 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 Use PHP arrays to achieve unlimited classification, no database, no recursion
Use PHP arrays to achieve unlimited classification, no database, no recursion
Use PHP arrays to achieve unlimited classification, no database, no recursion
Copy the code The code is as follows:
class cat
{
public $data;
public function __construct()
{
@include "data.php";
$this->data = $class;
}
public function CreateSortLevel($fatherlevel)
{
if(empty($fatherlevel))
{
if(is_array($this->data))
{
$fast_level = array();
foreach($this->data as $value)
{
if(strlen($value["sortlevel"]) == 3)
{
$fast_level[] = $value["sortlevel"];
}
}
$max_fast_level = max($fast_level);
unset($fast_level);
$sub = ceil($max_fast_level) + 1;
switch(strlen($sub))
{
case 1:
return "00{$sub}";
break;
case 2:
return "0{$sub}";
break;
case 3:
return $sub;
break;
}
}
else
{
return "001";
}
}
foreach($this->data as $val)
{
if(eregi("^".$fatherlevel.".{3}$",$val["sortlevel"]))
{
$level[] = $val["sortlevel"];
}
}
if(is_array($level))
{
$max_two_level = max($level);
$sub = ceil(substr($max_two_level,-3)) + 1;
switch(strlen($sub))
{
case 1:
return substr($max_two_level,0,strlen($max_two_level)-1).$sub;
break;
case 2:
return substr($max_two_level,0,strlen($max_two_level)-2).$sub;
break;
case 3:
return substr($max_two_level,0,strlen($max_two_level)-3).$sub;
break;
}
}
else
{
return $fatherlevel."001";
}
}
public function orders()
{
$op = $this->data;
$this->array_usort($op,"sortlevel",SORT_ASC);
return $op;
}
public function add_cat($sortname,$sortlevel)
{
$data = time();
$arr = array
(
"{$data}" => array
(
"sortname" => $sortname,
"sortlevel" => $this->CreateSortLevel($sortlevel)
)
);
$rs = $this->data + $arr;
$this->add_wirte($rs);
}
private function array_usort(&$array)
{
$args = func_get_args();
for($i=1,$cmd='',$size=count($args);$i<$size;$i++)
{
$num = $i;
$order = "";
$con = "@strcmp($a['$args[$num]'],$b['$args[$num]'])";
while(++$i < $size)
{
if($args[$i] === SORT_NUMERIC)
{
$con = "($a['$args[$num]']-$b['$args[$num]'])";
}
else if($args[$i] === SORT_DESC)
{
$order = "-1*";
}
else if(is_string($args[$i]))
{
$i--;
break;
}
}
$cmd .= "if($num = $con)return $order$num;else ";
if($order != '')
{
$i++;
}
}
@usort($array,@create_function('$a,$b',"$cmd return 0;"));
}
public function wirte($sortname,$sortlevel)
{
$array = " $array .= '$class = array'."rn(rn";
$array .= ' "'.time().'" => array'."rn";
$array .= ' ('."rn";
$array .= ' "sortname" => "'.$sortname.'"'.",rn";
$array .= ' "sortlevel" => "'.$this->CreateSortLevel($sortlevel).'"'."rn";
$array .= ' )'."rn";
$array .= ")rn?>";
file_put_contents("data.php",$array);
}
public function add_wirte($rs)
{
$array = " $array .= '$class = array'."rn(rn";
foreach($rs as $key=>$value)
{
$array .= "rn";
$array .= ' "'.$key.'" => array'."rn";
$array .= ' ('."rn";
$array .= ' "sortname" => "'.$value["sortname"].'"'.",rn";
$array .= ' "sortlevel" => "'.$value["sortlevel"].'"'."rn";
$array .= ' ),';
}
$array = substr($array,0,-1);
$array .= "rn)rn?>";
file_put_contents("data.php",$array);
}
}
$cat = new cat();
if($_GET["action"] == "add")
{
if(strlen($_POST["sortname"]) < 2)
{
echo '
echo '
exit;
}
