 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 Detailed explanation based on PHP5 magic constants and magic methods_PHP tutorial
Detailed explanation based on PHP5 magic constants and magic methods_PHP tutorial
Detailed explanation based on PHP5 magic constants and magic methods_PHP tutorial
魔术常量:
1。__LINE__
返回文件中的当前行号。
2。__FILE__
返回文件的完整路径和文件名。如果用在包含文件中,则返回包含文件名。自PHP4.0.2 起,__FILE__总是包含一个绝对路径,而在此之前的版本有时会包含一个相对路径。
3。__FUNCTION__
返回函数名称(PHP4.3.0 新加)。自PHP5 起本常量返回该函数被定义时的名字(区分大小写)。在PHP4 中该值总是小写字母的。
4。__CLASS__
返回类的名称(PHP4.3.0 新加)。自PHP5 起本常量返回该类被定义时的名字(区分大小写)。在PHP4 中该值总是小写字母的。
5。__METHOD__
返回类的方法名(PHP5.0.0 新加)。返回该方法被定义时的名字(区分大小写)。
魔术函数:
1。__construct()
构造函数: 实例化对象时被调用,
当__construct和以类名为函数名的构造函数同时存在时,__construct将被调用,另一个不被调用。
4。__get()
读取一个对象的属性时,若属性存在,则直接返回属性值;若不存在,则会调用__get函数。
5。__set()
设置一个对象的属性时,
若属性存在,则直接赋值;
若不存在,则会调用__set函数。
6。__toString()
打印一个对象的时被调用。如echo$obj;或print$obj;
7。__clone()
克隆对象时被调用。如:$t=newTest();$t1=clone $t;
8。__sleep()
serialize之前被调用。若对象比较大,想删减一点东东再序列化,可考虑一下此函数。
9。__wakeup()
unserialize时被调用,做些对象的初始化工作。
10。__isset()
检测一个对象的属性是否存在时被调用。如:isset($c->name)。
11。__unset()
unset一个对象的属性时被调用。如:unset($c->name)。
12。__set_state()
调用var_export时,被调用。用__set_state的返回值做为var_export的返回值。
13。__autoload()
实例化一个对象时,如果对应的类不存在,则该方法被调用。
初识魔术方法
Php5.0发布以来为我们提供了很多面向对象的特性,尤其是为我们提供了好多易用的魔术方法,这些魔术方法可以让我们简化我们的编码,更好的设计我们的系统。今天我们就来认识下php5.0给我们提供的魔术方法。
PHP| 魔术方法|__toString(),__clone(),__call(),__autoload() 详解
__toString()
如果我有一个类:
classPerson
{
private $name = “”;
private $age = 0;
function__construct($name = “”, $age = “”)
{
$this->name =$name;
$this->age = $age;
}
functionsay()
{
echo“name:”.$this->name.”
”.”age:”.$this->age.”
”;
}
}
现在我去实例化这个类,然后去打印这个实例:
$p1= new person(“liuzy”,20);
echo $p1; //直接打印会出错
显然这样直接打印对象是会出现错误的,因为对象是引用句柄,不能直接打印。这时,我们可以用到__toString()方法。我们在Person类里加一个__toString()方法:
function__toString()
{
return “I am Person,my name is“.$this->name.”
”;
}
然后再刷新页面,发现什么了?
现在我们明白,__toString()是在直接打印对象时执行的方法,我们可以用该方法打印类的一些相关信息。注意:是两个下划线,方法必须有返回值。
__clone()
我们知道对象是可以直接赋值的,比如
$p2= $p1; //这里是一个对象有两个引用
那么我执行:
$p1->say();
$p2->say();
是都可以执行的,而且效果一样。
We have another method:
$p3= clone $p1; //Note that clone is the clone keyword. The difference here is that $p3 is a new object.
