 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Analysis of JavaScript script loading and execution in browser environment: defer and async characteristics_javascript skills
Analysis of JavaScript script loading and execution in browser environment: defer and async characteristics_javascript skills
Analysis of JavaScript script loading and execution in browser environment: defer and async characteristics_javascript skills
The defer and async features are believed to be two features that many JavaScript developers are "familiar but not familiar with". From a literal point of view, the functions of the two are easy to understand. They are "delay script" and "asynchronous script" respectively. effect. However, taking defer as an example, developers may not necessarily be familiar with some details, such as: when will a script with the defer feature be delayed to be executed; whether both internal scripts and external scripts can support defer; scripts after defer In addition to delayed execution, what are the special features, etc. This article combines some existing articles and the description of the two features in MDN documents to conduct a more comprehensive study and summary of defer and async, hoping to help developers better master these two features.
1 Introduction
In "Analysis of JavaScript Script Loading and Execution in the Browser Environment: Code Execution Sequence" we mentioned that the execution of JavaScript code will block the parsing and rendering of the page and the downloading of other resources. Of course, due to JavaScript is a single-threaded language, which means that under normal circumstances, the JavaScript code in a page can only be executed in order from top to bottom. Of course, as in " Analysis of JavaScript Script Loading and Execution in the Browser Environment As we analyzed in "Execution Sequence ", in some cases, such as when entering a script through document.write or introducing a script through dynamic script technology, the execution order of JavaScript code does not necessarily follow the strict order from top to bottom. defer and async are also what we call "abnormal situations".
We often say that the execution of JavaScript is blocking. In actual development, the blocking that we are usually most concerned about and the blocking that affects the user experience the most should be the following aspects:
[1] Blocking of page parsing and rendering
[2] The page initialization script we wrote (generally the script bound to listen to the DOMContentLoaded event). This part of the script is the script we want to execute first, because we will write the code most relevant to user interaction here. )
[3] Blocking of downloading external resources on the page (such as pictures)
If we have a time-consuming script operation, and this script blocks the three places we mentioned above, then the performance or user experience of this web page will be very poor.
The original intention of the two features of defer and async is also to solve or alleviate the impact of blocking on the page experience. Let’s analyze these two features below. We mainly understand these two from the following aspects. Features:
[1]When is the execution time of delayed or asynchronous scripts? What about page blocking?
[2] Are both internal and external scripts capable of delay or asynchronous implementation?
[3]How well does the browser support these two features? Are there any related bugs?
[4] Is there anything else that needs to be paid attention to when using scripts that use these two features?
2 defer feature
2.1 About the execution timing of defer script
The defer feature is an extended feature defined in the HTML4 specification. Initially, it was only supported by IE4 and Firefox3.5. Later, browsers such as Chrome also added support for it, using defer="defer". defer means delay, which means it will delay the execution of the script. Under normal circumstances, the script we introduce will be downloaded and executed immediately. However, with the defer feature, the script will not be executed immediately after downloading, but will be executed after the page is parsed. Let’s take a look at the HTML4 standard’s explanation of defer:
defer: When set, this boolean attribute provides a hint to the user agent that the script is not going to generate any document content (e.g., no "document.write" in javascript) and thus, the user agent can continue parsing and rendering.
In other words, if defer is set, it tells the user agent that this script will not produce any document content, so that the user agent can continue to parse and render. Let’s take another look at the key description of defer in MDN:
defer: If the async attribute is not present but the defer attribute is present, then the script is executed when the page has finished parsing.
Through the definition in the standard, we can make it clear that the defer script will not block the parsing of the page, but will wait until the page parsing is completed before executing it. However, the time-consuming defer may still block the download of external resources, then Will it block the DOMContentLoaded event? In fact, the defer script is still executed before the DOMContentLoaded event, so it will still block the script in DOMContentLoaded. We can use the following figure to help understand the execution timing of the defer script:

According to the definition in the standard, internal scripts do not support defer, but browsers IE9 and below provide defer support for internal scripts.
