Analyze whether unset in PHP will release memory_PHP tutorial
First let us look at an example
var_dump(memory_get_usage ());
$a = "laruence";
var_dump(memory_get_usage());
unset($a);
var_dump(memory_get_usage());
Output (on my personal computer, it may vary depending on the system, PHP version, and loaded extensions):
int(90440)
int(90640)
int(90472
Noticed 90472-90440=32, so there are various conclusions. Some people say that PHP's unset does not really release memory, and some say that PHP's unset only releases large memory. Only when variables (a large number of strings, large arrays) are used, the memory will be truly free. Some people even say that it is meaningless to discuss memory at the PHP level.
So, will unset release memory? Where do these 32 bytes go?
To answer this question, I will start from two aspects :
Where did these 32 bytes go?
First of all we have to break a thought: PHP is not like the C language, only when you explicitly call the memory allocation related API. Memory allocation.
That is to say, in PHP, there are many memory allocation processes that we cannot see.
For example:
$a = "laruence";
The implicit memory allocation point is:
1. Allocate memory for the variable name and store it in the symbol table
2. Allocate memory for the variable value
So, you can’t just look at the appearance.
Second, Don’t doubt that PHP’s unset will indeed release memory (of course, it must also be combined with references and counting. Please refer to my previous article for an in-depth understanding of PHP principles of variable separation/reference for this part), but this Release is not a release in the sense of C programming, it is not a return to the OS.
For PHP, it provides a set of memory management APIs similar to the C language for memory allocation. These APIs correspond to the meaning of C APIs. Within PHP, memory is managed through these APIs.
When we call emalloc to apply for memory, PHP does not simply ask the OS for memory, but asks the OS for a large piece of memory, and then allocates a piece of it to the applicant, so that when there is logic When applying for memory, you no longer need to apply for memory from the OS, avoiding frequent system calls.
For example, the following example:
$a = "laruence";
var_dump(memory_get_usage(TRUE));
unset($a);
var_dump(memory_get_usage(TRUE));
Output:
int( 262144)
int(262144)
int(262144
That is, when we define the variable $a, PHP does not apply for new memory from the system.
Similarly, when we call efree to release memory, PHP will not return the memory to the OS, but will add this memory to the free memory list it maintains. For small pieces of memory, it is more The possibility is to put it in the memory cache list (postscript, some versions of PHP, such as PHP5.2.4, 5.2.6, 5.2.8 that I have verified, will not decrease when calling get_memory_usage() Remove the available memory block size in the memory cache list, causing it to appear that the memory remains unchanged after unset).
Now let me answer where these 32 bytes go. As I just said, many memory allocation processes are not explicit. You will understand after reading the following code:
var_dump("I am www.jb51.net ");
var_dump(memory_get_usage());
$a = "laruence";
var_dump(memory_get_usage());
unset($a);
var_dump(memory_get_usage() );
Output:
string(43) "I am www.jb51.net"
int(90808) //Before assignment
int(90976)
int( 90808) //Yes, the memory is released normally
90808-90808 = 0, normal, that is to say, these 32 bytes are occupied by the output function (strictly speaking, they are occupied by the output Header)
Only Increasing array
Hashtable is the core structure of PHP (to understand Hashtable, you can refer to my previous article for an in-depth understanding of PHP arrays (traversal order)). Arrays are also represented by it, and symbol tables are also used. An associative array, for the following code:
var_dump("I am www.jb51. net");
var_dump(memory_get_usage());
$array = array_fill(1, 100, "laruence");
foreach ($array as $key => $value) {
${$value . $key} = NULL;
$value . $key});
}
var_dump(memory_get_usage());
We defined 100 variables, and then pressed Unset to see the output :
string(43) "I am www.jb51.net"
int(118848)
int(104448
Wow, why is there so much less memory?
This is because for Hashtable, when defining it, it is impossible to allocate enough memory blocks at once to store an unknown number. elements, so PHP will only allocate a small portion of the memory block to the HashTable during initialization, and then RESIZE to expand the capacity when it is not enough,
The Hashtable can only be expanded, not reduced. For the above example, when we stored 100 variables, the symbol table was not enough, so we did an expansion, and when we unset the 100 variables one by one Afterwards, the memory occupied by the variables is released (118848 – 104448), but the symbol table does not shrink, so the small memory is occupied by the symbol table itself...
Now, do you have a preliminary understanding of PHP’s memory management?
http://www.bkjia.com/PHPjc/328036.html

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 CakePHP Project Configuration
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Project Configuration
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
In this chapter, we will understand the Environment Variables, General Configuration, Database Configuration and Email Configuration in CakePHP.
 PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 brings several new features, security improvements, and performance improvements with healthy amounts of feature deprecations and removals. This guide explains how to install PHP 8.4 or upgrade to PHP 8.4 on Ubuntu, Debian, or their derivati
 CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work with date and time in cakephp4, we are going to make use of the available FrozenTime class.
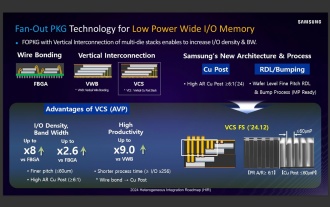 Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
According to news from this website on September 3, Korean media etnews reported yesterday (local time) that Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix’s “HBM-like” stacked structure mobile memory products will be commercialized after 2026. Sources said that the two Korean memory giants regard stacked mobile memory as an important source of future revenue and plan to expand "HBM-like memory" to smartphones, tablets and laptops to provide power for end-side AI. According to previous reports on this site, Samsung Electronics’ product is called LPWide I/O memory, and SK Hynix calls this technology VFO. The two companies have used roughly the same technical route, which is to combine fan-out packaging and vertical channels. Samsung Electronics’ LPWide I/O memory has a bit width of 512
 CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work on file upload we are going to use the form helper. Here, is an example for file upload.
 CakePHP Routing
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Routing
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
In this chapter, we are going to learn the following topics related to routing ?
 Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
CakePHP is an open-source framework for PHP. It is intended to make developing, deploying and maintaining applications much easier. CakePHP is based on a MVC-like architecture that is both powerful and easy to grasp. Models, Views, and Controllers gu
 CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
Validator can be created by adding the following two lines in the controller.