At the same time, we add a method to the class:
function__clone()
{
$this->name = "I am a copy"; //Note: $this here is generated by cloning The object itself, not the current class
}
Then we execute:
$p3->say();
Print out:
name:I am a copy
age:20
At this point we understand that the __clone() method is a method executed when cloning an object. Its function is to initialize properties and other operations on the newly cloned copy.
__call()
The main function of this method is to execute the __call() method when an instance of this class calls a non-existent method. Note that it needs to be declared in the class in advance:
function__call($fname,$argus)
{
echo "The method you called: ".$fname." does not exist
";
echo" parameter is".print_r($argus);
}
__autoload()
When we usually call a class, we must first introduce the file where the class is located (include "xxx .php"), if we call many classes in one page, then we have to use many include "xxx.php". Obviously this is troublesome.
__autoload() method can help us solve this problem.
For example, we define the file where the Person class above is located as Person_class.php.
Create a new php file test.php and edit the content:
function __autoload($calssName)
{
include $className.”_class.php”; //Maybe you will understand after seeing this, right? Haha
}
$p= new Person(“mifan”, 22);
$p->say();
There will be no errors when executing the test.php page.
The __autoload() method is a method called when a class does not exist. It has a string type parameter that declares the class name of the non-existent class.
Of course, the naming of class files is also very particular. It is best to have something to do with a class, such as Person_class.php

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to write a novel in the Tomato Free Novel app. Share the tutorial on how to write a novel in Tomato Novel.
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
How to write a novel in the Tomato Free Novel app. Share the tutorial on how to write a novel in Tomato Novel.
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
Tomato Novel is a very popular novel reading software. We often have new novels and comics to read in Tomato Novel. Every novel and comic is very interesting. Many friends also want to write novels. Earn pocket money and edit the content of the novel you want to write into text. So how do we write the novel in it? My friends don’t know, so let’s go to this site together. Let’s take some time to look at an introduction to how to write a novel. Share the Tomato novel tutorial on how to write a novel. 1. First open the Tomato free novel app on your mobile phone and click on Personal Center - Writer Center. 2. Jump to the Tomato Writer Assistant page - click on Create a new book at the end of the novel.
 How to recover deleted contacts on WeChat (simple tutorial tells you how to recover deleted contacts)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
How to recover deleted contacts on WeChat (simple tutorial tells you how to recover deleted contacts)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
Unfortunately, people often delete certain contacts accidentally for some reasons. WeChat is a widely used social software. To help users solve this problem, this article will introduce how to retrieve deleted contacts in a simple way. 1. Understand the WeChat contact deletion mechanism. This provides us with the possibility to retrieve deleted contacts. The contact deletion mechanism in WeChat removes them from the address book, but does not delete them completely. 2. Use WeChat’s built-in “Contact Book Recovery” function. WeChat provides “Contact Book Recovery” to save time and energy. Users can quickly retrieve previously deleted contacts through this function. 3. Enter the WeChat settings page and click the lower right corner, open the WeChat application "Me" and click the settings icon in the upper right corner to enter the settings page.
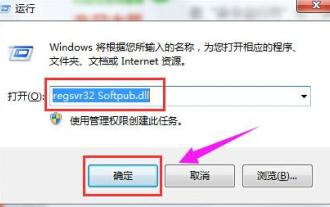 What to do if the 0x80004005 error code appears. The editor will teach you how to solve the 0x80004005 error code.
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:17 PM
What to do if the 0x80004005 error code appears. The editor will teach you how to solve the 0x80004005 error code.
