NGINX study notes - passing request headers
Original address: https://www.nginx.com/resources/admin-guide/reverse-proxy/
Original title: Passing Request Headers
By default, NGINX will redefine two HTTP header fields, "Host" and "Connection" when proxying a request, and delete the header fields with empty values. "Host" will be set to the value of the $proxy_host variable, and "Connection" will be set to close.
By default, NGINX redefines two header fields in proxied requests, “Host” and “Connection”, and eliminates the header fields whose values are empty strings. “Host” is set to the $proxy_host variable, and “Connection” is set to close .
To change these settings, including modifying other header fields, use the proxy_set_header command. This directive can be used in location or higher. Can also be in a specific server context or in an http block, for example:
To change these setting, as well as modify other header fields, use the proxy_set_header directive. This directive can be specified in a location or higher. It can also be specified in a particular server context or in the http block. For example:
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
In this configuration, the "Host" field is set to the $host variable.
In this configuration the “Host” field is set to the $host variable. To prevent a header field from being passed to the proxied server, just set it to the empty string.
1 2 3 4 |
|
').addClass('pre-numbering').hide(); $(this).addClass('has-numbering').parent().append($numbering); for (i = 1; i ').text(i)); }; $numbering.fadeIn(1700); }); }); The above introduces the NGINX study notes - passing request headers, including aspects of the content. I hope it will be helpful to friends who are interested in PHP tutorials.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
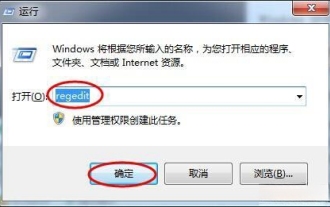 Windows 11 shutdown prompts task host window task host is executing the shutdown task solution
Feb 12, 2024 pm 12:40 PM
Windows 11 shutdown prompts task host window task host is executing the shutdown task solution
Feb 12, 2024 pm 12:40 PM
Recently, many Win11 users have reported that when shutting down, they are prompted that the taskhostwindow task host is executing the shutdown task. So what is going on? Users can enter the Desktop folder under the local registry editor, and then select AutoEndTasks in the right window to set it. Let this site carefully introduce to users the solution to this problem when shutting down. Windows 11 shutdown prompts that the taskhostwindow task host is executing the shutdown task. Solution 1. Use the key combination win key + r key, enter "regedit" and press Enter, as shown in the figure below. 2. Search for [HKEY
 How to check if aggregator host.exe is safe in Windows 11
Apr 13, 2023 pm 04:22 PM
How to check if aggregator host.exe is safe in Windows 11
Apr 13, 2023 pm 04:22 PM
When we launch Task Manager to terminate a task or stop an application, we usually find a large number of processes running. This is completely normal. However, sometimes we see programs that are using system resources that we are completely unaware of. One of these processes is the aggregator host.exe, which has been causing some confusion among users recently. Some of these processes may be legitimate Windows requirements, but others may be malicious programs running in the background and causing problems without the user's knowledge or consent. After we've seen the five ways you can launch Task Manager in Windows 11, we'll show you how to check if aggregator host.exe is safe or a virus. keep up
 Nginx Proxy Manager configuration analysis and optimization
Sep 26, 2023 am 09:24 AM
Nginx Proxy Manager configuration analysis and optimization
Sep 26, 2023 am 09:24 AM
Overview of NginxProxyManager configuration analysis and optimization: NginxProxyManager is a reverse proxy management tool based on Nginx, which can help us easily configure and manage reverse proxy servers. In the process of using NginxProxyManager, we can improve the performance and security of the server by parsing and optimizing its configuration. Configuration analysis: Configuration file location and structure: NginxProxyManag
 What is the difference between master and host
Sep 28, 2023 pm 01:34 PM
What is the difference between master and host
Sep 28, 2023 pm 01:34 PM
The differences between master and host are: 1. Host can play the role of client or server, while master is the central server responsible for coordinating and managing other slave servers in a distributed system; 2. Host is an ordinary computer device, and master usually has Higher processing power and resources are used to process and distribute tasks, manage data, and maintain the stability of the entire system; 3. The host is a node in the network, and the master is the server that plays a core role in the distributed system.
 What to do if no route to host
Oct 07, 2023 am 10:50 AM
What to do if no route to host
Oct 07, 2023 am 10:50 AM
The solutions to "no route to host" include checking the network connection, checking the IP address and port, checking the firewall configuration, checking the routing configuration, checking the network device configuration, checking the network service status, checking the network configuration and contacting the network administrator. Detailed introduction: 1. Check the network connection to ensure that the network connection between the client and the target host is normal. You can try to test network connectivity through the ping command or other network tools, and check whether hardware devices such as network cables, wireless networks, and routers are working properly. Make sure the network connection is stable, etc.
 Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Interpretation of MyBatis dynamic SQL tags: Detailed explanation of Set tag usage MyBatis is an excellent persistence layer framework. It provides a wealth of dynamic SQL tags and can flexibly construct database operation statements. Among them, the Set tag is used to generate the SET clause in the UPDATE statement, which is very commonly used in update operations. This article will explain in detail the usage of the Set tag in MyBatis and demonstrate its functionality through specific code examples. What is Set tag Set tag is used in MyBati
 How to configure and use proxy protocol in nginx
May 18, 2023 am 08:47 AM
How to configure and use proxy protocol in nginx
May 18, 2023 am 08:47 AM
When proxyprotocol is used in nginx, we know that nginx is a web server and proxy server. It generally works behind proxyserver or load balancing software (Haproxy, Amazon Elastic LoadBalancer (ELB)). The client first requests proxyserver or LSB load balancing software, and then to nginx Perform real web access. Because it has gone through multiple layers of software, some client information such as IP address, port number, etc. may be hidden, which is detrimental to our problem analysis and data statistics. Because for nginx, We want to be able to get real clients
 Deployment strategy of containers and microservices under Nginx Proxy Manager
Sep 27, 2023 pm 01:06 PM
Deployment strategy of containers and microservices under Nginx Proxy Manager
Sep 27, 2023 pm 01:06 PM
The deployment strategy of containers and microservices under NginxProxyManager requires specific code examples. Summary: With the popularity of microservice architecture, containerization technology has become an important part of modern software development. In the microservice architecture, NginxProxyManager plays a very important role, used to manage and proxy the traffic of microservices. This article will introduce how to use NginxProxyManager to deploy and manage containerized microservices, and provide relevant code examples.






