 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Python tutorial on how to use cookielib module to manipulate cookies
Python tutorial on how to use cookielib module to manipulate cookies
Python tutorial on how to use cookielib module to manipulate cookies
Cookielib is a module that automatically handles cookies. If we need to save cookies when using technologies such as crawlers, cookielib will allow you to get twice the result with half the effort! His most common partner modules are urllib and request under python.
Core classes
1.Cookie
This class implements the cookie standard defined by Netscape and RFC 2965 cookies, and can basically be understood as a certain piece of cookie data.
Part of the code is as follows. Do many attributes look familiar?
self.domain_initial_dot = domain_initial_dot
self.path = path
self.path_specified = path_specified
self.secure = secure
self.expires = expires
self.discard = discard
self.comment = comment
self.comment_url = comment_url
self.rfc2109 = rfc2109
2.CookiePolicy
The main function of this class is to send and receive cookies, that is, to ensure that the correct cookie is sent to the corresponding domain name, and vice versa.
3.DefaultCookiePolicy
This class implements the CookiePolicy interface.
4.CookieJar
CookieJar is a collection of cookies, which can contain many Cookie classes and is our main operation object. There are a series of methods to support more detailed operations!
5.FileCookieJar
This class inherits from CookieJar. CookieJar only completes its life cycle in memory. The subclass of FileCookieJar can achieve data persistence and defines three interfaces: save, load, and revert.
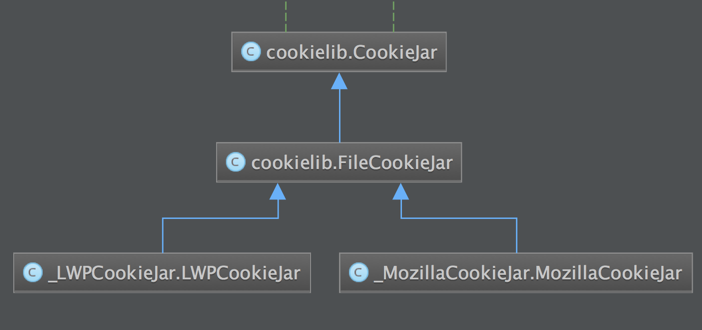
6.MozillaCookieJar & LWPCookieJar
Two implementation classes, the inheritance relationship is as follows:
Example: Log in to Renren
Use the httpFox plug-in under firefox to find out the POST address required when logging in to Renren.com is http://www.renren.com/ajaxLogin
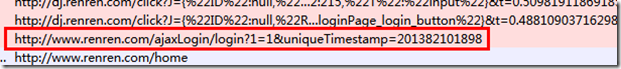
And I saw that the DATA required for POST includes email and password
python handles cookies through cookielib, the following is a simple code
>>> import urllib
>>> import urllib2,cookielib
>>> login_page = "http://www.renren.com/ajaxLogin"
>>> cj = cookielib.CookieJar()
>>> opener = urllib2.build_opener(urllib2.HTTPCookieProcessor(cj))
>>> opener.add_handler = [('User-agent','Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1)')]
>>> data = urllib.urlencode({"email":'username',"password":'password'})
>>> opener.open(login_page,data)
<addinfourl at 53653216 whose fp = <socket._fileobject object at 0x03307B70>>
>>> if cj:
... for index,cookie in enumerate(cj):
... print index,':',cookie
...
0 : <Cookie _de=90D533AE20EB964CA96710977F452897 for .renren.com/>
1 : <Cookie anonymid=hlehtdzg-8359yw for .renren.com/>
2 : <Cookie first_login_flag=1 for .renren.com/>
3 : <Cookie id=224967207 for .renren.com/>
4 : <Cookie loginfrom=null for .renren.com/>
5 : <Cookie p=9beb60859c004bcaf0a32ff2c973473d7 for .renren.com/>
6 : <Cookie societyguester=86b6a6006002ab6316f708521ab50bfc7 for .renren.com/>
7 : <Cookie t=86b6a6006002ab6316f708521ab50bfc7 for .renren.com/>
8 : <Cookie xnsid=fa53da51 for .renren.com/>
9 : <Cookie t=30af9ffe774f4d6f242e92da1ccd6670 for .renren.com/xtalk/>
10 : <Cookie feedType=224967207_hot for .www.renren.com/>
11 : <Cookie JSESSIONID=abc3IP9kEhTExblxcRfeu for www.renren.com/>
>>>
You can compare it with the cookie obtained in firebug or httpFox. The value may be inconsistent, but the key is basically the same. It should be inconsistent every time you log in
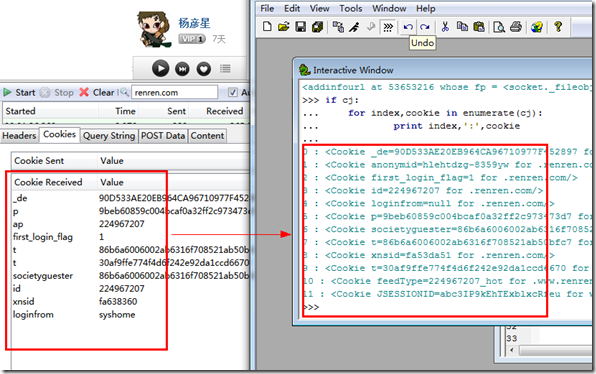
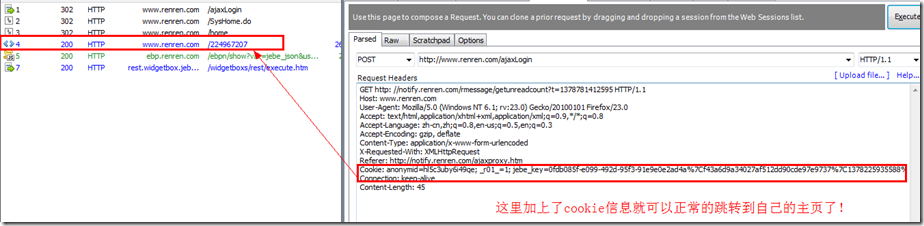
I also tried using fidder to simulate sending POST data without cookies, but I didn’t get the desired return value
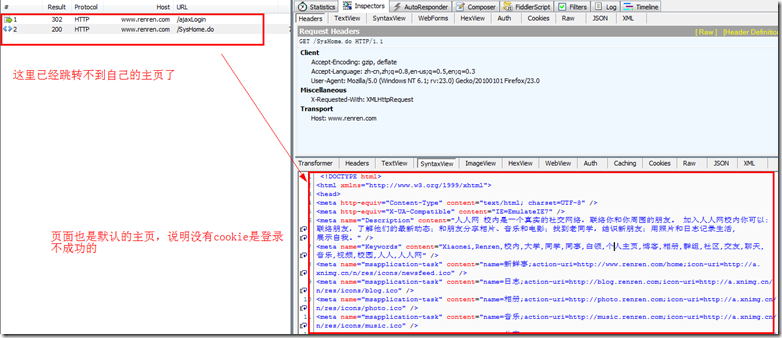
After adding the cookie information, you can jump to your homepage normally
Okay, we basically understand the use of cookies in python to send login information. Now let’s write a small script to log in to our Renren website.
#encoding=utf-8
import urllib2
import urllib
import cookielib
def renrenBrower(url,user,password):