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:17 PM
When deleting or decompressing a folder on your computer, sometimes a prompt dialog box "Error 0x80004005: Unspecified Error" will pop up. How should you solve this situation? There are actually many reasons why the error code 0x80004005 is prompted, but most of them are caused by viruses. We can re-register the dll to solve the problem. Below, the editor will explain to you the experience of handling the 0x80004005 error code. Some users are prompted with error code 0X80004005 when using their computers. The 0x80004005 error is mainly caused by the computer not correctly registering certain dynamic link library files, or by a firewall that does not allow HTTPS connections between the computer and the Internet. So how about
 How to set font size on mobile phone (easily adjust font size on mobile phone)
May 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
How to set font size on mobile phone (easily adjust font size on mobile phone)
May 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Setting font size has become an important personalization requirement as mobile phones become an important tool in people's daily lives. In order to meet the needs of different users, this article will introduce how to improve the mobile phone use experience and adjust the font size of the mobile phone through simple operations. Why do you need to adjust the font size of your mobile phone - Adjusting the font size can make the text clearer and easier to read - Suitable for the reading needs of users of different ages - Convenient for users with poor vision to use the font size setting function of the mobile phone system - How to enter the system settings interface - In Find and enter the "Display" option in the settings interface - find the "Font Size" option and adjust it. Adjust the font size with a third-party application - download and install an application that supports font size adjustment - open the application and enter the relevant settings interface - according to the individual
 The secret of hatching mobile dragon eggs is revealed (step by step to teach you how to successfully hatch mobile dragon eggs)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
The secret of hatching mobile dragon eggs is revealed (step by step to teach you how to successfully hatch mobile dragon eggs)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
Mobile games have become an integral part of people's lives with the development of technology. It has attracted the attention of many players with its cute dragon egg image and interesting hatching process, and one of the games that has attracted much attention is the mobile version of Dragon Egg. To help players better cultivate and grow their own dragons in the game, this article will introduce to you how to hatch dragon eggs in the mobile version. 1. Choose the appropriate type of dragon egg. Players need to carefully choose the type of dragon egg that they like and suit themselves, based on the different types of dragon egg attributes and abilities provided in the game. 2. Upgrade the level of the incubation machine. Players need to improve the level of the incubation machine by completing tasks and collecting props. The level of the incubation machine determines the hatching speed and hatching success rate. 3. Collect the resources required for hatching. Players need to be in the game
 Quickly master: How to open two WeChat accounts on Huawei mobile phones revealed!
Mar 23, 2024 am 10:42 AM
Quickly master: How to open two WeChat accounts on Huawei mobile phones revealed!
Mar 23, 2024 am 10:42 AM
In today's society, mobile phones have become an indispensable part of our lives. As an important tool for our daily communication, work, and life, WeChat is often used. However, it may be necessary to separate two WeChat accounts when handling different transactions, which requires the mobile phone to support logging in to two WeChat accounts at the same time. As a well-known domestic brand, Huawei mobile phones are used by many people. So what is the method to open two WeChat accounts on Huawei mobile phones? Let’s reveal the secret of this method. First of all, you need to use two WeChat accounts at the same time on your Huawei mobile phone. The easiest way is to
 The difference between Go language methods and functions and analysis of application scenarios
Apr 04, 2024 am 09:24 AM
The difference between Go language methods and functions and analysis of application scenarios
Apr 04, 2024 am 09:24 AM
The difference between Go language methods and functions lies in their association with structures: methods are associated with structures and are used to operate structure data or methods; functions are independent of types and are used to perform general operations.
 How to choose a mobile phone screen protector to protect your mobile phone screen (several key points and tips for purchasing mobile phone screen protectors)
May 07, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
How to choose a mobile phone screen protector to protect your mobile phone screen (several key points and tips for purchasing mobile phone screen protectors)
May 07, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
Mobile phone film has become one of the indispensable accessories with the popularity of smartphones. To extend its service life, choose a suitable mobile phone film to protect the mobile phone screen. To help readers choose the most suitable mobile phone film for themselves, this article will introduce several key points and techniques for purchasing mobile phone film. Understand the materials and types of mobile phone films: PET film, TPU, etc. Mobile phone films are made of a variety of materials, including tempered glass. PET film is relatively soft, tempered glass film has good scratch resistance, and TPU has good shock-proof performance. It can be decided based on personal preference and needs when choosing. Consider the degree of screen protection. Different types of mobile phone films have different degrees of screen protection. PET film mainly plays an anti-scratch role, while tempered glass film has better drop resistance. You can choose to have better



