.
CURLOPT_RESUME_FROM: Pass a byte offset when resuming transmission (used to resume transmission from breakpoint)
CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYHOST:
1 to check the existence of a common name in the SSL peer certificate.
2 to check the existence of a common name and also verify that it matches the hostname provided.
CURLOPT_SSLVERSION: The SSL version (2 or 3) to use. By default PHP will try to determine this itself, although in some cases this must be set manually.
CURLOPT_TIMECONDITION: If it has been edited after a certain time specified by CURLOPT_TIMEVALUE, use CURL_TIMECOND_IFMODSINCE to return the page. If it has not been modified and CURLOPT_HEADER is true, a "304 Not Modified" header is returned. If CURLOPT_HEADER is false, use CURL_TIMECOND_ISUNMODSINCE. , the default value is CURL_TIMECOND_IFMODSINCE
CURLOPT_TIMEOUT: Set the maximum number of seconds curl is allowed to execute
CURLOPT_TIMEVALUE: Set a timestamp used by CURLOPT_TIMECONDITION. By default, CURL_TIMECOND_IFMODSINCE
is usedCURLOPT_CAINFO: The name of a file holding one or more certificates to verify the peer with. This only makes sense when used in combination with CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER.
CURLOPT_CAPATH: A directory that holds multiple CA certificates. Use this option alongside CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER.
CURLOPT_COOKIE: Set the content of the "Set-Cookie:" part of the HTTP request.
CURLOPT_COOKIEFILE: The name of the file containing cookie information. This cookie file can be Netscape format or HTTP style header information.
CURLOPT_COOKIEJAR: After the connection is closed, the file name to store cookie information
CURLOPT_CUSTOMREQUEST: A custom request method to use instead of "GET" or "HEAD" when doing a HTTP request. This is useful for doing "DELETE" or other, more obscure HTTP requests. Valid values are things like "GET", "POST ", "CONNECT" and so on; i.e. Do not enter a whole HTTP request line here. For instance, entering "GET /index.html HTTP/1.0rnrn" would be incorrect.
Note: Don't do this without making sure the server supports the custom request method first.
CURLOPT_EGBSOCKET: Like CURLOPT_RANDOM_FILE, except a filename to an Entropy Gathering Daemon socket.
CURLOPT_ENCODING: The content of the "Accept-Encoding:" part in the header. The supported encoding formats are: "identity", "deflate", "gzip". If set to an empty string, it means that all encoding formats are supported
CURLOPT_FTPPORT: The value which will be used to get the IP address to use for the FTP "POST" instruction. The "POST" instruction tells the remote server to connect to our specified IP address. The string may be a plain IP address, a hostname, a network interface name (under Unix), or just a plain '-' to use the systems default IP address.
CURLOPT_INTERFACE: The name used in the external network interface, which can be an interface name, IP or host name.
CURLOPT_KRB4LEVEL: KRB4 (Kerberos 4) security level setting, which can be one of the following values: "clear", "safe", "confidential", "private". The default value is "private". When set to null, KRB4 is disabled. Now KRB4 security can only be used in FTP transmission.
CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS: "POST" operation in HTTP. If you want to transfer a file, you need a file name starting with @
CURLOPT_PROXY: Set the HTTP proxy server passed
CURLOPT_PROXYUSERPWD: Username and password in the format of "[username]:[password]" to connect to the proxy server.
CURLOPT_RANDOM_FILE: Set the file name to store the random number seed used by SSL
CURLOPT_RANGE: Set the HTTP transmission range. You can set a transmission range in the form of "X-Y". If there are multiple HTTP transmissions, use commas to separate multiple values, such as: "X-Y,N-M".
CURLOPT_REFERER: Set the value of the "Referer: " part in the header.
CURLOPT_SSL_CIPHER_LIST: A list of ciphers to use for SSL. For example, RC4-SHA and TLSv1 are valid cipher lists.
CURLOPT_SSLCERT: Pass a string containing the certificate in PEM format
CURLOPT_SSLCERTPASSWD: Pass a password containing the necessary password to use the CURLOPT_SSLCERT certificate.
CURLOPT_SSLCERTTYPE:The format of the certificate. Supported formats are "PEM" (default), "DER", and "ENG".
CURLOPT_SSLENGINE: The identifier for the crypto engine of the private SSL key specified in CURLOPT_SSLKEY.
CURLOPT_SSLENGINE_DEFAULT: The identifier for the crypto engine used for asymmetric crypto operations.
CURLOPT_SSLKEY: The name of a file containing a private SSL key.
CURLOPT_SSLKEYPASSWD: The secret password needed to use the private SSL key specified in CURLOPT_SSLKEY.
Note: Since this option contains a sensitive password, remember to keep the PHP script it is contained within safe.
CURLOPT_SSLKEYTYPE: The key type of the private SSL key specified in CURLOPT_SSLKEY. Supported key types are "PEM" (default), "DER", and "ENG".
CURLOPT_URL: The URL address to be obtained can also be set in PHP's curl_init() function.
CURLOPT_USERAGENT: A string containing a "user-agent" header in the HTTP request.
CURLOPT_USERPWD: Pass the username and password required in a connection, in the format: "[username]:[password]".
CURLOPT_HTTP200ALIASES: Set to no longer handle HTTP 200 responses in the form of error. The format is an array.
CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER: Set an array of transmission content in the header.
CURLOPT_POSTQUOTE: An array of FTP commands to execute on the server after the FTP request has been performed.
CURLOPT_QUOTE: An array of FTP commands to execute on the server prior to the FTP request.
CURLOPT_FILE: Set the location of the output file. The value is a resource type. The default is STDOUT (browser).
CURLOPT_INFILE: The file address that needs to be read when uploading a file. The value is a resource type.
CURLOPT_STDERR: Set an error output address, the value is a resource type, replacing the default STDERR.
CURLOPT_WRITEHEADER: Sets the file address where the header part is written, and the value is a resource type.
CURLOPT_HEADERFUNCTION: Set a callback function. This function has two parameters. The first is the resource handle of curl, and the second is the output header data. The output of header data must rely on this function, which returns the size of the written data.
CURLOPT_PASSWDFUNCTION: Set a callback function with three parameters. The first is curl's resource handle, the second is a password prompt, and the third parameter is the maximum allowed password length. Returns the value of the password.
CURLOPT_READFUNCTION: Set a callback function with two parameters. The first is the resource handle of curl, and the second is the read data. Data reading must rely on this function. Returns the size of the read data, such as 0 or EOF.
CURLOPT_WRITEFUNCTION: Set a callback function with two parameters. The first is the resource handle of curl, and the second is the written data. Data writing must rely on this function. Returns the exact size of the data written
The function of curl_copy_handle() is to copy all the contents and parameters of a curl connection resource
PHP code
$ch = curl_init("http://qzone.myqq.us/");
$another = curl_copy_handle($ch);
curl_exec($another);
curl_close($another);
?>
The curl_error() function returns a string containing error information for the current session.
The function of curl_errno() function is to return a numeric number containing error information of the current session.
The curl_multi_init() function is used to initialize a curl batch handle resource.
The curl_multi_add_handle() function is used to add individual curl handle resources to the curl batch session. The curl_multi_add_handle() function has two parameters. The first parameter represents a curl batch handle resource, and the second parameter represents a separate curl handle resource.
The function of the curl_multi_exec() function is to parse a curl batch handle. The curl_multi_exec() function has two parameters. The first parameter represents a batch handle resource, and the second parameter is a reference value parameter, indicating the remaining needs to be processed. The number of individual curl handle resources.
The curl_multi_remove_handle() function represents the removal of a handle resource in the curl batch handle resource. The curl_multi_remove_handle() function has two parameters. The first parameter represents a curl batch handle resource, and the second parameter represents a separate curl handle. resource.
The function of curl_multi_close() is to close a batch handle resource.
PHP code
$ch1 = curl_init();
$ch2 = curl_init();
curl_setopt($ch1, CURLOPT_URL, "http://www.BkJia.com/");
curl_setopt($ch1, CURLOPT_HEADER, 0);
curl_setopt($ch2, CURLOPT_URL, "http://test.huangchao.org/");
curl_setopt($ch2, CURLOPT_HEADER, 0);
$mh = curl_multi_init();
curl_multi_add_handle($mh,$ch1);
curl_multi_add_handle($mh,$ch2);
do {
curl_multi_exec($mh,$flag);
} while ($flag > 0);
curl_multi_remove_handle($mh,$ch1);
curl_multi_remove_handle($mh,$ch2);
curl_multi_close($mh);
?>
The function of the curl_multi_getcontent() function is to return the obtained output text stream when CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER is set.
The function of curl_multi_info_read() function is to obtain the relevant transmission information of the currently parsed curl.
curl_multi_select():Get all the sockets associated with the cURL extension, which can then be "selected"

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 brings several new features, security improvements, and performance improvements with healthy amounts of feature deprecations and removals. This guide explains how to install PHP 8.4 or upgrade to PHP 8.4 on Ubuntu, Debian, or their derivati
 CakePHP Working with Database
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Working with Database
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
Working with database in CakePHP is very easy. We will understand the CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations in this chapter.
 CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work with date and time in cakephp4, we are going to make use of the available FrozenTime class.
 CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work on file upload we are going to use the form helper. Here, is an example for file upload.
 Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
CakePHP is an open-source framework for PHP. It is intended to make developing, deploying and maintaining applications much easier. CakePHP is based on a MVC-like architecture that is both powerful and easy to grasp. Models, Views, and Controllers gu
 CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
Validator can be created by adding the following two lines in the controller.
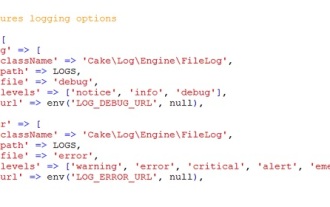 CakePHP Logging
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP Logging
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
Logging in CakePHP is a very easy task. You just have to use one function. You can log errors, exceptions, user activities, action taken by users, for any background process like cronjob. Logging data in CakePHP is easy. The log() function is provide
 How To Set Up Visual Studio Code (VS Code) for PHP Development
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
How To Set Up Visual Studio Code (VS Code) for PHP Development
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
Visual Studio Code, also known as VS Code, is a free source code editor — or integrated development environment (IDE) — available for all major operating systems. With a large collection of extensions for many programming languages, VS Code can be c