2.2 defer browser support
Let’s take a look at browser support for the defer feature:
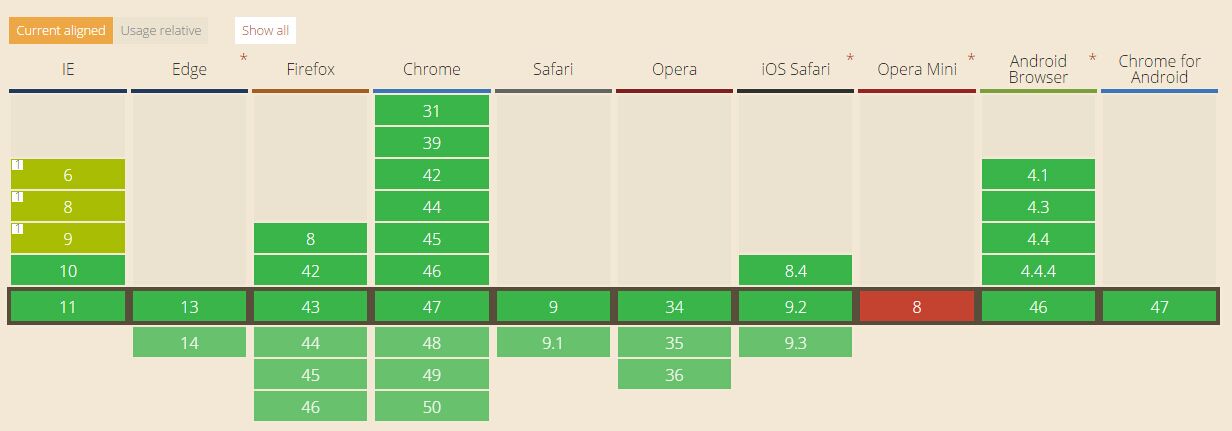
There is a bug in IE9 and below browsers, which will be explained in detail in the DEMO later.
2.3 DEMO: Function verification of defer feature
We imitate the method used by Olivier Rochard in "the script defer attribute" to verify the function of the defer attribute:
First we prepared 6 external scripts:
1.js:
test = "I am head external script n";
2.js
test = "I am a body external script n";
3.js
test = "I am the bottom external script n";
defer1.js
test = "I am head external delay script n";
defer2.js
test = "I am body external delay script n";
defer3.js
test = "I am the bottom external delay script n";
The code in HTML is:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>defer attribute test</title>
<script src="http://lib.sinaapp.com/js/jquery/1.9.1/jquery-1.9.1.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">var test = "";</script>
<script src="defer1.js" type="text/javascript" defer="defer"></script>
<script src="1.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script defer="defer">
test += "我是head延迟内部脚本\n";
</script>
<script>
test += "我是head内部脚本\n";
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="test">点击一下</button>
<script src="defer2.js" type="text/javascript" defer="defer"></script>
<script src="2.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</body>
<script src="defer3.js" type="text/javascript" defer="defer"></script>
<script src="3.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script>
$(function(){
test += "我是DOMContentLoaded里面的脚本
";
})
window.onload = function(){
test += "我是window.onload里面的脚本
";
var button = document.getElementById("test");
button.onclick = function(){
alert(test);
}
}
</script>
</html> In the code, in order to facilitate the implementation of the DOMContentLoaded event, we introduced jQuery (later articles will introduce how to implement compatible DOMContentLoaded yourself). Then, we introduced delay scripts in the head, inside the body and outside the body of the script. and normal scripts, and records the execution status of each piece of code through a global string. Let’s take a look at the execution results in each browser:
| IE7 | IE9 | IE10 | CHROME | firefox | ||||||||||
|
<🎜>I am head external script<🎜> I am head internal script<🎜> I am a body external script <🎜> I am the bottom external script <🎜> I am head external delay script <🎜> I am head delay internal script<🎜> I am a body external delay script <🎜> I am the bottom external delay script <🎜> I am the script in DOMContentLoaded<🎜> I am the script in window.onload<🎜> | <🎜>I am head external script<🎜> I am head delayed internal script<🎜> I am head internal script<🎜> I am a body external script <🎜> I am the bottom external script <🎜> I am head external delay script <🎜> I am a body external delay script <🎜> I am the bottom external delay script <🎜> I am the script in DOMContentLoaded<🎜> I am the script in window.onload<🎜> | <🎜>I am head external script<🎜> I am head delayed internal script<🎜> I am head internal script<🎜> I am a body external script<🎜> I am the bottom external script <🎜> I am head external delay script <🎜> I am a body external delay script <🎜> I am the bottom external delay script <🎜> I am the script in DOMContentLoaded<🎜> I am the script in window.onload<🎜> | <🎜> |
