 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 PHP Task Learning 1: Using Variables in Web Pages_PHP Tutorial
PHP Task Learning 1: Using Variables in Web Pages_PHP Tutorial
PHP Task Learning 1: Using Variables in Web Pages_PHP Tutorial
⚑Definition of variables
⚑Type of variables
⚑Use of variables
Variables can exist in memory. Objects are constantly changing. We can imagine the memory as a street. There are many residents in the street. Each resident will have his own house number. This is like an address in the memory (a concept often mentioned in the C language). , we won’t discuss it much here), for one of the residents we can say it is Building 1, No. 1, or it can be said to be Wang Xiaoming’s home, using a name to replace an address. The number of people in Wang Xiaoming's family at a given time is a variable quantity. There may be 3 people at noon, only 1 person in the afternoon, and 5 people at night. Therefore, if we want to refer to a certain address in the memory, we can also call it A, or area. This is the variable.
Let’s demonstrate the declaration of variables in PHP.
Use "$" to add a variable name, such as $a, $var_name.
Note three points when declaring variables in PHP:
1. Variable names can only consist of English letters (A-Z, a-z), numbers (0-9) and underscores.
2. Variable names in PHP are case-sensitive, that is, $VAR_NAME and $var_name are two different variables.
3. A variable declaration or assignment must end with a semicolon (;).
The type definition of variables in PHP is very simple. Generally, there is no need to use keyword declarations, and it can be reflected in the form of assignment.
For example, declare an integer variable
$x=100;
Declare a character variable
$str="Iam a Chinese!" ;
Declare a Boolean variable
$bool=true;
Use variables in web pages.
For example, we want to display a sentence on the web page, "I am a Chinese", "I am 28 years old this year".
 Quoted content: [www.bkjia.com]
$str="I am a Chinese";
Quoted content: [www.bkjia.com]
$str="I am a Chinese"; $age=28;
echo$str."
";
echo"I am this year".$ age."Age";
?>
Line 1 "
Line 2 $str="I am a Chinese"; defines a string variable str, whose value is "I am a Chinese".
Line 3 $age=28; defines an integer variable age and assigns it a value of 28.
Line 4 echo$str."
";, echo is the keyword used for output in PHP, and the content following it indicates that it is the content that needs to be output, that is, $str is the need Output variables, and the . after $str is a mark used to connect multiple variables or variables with general content. Here, a newline symbol
will be displayed after $str.
Line 5 echo "I am this year".$age."years old";, this sentence is understood in the same way as line 4. The sentence "I am 28 years old this year" is divided into three parts. "I am this year" is the first part. 28 is replaced by the variable $age. "Age" is the third part. They are connected by .
Line 6 "?>" indicates the end of this PHP file.
At this point, mission 1 is over. Up to now, you can express what you want to say on the web page in the form of PHP.
Author’s blog: http://walkbro.cnblogs.com/

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 CakePHP Project Configuration
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Project Configuration
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
In this chapter, we will understand the Environment Variables, General Configuration, Database Configuration and Email Configuration in CakePHP.
 PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 brings several new features, security improvements, and performance improvements with healthy amounts of feature deprecations and removals. This guide explains how to install PHP 8.4 or upgrade to PHP 8.4 on Ubuntu, Debian, or their derivati
 CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work with date and time in cakephp4, we are going to make use of the available FrozenTime class.
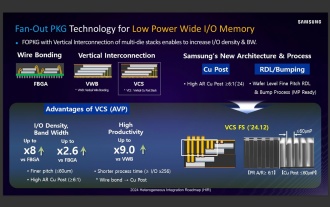 Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
According to news from this website on September 3, Korean media etnews reported yesterday (local time) that Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix’s “HBM-like” stacked structure mobile memory products will be commercialized after 2026. Sources said that the two Korean memory giants regard stacked mobile memory as an important source of future revenue and plan to expand "HBM-like memory" to smartphones, tablets and laptops to provide power for end-side AI. According to previous reports on this site, Samsung Electronics’ product is called LPWide I/O memory, and SK Hynix calls this technology VFO. The two companies have used roughly the same technical route, which is to combine fan-out packaging and vertical channels. Samsung Electronics’ LPWide I/O memory has a bit width of 512
 CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work on file upload we are going to use the form helper. Here, is an example for file upload.
 CakePHP Routing
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Routing
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
In this chapter, we are going to learn the following topics related to routing ?
 Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
CakePHP is an open-source framework for PHP. It is intended to make developing, deploying and maintaining applications much easier. CakePHP is based on a MVC-like architecture that is both powerful and easy to grasp. Models, Views, and Controllers gu
 How To Set Up Visual Studio Code (VS Code) for PHP Development
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
How To Set Up Visual Studio Code (VS Code) for PHP Development
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
Visual Studio Code, also known as VS Code, is a free source code editor — or integrated development environment (IDE) — available for all major operating systems. With a large collection of extensions for many programming languages, VS Code can be c





