Analyze how php writes logs into syslog_PHP tutorial
In order to facilitate operation and maintenance when working on projects, we often need to write system logs to the system syslog. Below we will introduce the operation of php on syslog under Linux:
Configuration in Linux syslog
In Linux, facilities (devices) have the following types:
AUTH common security/authorization messages
AUTHPRIV private security/authorization messages
CRON timer process
DAEMON daemon
KERN kernel message
LOCAL0... LOCAL7 local application, not supported on windows
LPR line printer
MAIL mail service
NEWS news service
SYSLOG by Messages generated within syslogd
USER General user-level information
UUCP UUCP subsystem
Log in to the Linux system, enter the /etc directory, enter:
vim syslog.conf
Open the syslog configuration file
Here, you can see All configuration information to syslog, here defines the conditions used to store logs for each log type mentioned in the previous section, such as:
daemon.* -/var/log/daemon.log
definition Specifies the storage location of the logs generated by the daemon, where daemon is the log type, and "*" means that all levels of logs are placed in this file. The format is:
facility. level - the path where the log file is saved, such as -/var/log/daemon.log
level includes:
emerg - the system is unavailable
alert - conditions that need to be modified immediately
crit - error conditions that prevent certain tools or subsystem functions from being implemented
err - error conditions that prevent tools or some subsystem functions from being implemented
warning - early warning information
notice - important Ordinary conditions
info - informational messages
debug - does not contain function conditions or other information about the problem
none - no importance level, usually used for debugging
* All levels except none
Next we define a log rule for our own device in the configuration file: local4.info -/var/log/
Next, execute the command /etc/init.d/sysklogd restart or /etc/init.d/sysklogd reload makes the new configuration take effect. Now we can test the new log rules:
1. Enter the command logger -p local4.info "my test log" 2. Execute the command tail /var/log/event_log.log
You can see the log information you wrote:
Note: local4.info in syslog.conf represents all Logs of info level and above will be recorded hereok, now we have set up the logs we need in ubuntu, now we use syslog in php to write the logs to syslog in ubuntu.
The following is the php code directly:
syslog($level, "LOG MESSAGE: " . $errinfo);
closelog();
The first parameter of openlog is the log identifier, which is automatically added to the beginning of the log information to indicate what system wrote the log.
Since we want to write the log to local4.info, the third parameter needs to use LOG_LOCAL4, which represents the device information for writing the log.
$level in syslog is the log level, including:
LOG_EMERG system is unusable LOG_ALERT action must be taken immediately
LOG_CRIT critical conditions
LOG_ERR error conditions
LOG_WARNING warning conditions
LOG_NOTICE normal, but significant, condition
LOG_INFO informational message
LOG_DEBUG debug-level message
The second parameter is the specific log content.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1375
1375
 52
52
 PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 brings several new features, security improvements, and performance improvements with healthy amounts of feature deprecations and removals. This guide explains how to install PHP 8.4 or upgrade to PHP 8.4 on Ubuntu, Debian, or their derivati
 CakePHP Working with Database
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Working with Database
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
Working with database in CakePHP is very easy. We will understand the CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations in this chapter.
 CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work with date and time in cakephp4, we are going to make use of the available FrozenTime class.
 CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work on file upload we are going to use the form helper. Here, is an example for file upload.
 Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
CakePHP is an open-source framework for PHP. It is intended to make developing, deploying and maintaining applications much easier. CakePHP is based on a MVC-like architecture that is both powerful and easy to grasp. Models, Views, and Controllers gu
 CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
Validator can be created by adding the following two lines in the controller.
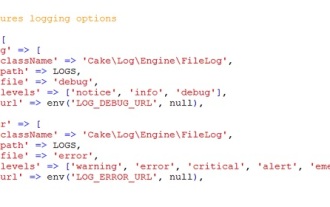 CakePHP Logging
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP Logging
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
Logging in CakePHP is a very easy task. You just have to use one function. You can log errors, exceptions, user activities, action taken by users, for any background process like cronjob. Logging data in CakePHP is easy. The log() function is provide
 How To Set Up Visual Studio Code (VS Code) for PHP Development
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
How To Set Up Visual Studio Code (VS Code) for PHP Development
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
Visual Studio Code, also known as VS Code, is a free source code editor — or integrated development environment (IDE) — available for all major operating systems. With a large collection of extensions for many programming languages, VS Code can be c