从输出的结果中我们可以确定,只有IE9及以下浏览器支持内部延迟脚本,并且defer后的脚本都会在DOMContentLoaded事件之前触发,因此也是会堵塞DOMContentLoaded事件的。
2.4 DEMO:IE<=9的defer特性bug
从2.3节中的demo可以看出,defer后的脚本还是能够保持执行顺序的,也就是按照添加的顺序依次执行。而在IE<=9中,这个问题存在一个bug:假如我们向文档中增加了多个defer的脚本,而且之前的脚本中有appendChild,innerHTML,insertBefore,replaceChild等修改了DOM的接口调用,那么后面的脚本可能会先于该脚本执行。可以参考github的issue:https://github.com/h5bp/lazyweb-requests/issues/42
我们通过DEMO验证一下,首先修改1.js的代码为(这段代码只为模拟,事实上这段代码存在极大的性能问题):
document.body.innerHTML = "
document.body.innerHTML += "
document.body.innerHTML += "
document.body.innerHTML += "
document.body.innerHTML += "
document.body.innerHTML += "
document.body.innerHTML += "
alert("我是第1个脚本");
2.js
alert("我是第2个脚本");
修改HMTL中的代码为:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"/> <title>defer bug in IE=9 test</title> <script src="1.js" type="text/javascript" defer="defer"></script> <script src="2.js" type="text/javascript" defer="defer"></script> </head> <body> </body> </html>
正常情况下,浏览器中弹出框的顺序肯定是:我是第1个脚本-》我是第2个脚本,然而在IE<=9中,执行结果却为:我是第2个脚本-》我是第1个脚本,验证了这个bug。
2.5 defer总结
在总结之前,首先要说一个注意点:正如标准中提到的,defer的脚本中不应该出现document.write的操作,浏览器会直接忽略这些操作。
总的来看,defer的作用一定程度上与将脚本放置在页面底部有一定的相似,但由于IE<=9中的bug,如果页面中出现多个defer时,脚本的执行顺序可能会被打乱从而导致代码依赖可能会出错,因此实际项目中很少会使用defer特性,而将脚本代码放置在页面底部可以替代defer所提供的功能。
3 async特性
3.1 关于async脚本的执行时机
async特性是HTML5中引入的特性,使用方式为:async="async",我们首先看一下标准中对于async特性的相关描述:
async:If the async attribute is present, then the script will be executed asynchronously, as soon as it is available.
需要指出,这里的异步,指的其实是异步加载而不是异步执行,也就是说,浏览器遇到一个async的script标签时,会异步的去加载(个人认为这个过程主要是下载的过程),一旦加载完毕就会执行代码,而执行的过程肯定还是同步的,也就是阻塞的。我们可以通过下图来综合理解defer和async:
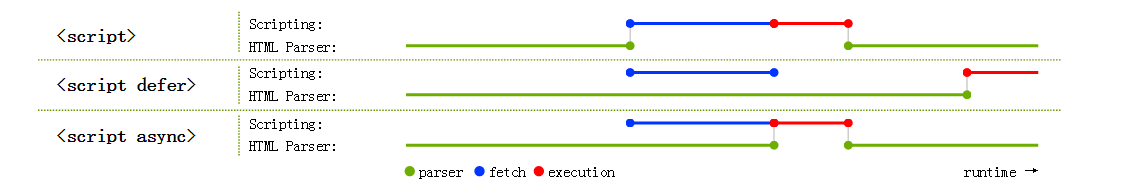
这样来看的话,async脚本的执行时机是无法确定的,因为脚本何时加载完毕也是不确定的。我们通过下面的demo来感受一下:
async1.js
alert("我是异步的脚本");
HTML代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>async attribute test</title>
<script src="/delayfile.php?url=http://localhost/js/load/async1.js&delay=2" async="async" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script>
alert("我是同步的脚本");
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html> Here we borrow the delayfile script in "Analysis of JavaScript Script Loading and Execution in Browser Environment: Code Execution Sequence" to provide a delay. In browsers that support async, the order of the pop-up boxes of this script is generally: I am a synchronous script -> I am an asynchronous script.
3.2 Browser support for async
Let’s take a look at browser support for async features:
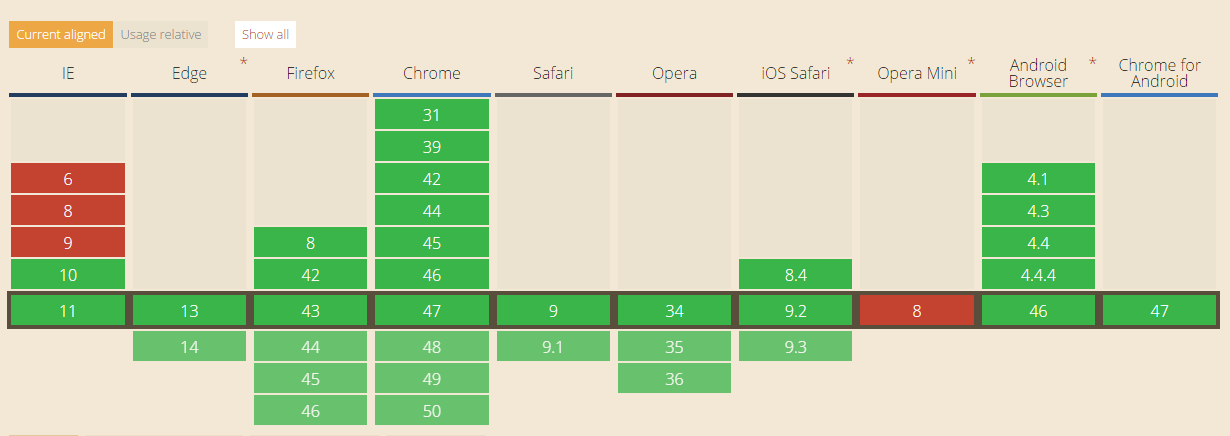
As you can see, only IE10 supports the async feature. Opera mini does not support the async feature. In addition, async does not support internal scripts.
