
display is used to set the display mode of elements
display : block | none | inline | inline-block
inline: Specify the object as an inline element
block: Specify the object as a block element
inline-block: Specify the object as an inline block element
none: hidden objects
float Control whether the element is displayed as floating
float : none | left | right
none: Set the object not to float
left: Set the object to float on the left
right: Set the object to float on the right
Purpose of floating:
is to break the default display rules of document flow. If you want the elements to be displayed according to our layout requirements. At this time, you need to use the float attribute
clear clear float
clear : none | left | right | both
none: Default value. Allow floating objects on both sides
left: No floating objects are allowed on the left
right: No floating objects are allowed on the right
both: No floating objects allowed
position How the object is positioned
position : static | absolute | fixed | relative
static: Default value. Without positioning, objects follow normal flow. At this time, the 4 positioning offset attributes will not be applied
relative: Relative positioning, the object follows the regular flow, and will not affect any element in the regular flow when it is offset with reference to its position in the regular flow through the four positioning offset attributes of top, right, bottom, and left
absolute: Absolute positioning, the object breaks away from the regular flow. At this time, the offset attribute refers to the positioned ancestor element closest to itself. If there is no positioned ancestor element, it goes back to the body element. The offset position of the box does not affect any elements in the regular flow, and its margins are not collapsed with any other margins
fixed: fixed positioning, consistent with absolute, but the offset positioning is based on the window. When the scroll bar appears, the object will not scroll with it
absolute Description:
Example: div { position: absolute; left:100px; top:100px;}
relative Description:
Example: div { position: relative; left:100px; top:100px;}
fixed Description:
Fixed positioning is actually just a special form of absolute positioning. Fixed-positioned elements are fixed relative to the browser window, not relative to their containing elements. Even if the page is scrolled, they will still be in the browser window as before. Exactly the same place
Example: div { position: fixed; right:0; bottom:0;}
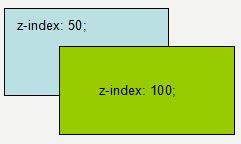
z-index Stacking order of objects
z-index : auto | number
When elements overlap, you can set the order of their stacking through the z-index attribute
Objects with larger number values will be overlaid on objects with smaller number values
 float usage in css
float usage in css
 What are the basic components of a computer?
What are the basic components of a computer?
 How to set the URL of tplink router
How to set the URL of tplink router
 What protocol is udp?
What protocol is udp?
 Summary of java basic knowledge
Summary of java basic knowledge
 Tutorial on turning off Windows 11 Security Center
Tutorial on turning off Windows 11 Security Center
 Three methods of gpu virtualization
Three methods of gpu virtualization
 How to solve the problem that suddenly all folders cannot be opened in win10
How to solve the problem that suddenly all folders cannot be opened in win10
 What is a browser plug-in
What is a browser plug-in