if(file_exists("data.php"))
{
$cat->add_cat($_POST["sortname"],$_POST["sortlevel"]);
echo '
echo '
exit;
}
else
{
$cat->wirte($_POST["sortname"],$_POST["sortlevel"]);
echo '
echo '
exit;
exit;
}
}
if($_GET["action"] == "tpl")
{
echo '
echo '
echo '
foreach($cat->orders() as $val)
{
echo '
$clevel = strlen(substr($val['sortlevel'],0,-3));
for($i = 0; $i < $clevel; $i++)
{
echo "-";
}
echo $val['sortname']."rn";
}
echo "rn";
echo ' '."rn";
echo '';
echo "";
exit;
}
foreach($cat->orders() as $value)
{
$level = strlen(substr($value['sortlevel'],0,-3));
for($i = 0; $i < $level; $i++)
{
echo "-";
}
echo $value["sortname"];
echo "
";
}
?>
The above has introduced the use of PHP arrays to achieve unlimited classification without using a database or recursion, including aspects of the content. I hope it will be helpful to friends who are interested in PHP tutorials.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
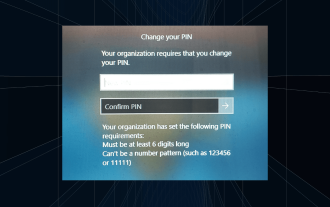 Solution: Your organization requires you to change your PIN
Oct 04, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
Solution: Your organization requires you to change your PIN
Oct 04, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
The message "Your organization has asked you to change your PIN" will appear on the login screen. This happens when the PIN expiration limit is reached on a computer using organization-based account settings, where they have control over personal devices. However, if you set up Windows using a personal account, the error message should ideally not appear. Although this is not always the case. Most users who encounter errors report using their personal accounts. Why does my organization ask me to change my PIN on Windows 11? It's possible that your account is associated with an organization, and your primary approach should be to verify this. Contacting your domain administrator can help! Additionally, misconfigured local policy settings or incorrect registry keys can cause errors. Right now
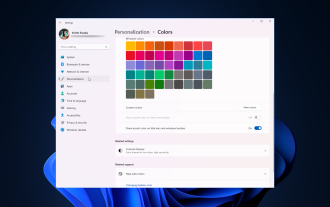 How to adjust window border settings on Windows 11: Change color and size
Sep 22, 2023 am 11:37 AM
How to adjust window border settings on Windows 11: Change color and size
Sep 22, 2023 am 11:37 AM
Windows 11 brings fresh and elegant design to the forefront; the modern interface allows you to personalize and change the finest details, such as window borders. In this guide, we'll discuss step-by-step instructions to help you create an environment that reflects your style in the Windows operating system. How to change window border settings? Press + to open the Settings app. WindowsI go to Personalization and click Color Settings. Color Change Window Borders Settings Window 11" Width="643" Height="500" > Find the Show accent color on title bar and window borders option, and toggle the switch next to it. To display accent colors on the Start menu and taskbar To display the theme color on the Start menu and taskbar, turn on Show theme on the Start menu and taskbar
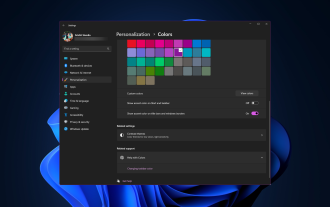 How to change title bar color on Windows 11?
Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:33 PM
How to change title bar color on Windows 11?
Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:33 PM
By default, the title bar color on Windows 11 depends on the dark/light theme you choose. However, you can change it to any color you want. In this guide, we'll discuss step-by-step instructions for three ways to change it and personalize your desktop experience to make it visually appealing. Is it possible to change the title bar color of active and inactive windows? Yes, you can change the title bar color of active windows using the Settings app, or you can change the title bar color of inactive windows using Registry Editor. To learn these steps, go to the next section. How to change title bar color in Windows 11? 1. Using the Settings app press + to open the settings window. WindowsI go to "Personalization" and then
 OOBELANGUAGE Error Problems in Windows 11/10 Repair
Jul 16, 2023 pm 03:29 PM
OOBELANGUAGE Error Problems in Windows 11/10 Repair
Jul 16, 2023 pm 03:29 PM
Do you see "A problem occurred" along with the "OOBELANGUAGE" statement on the Windows Installer page? The installation of Windows sometimes stops due to such errors. OOBE means out-of-the-box experience. As the error message indicates, this is an issue related to OOBE language selection. There is nothing to worry about, you can solve this problem with nifty registry editing from the OOBE screen itself. Quick Fix – 1. Click the “Retry” button at the bottom of the OOBE app. This will continue the process without further hiccups. 2. Use the power button to force shut down the system. After the system restarts, OOBE should continue. 3. Disconnect the system from the Internet. Complete all aspects of OOBE in offline mode
 How to enable or disable taskbar thumbnail previews on Windows 11
Sep 15, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
How to enable or disable taskbar thumbnail previews on Windows 11
Sep 15, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
Taskbar thumbnails can be fun, but they can also be distracting or annoying. Considering how often you hover over this area, you may have inadvertently closed important windows a few times. Another disadvantage is that it uses more system resources, so if you've been looking for a way to be more resource efficient, we'll show you how to disable it. However, if your hardware specs can handle it and you like the preview, you can enable it. How to enable taskbar thumbnail preview in Windows 11? 1. Using the Settings app tap the key and click Settings. Windows click System and select About. Click Advanced system settings. Navigate to the Advanced tab and select Settings under Performance. Select "Visual Effects"
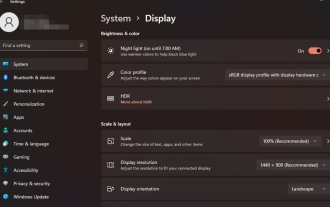 Display scaling guide on Windows 11
Sep 19, 2023 pm 06:45 PM
Display scaling guide on Windows 11
Sep 19, 2023 pm 06:45 PM
We all have different preferences when it comes to display scaling on Windows 11. Some people like big icons, some like small icons. However, we all agree that having the right scaling is important. Poor font scaling or over-scaling of images can be a real productivity killer when working, so you need to know how to customize it to get the most out of your system's capabilities. Advantages of Custom Zoom: This is a useful feature for people who have difficulty reading text on the screen. It helps you see more on the screen at one time. You can create custom extension profiles that apply only to certain monitors and applications. Can help improve the performance of low-end hardware. It gives you more control over what's on your screen. How to use Windows 11
 What are the differences between Huawei GT3 Pro and GT4?
Dec 29, 2023 pm 02:27 PM
What are the differences between Huawei GT3 Pro and GT4?
Dec 29, 2023 pm 02:27 PM
Many users will choose the Huawei brand when choosing smart watches. Among them, Huawei GT3pro and GT4 are very popular choices. Many users are curious about the difference between Huawei GT3pro and GT4. Let’s introduce the two to you. . What are the differences between Huawei GT3pro and GT4? 1. Appearance GT4: 46mm and 41mm, the material is glass mirror + stainless steel body + high-resolution fiber back shell. GT3pro: 46.6mm and 42.9mm, the material is sapphire glass + titanium body/ceramic body + ceramic back shell 2. Healthy GT4: Using the latest Huawei Truseen5.5+ algorithm, the results will be more accurate. GT3pro: Added ECG electrocardiogram and blood vessel and safety
 10 Ways to Adjust Brightness on Windows 11
Dec 18, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
10 Ways to Adjust Brightness on Windows 11
Dec 18, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
Screen brightness is an integral part of using modern computing devices, especially when you look at the screen for long periods of time. It helps you reduce eye strain, improve legibility, and view content easily and efficiently. However, depending on your settings, it can sometimes be difficult to manage brightness, especially on Windows 11 with the new UI changes. If you're having trouble adjusting brightness, here are all the ways to manage brightness on Windows 11. How to Change Brightness on Windows 11 [10 Ways Explained] Single monitor users can use the following methods to adjust brightness on Windows 11. This includes desktop systems using a single monitor as well as laptops. let's start. Method 1: Use the Action Center The Action Center is accessible