3.3 async summary
async refers to asynchronous scripts, that is, scripts are loaded asynchronously. The loading process will not cause blocking, but the execution timing of async scripts is uncertain, and the order of execution is also uncertain, so scripts using async should be Scripts that do not rely on any code (such as third-party statistics code or advertising code), otherwise it will cause execution errors.
4 Priority issues between defer and async
This is easier to understand. The standard stipulates:
[1] If the

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 Replace String Characters in JavaScript
Mar 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Replace String Characters in JavaScript
Mar 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Detailed explanation of JavaScript string replacement method and FAQ This article will explore two ways to replace string characters in JavaScript: internal JavaScript code and internal HTML for web pages. Replace string inside JavaScript code The most direct way is to use the replace() method: str = str.replace("find","replace"); This method replaces only the first match. To replace all matches, use a regular expression and add the global flag g: str = str.replace(/fi
 Build Your Own AJAX Web Applications
Mar 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Build Your Own AJAX Web Applications
Mar 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
So here you are, ready to learn all about this thing called AJAX. But, what exactly is it? The term AJAX refers to a loose grouping of technologies that are used to create dynamic, interactive web content. The term AJAX, originally coined by Jesse J
 10 jQuery Fun and Games Plugins
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:42 AM
10 jQuery Fun and Games Plugins
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:42 AM
10 fun jQuery game plugins to make your website more attractive and enhance user stickiness! While Flash is still the best software for developing casual web games, jQuery can also create surprising effects, and while not comparable to pure action Flash games, in some cases you can also have unexpected fun in your browser. jQuery tic toe game The "Hello world" of game programming now has a jQuery version. Source code jQuery Crazy Word Composition Game This is a fill-in-the-blank game, and it can produce some weird results due to not knowing the context of the word. Source code jQuery mine sweeping game
 How do I create and publish my own JavaScript libraries?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How do I create and publish my own JavaScript libraries?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
Article discusses creating, publishing, and maintaining JavaScript libraries, focusing on planning, development, testing, documentation, and promotion strategies.
 jQuery Parallax Tutorial - Animated Header Background
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:39 AM
jQuery Parallax Tutorial - Animated Header Background
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:39 AM
This tutorial demonstrates how to create a captivating parallax background effect using jQuery. We'll build a header banner with layered images that create a stunning visual depth. The updated plugin works with jQuery 1.6.4 and later. Download the
 Getting Started With Matter.js: Introduction
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:53 AM
Getting Started With Matter.js: Introduction
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:53 AM
Matter.js is a 2D rigid body physics engine written in JavaScript. This library can help you easily simulate 2D physics in your browser. It provides many features, such as the ability to create rigid bodies and assign physical properties such as mass, area, or density. You can also simulate different types of collisions and forces, such as gravity friction. Matter.js supports all mainstream browsers. Additionally, it is suitable for mobile devices as it detects touches and is responsive. All of these features make it worth your time to learn how to use the engine, as this makes it easy to create a physics-based 2D game or simulation. In this tutorial, I will cover the basics of this library, including its installation and usage, and provide a
 Auto Refresh Div Content Using jQuery and AJAX
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:58 AM
Auto Refresh Div Content Using jQuery and AJAX
Mar 08, 2025 am 12:58 AM
This article demonstrates how to automatically refresh a div's content every 5 seconds using jQuery and AJAX. The example fetches and displays the latest blog posts from an RSS feed, along with the last refresh timestamp. A loading image is optiona
 How do I optimize JavaScript code for performance in the browser?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:14 PM
How do I optimize JavaScript code for performance in the browser?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:14 PM
The article discusses strategies for optimizing JavaScript performance in browsers, focusing on reducing execution time and minimizing impact on page load speed.