login_page = "http://www.renren.com/ajaxLogin"
try:
cj = cookielib.CookieJar()
opener=urllib2.build_opener(urllib2.HTTPCookieProcessor(cj))
opener.addheaders = [('User-agent','Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1)')]
data = urllib.urlencode({"email":user,"password":password})
opener.open(login_page,data)
op=opener.open(url)
data= op.read()
return data
except Exception,e:
print str(e)
print renrenBrower("http://www.renren.com/home","用户名","密码")
In this way, you can display the information on your homepage. In fact, after logging in, you can continue to write scripts to get the information you want, such as friends’ latest news, etc. I won’t explain too much here~

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python is widely used in the fields of web development, data science, machine learning, automation and scripting. 1) In web development, Django and Flask frameworks simplify the development process. 2) In the fields of data science and machine learning, NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-learn and TensorFlow libraries provide strong support. 3) In terms of automation and scripting, Python is suitable for tasks such as automated testing and system management.
 The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
You can learn basic programming concepts and skills of Python within 2 hours. 1. Learn variables and data types, 2. Master control flow (conditional statements and loops), 3. Understand the definition and use of functions, 4. Quickly get started with Python programming through simple examples and code snippets.
 Navicat's method to view MongoDB database password
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:39 PM
Navicat's method to view MongoDB database password
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:39 PM
It is impossible to view MongoDB password directly through Navicat because it is stored as hash values. How to retrieve lost passwords: 1. Reset passwords; 2. Check configuration files (may contain hash values); 3. Check codes (may hardcode passwords).
 How to use AWS Glue crawler with Amazon Athena
Apr 09, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use AWS Glue crawler with Amazon Athena
Apr 09, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
As a data professional, you need to process large amounts of data from various sources. This can pose challenges to data management and analysis. Fortunately, two AWS services can help: AWS Glue and Amazon Athena.
 How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
The steps to start a Redis server include: Install Redis according to the operating system. Start the Redis service via redis-server (Linux/macOS) or redis-server.exe (Windows). Use the redis-cli ping (Linux/macOS) or redis-cli.exe ping (Windows) command to check the service status. Use a Redis client, such as redis-cli, Python, or Node.js, to access the server.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to view server version of Redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:27 PM
How to view server version of Redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:27 PM
Question: How to view the Redis server version? Use the command line tool redis-cli --version to view the version of the connected server. Use the INFO server command to view the server's internal version and need to parse and return information. In a cluster environment, check the version consistency of each node and can be automatically checked using scripts. Use scripts to automate viewing versions, such as connecting with Python scripts and printing version information.
 How secure is Navicat's password?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:24 PM
How secure is Navicat's password?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:24 PM
Navicat's password security relies on the combination of symmetric encryption, password strength and security measures. Specific measures include: using SSL connections (provided that the database server supports and correctly configures the certificate), regularly updating Navicat, using more secure methods (such as SSH tunnels), restricting access rights, and most importantly, never record passwords.



