 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 Experience Sharing: PHP Array Loop Data Fetching Techniques_PHP Tutorial
Experience Sharing: PHP Array Loop Data Fetching Techniques_PHP Tutorial
Experience Sharing: PHP Array Loop Data Fetching Techniques_PHP Tutorial
If we want to get a lot of data, you have to loop through the array. Let’s take a look at PHPlooping through the array to get the data. Since you're responsible for placing the data inside the array, now, how do you get it out? Retrieving data from an array is very simple: all you need to do is use the index number to access the appropriate element of the array. To read the contents of the entire array, you simply loop over it using the loop construct you learned in Chapter 3 of this tutorial.
How about a quick example?
<ol class="dp-c">
<li class="alt"><span><span><html> <head></head> <body> My favourite bands are: <ul> <?php </span></span></li><li><span class="comment">// define array $artists = array('Metallica', 'Evanescence', 'Linkin Park', 'Guns n Roses'); </span><span> </span></li><li class="alt"><span class="comment">// loop over it and print array elements for ($x = 0; $x < sizeof($artists</span><span> </span></li></ol>When you run the script, you will see the following results:
<ol class="dp-xml"><li class="alt"><span><span>My favourite bands are: Metallica Evanescence Linkin Park Guns n Roses </span></span></li></ol>
In this example, I first defined an array, and then used a for() loop to do the following: traverse the array, use index notation to get the elements, and then display them one by one. Here, I will draw your attention to the sizeof() function. This function is one of the most important and commonly used array functions. It returns the size of the array (read: the number of elements in the array). It is mostly used in loop counters to ensure that the number of loops is consistent with the number of all elements in the array. If you are using associative arrays, the array_keys() and array_values() functions are readily available to get a list of all the keys and corresponding values in the array.
<ol class="dp-c"><li class="alt"><span><span class="string">'bacon and eggs'</span><span>, </span><span class="string">'lunch'</span><span> => </span><span class="string">'roast beef'</span><span>, </span><span class="string">'dinner'</span><span> => </span><span class="string">'lasagna'</span><span>);</span></span></li>
<li class="alt"><span><span> </span><span class="comment">/* returns the array ('breakfast', 'lunch', 'dinner') with numeric indices */</span><span> </span></span></li>
<li class="alt"><span><span class="vars">$result</span><span> = </span><span class="func">array_keys</span><span>(</span><span class="vars">$menu</span><span>); print_r(</span><span class="vars">$result</span><span>); print " </span></span></li>
<li>
<span>"; </span><span class="comment">/* returns the array ('bacon and eggs', 'roast beef', 'lasagna') with numeric indices */</span><span> </span>
</li>
<li>
<span class="vars">$result</span><span> = </span><span class="func">array_values</span><span>(</span><span class="vars">$menu</span><span>); print_r(</span><span class="vars">$result</span><span>); ?> </span>
</li>
</ol>However, there is an easier way to extract all elements in an array. PHP 4.0 introduces a very new type of loop designed specifically for the purpose of repeatedly enumerating arrays: the foreach() loop (its syntactic structure is similar to the Perl structure of the same name).
The following is its syntax format:
<ol class="dp-c"><li class="alt"><span><span class="keyword">foreach</span><span> (</span><span class="vars">$array</span><span> </span><span class="keyword">as</span><span> </span><span class="vars">$temp</span><span>) { </span><span class="keyword">do</span><span> this! } </span></span></li></ol>The foreach() loop runs once for each element of the array passed to it as a parameter, repeating each time while traversing the array forward. Unlike the for() loop, it does not require a counter or calling the function sizeof() because it automatically keeps track of its position in the array. On each run, the statements within the curly braces are executed, and the currently selected array element is accessed through a temporary PHP array loop variable. To better understand how this works, consider a rewrite of the previous example using a foreach() loop:
<ol class="dp-xml"><li class="alt"><span><span class="tag"><</span><span class="tag-name">html</span><span class="tag">></span><span> </span><span class="tag"><</span><span class="tag-name">head</span><span class="tag">></span><span class="tag"></</span><span class="tag-name">head</span><span class="tag">></span><span> </span><span class="tag"><</span><span class="tag-name">body</span><span class="tag">></span><span> My favourite bands are: </span><span class="tag"><</span><span class="tag-name">ul</span><span class="tag">></span><span> </span><span class="tag"><?</span><span class="tag-name">php</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span><span>// define array $</span><span class="attribute">artists</span><span> = </span><span class="attribute-value">array</span><span> </span></span></li><li><span>('Metallica', 'Evanescence', 'Linkin Park', 'Guns n Roses'); </span></li><li><span>// loop over it // print array elements foreach ($artists as $a) </span></li><li class="alt"><span>{ echo '</span><span class="tag"><</span><span class="tag-name">li</span><span class="tag">></span><span>'.$a; } </span><span class="tag">?></span><span> </span><span class="tag"></</span><span class="tag-name">ul</span><span class="tag">></span><span> </span><span class="tag"></</span><span class="tag-name">body</span><span class="tag">></span><span> </span><span class="tag"></</span><span class="tag-name">html</span><span class="tag">></span><span> </span></span></li></ol>Each time the loop is executed, it will select The value of the array element is placed in the temporary variable $a. This variable can then be used by statements within the PHP array loop block. Because the foreach() loop does not require a counter to keep track of its position in the array, it requires less maintenance and is more readable than a standard for() loop. Oh, yes... it also works with associative arrays, with no additional programming required.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 brings several new features, security improvements, and performance improvements with healthy amounts of feature deprecations and removals. This guide explains how to install PHP 8.4 or upgrade to PHP 8.4 on Ubuntu, Debian, or their derivati
 CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work with date and time in cakephp4, we are going to make use of the available FrozenTime class.
 CakePHP Working with Database
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Working with Database
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
Working with database in CakePHP is very easy. We will understand the CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations in this chapter.
 CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work on file upload we are going to use the form helper. Here, is an example for file upload.
 CakePHP Routing
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Routing
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
In this chapter, we are going to learn the following topics related to routing ?
 Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
CakePHP is an open-source framework for PHP. It is intended to make developing, deploying and maintaining applications much easier. CakePHP is based on a MVC-like architecture that is both powerful and easy to grasp. Models, Views, and Controllers gu
 CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
Validator can be created by adding the following two lines in the controller.
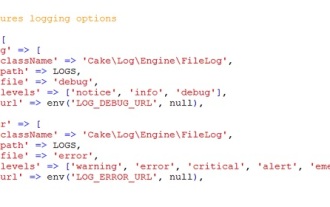 CakePHP Logging
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP Logging
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
Logging in CakePHP is a very easy task. You just have to use one function. You can log errors, exceptions, user activities, action taken by users, for any background process like cronjob. Logging data in CakePHP is easy. The log() function is provide



