js basic algorithm: bubble sort, binary search
Knowledge expansion:
Time complexity: The time complexity of an algorithm is a function that describes the running time of the algorithm. The lower the time complexity, the higher the efficiency.
Self-understanding: The time complexity of an algorithm will be determined by running it several times. If it is run n times, the time complexity will be O(n).
1. Bubble sort
Analysis: 1. Compare two adjacent elements. If the former one is larger than the latter one, swap positions.
2. In the first round, the last element should be the largest one.
3. Compare two adjacent elements according to step 1. At this time, since the last element is already the largest, there is no need to compare the last element.
function sort(elements){
for(var i=0;i<elements.length-1;i++){
for(var j=0;j<elements.length-i-1;j++){
if(elements[j]>elements[j+1]){
var swap=elements[j];
elements[j]=elements[j+1];
elements[j+1]=swap;
}
}
}
}
var elements = [3, 1, 5, 7, 2, 4, 9, 6, 10, 8];
console.log('before: ' + elements);
sort(elements);
console.log(' after: ' + elements);2. Quick sort
Analysis: Quick sort is an improvement on bubble sort. In the first sorting pass, the data is divided into two parts, one part is smaller than all the data in the other part. Then call it recursively, performing quick sort on both sides.
function quickSort(elements) {
if (elements.length <= 1) { return elements; }
var pivotIndex = Math.floor(elements.length / 2);
var pivot = elements.splice(pivotIndex, 1)[0];
var left = [];
var right = [];
for (var i = 0; i < elements.length; i++){
if (elements[i] < pivot) {
left.push(elements[i]);
} else {
right.push(elements[i]);
}
}
return quickSort(left).concat([pivot], quickSort(right));
};
var elements=[5,6,2,1,3,8,7,1.2,5.5,4.5];
alert(quickSort(elements));3. Insertion sort
Analysis:
(1) Starting from the first element, the element can be considered to have been sorted
(2) Take out the next element and proceed from backward in the sorted element sequence Front scan
(3) If the element (sorted) is greater than the new element, move the element to the next position
(4) Repeat step 3 until you find the position where the sorted element is less than or equal to the new element
(5) Insert the new element into the next position
(6) Repeat step 2
insertSort: function(elements) {
var i = 1,
j, step, key, len = elements.length;
for (; i < len; i++) {
step = j = i;
key = elements[j];
while (--j > -1) {
if (elements[j] > key) {
elements[j + 1] = elements[j];
} else {
break;
}
}
elements[j + 1] = key;
}
return elements;
}2. Binary search
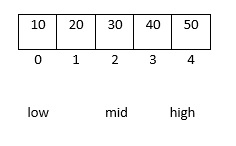
Analysis: Binary search, also a binary search. First, find a middle value. By comparing it with the middle value, the larger one is placed and the smaller one is placed on the left. Then find the middle value on both sides and continue the above operation until you find the location.
(1) Recursive method
function binarySearch(data,item,start,end){
var end=end || data.length-1;
var start=start || 0;
var m=Math.floor((start+end)/2);
if(item==data[m]){
return m;
}else if(item<data[m]){
return binarySearch(data,item,start,m-1) //递归调用
}else{
return binarySearch(data,item,m+1,end);
}
return false;
}
var arr=[34,12,5,123,2,745,32,4];
binary(arr,5);(2) Non-recursive method
function binarySearch(data, item){
var h = data.length - 1,
l = 0;
while(l <= h){
var m = Math.floor((h + l) / 2);
if(data[m] == item){
return m;
}
if(item > data[m]){
l = m + 1;
}else{
h = m - 1;
}
}
return false;
}
var arr=[34,12,5,123,2,745,32,4];
binarySearch(arr,5);
Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1371
1371
 52
52
 How to write a binary search algorithm using C#
Sep 19, 2023 pm 12:42 PM
How to write a binary search algorithm using C#
Sep 19, 2023 pm 12:42 PM
How to use C# to write a binary search algorithm. The binary search algorithm is an efficient search algorithm. It finds the position of a specific element in an ordered array with a time complexity of O(logN). In C#, we can write the binary search algorithm through the following steps. Step 1: Prepare data First, we need to prepare a sorted array as the target data for the search. Suppose we want to find the position of a specific element in an array. int[]data={1,3,5,7,9,11,13
 Binary search program written in C language, using pthread for multi-thread processing
Aug 26, 2023 pm 12:45 PM
Binary search program written in C language, using pthread for multi-thread processing
Aug 26, 2023 pm 12:45 PM
We know that the binary search method is the most suitable and effective sorting algorithm. This algorithm works on sorted sequences. The algorithm is simple, it just finds the element from the middle, then splits the list into two parts and moves to the left sublist or the right sublist. We know its algorithm. Now we will see how to use the binary search technique in a multi-threaded environment. The number of threads depends on the number of cores present in the system. Let's take a look at the code to get the idea. Example#include<iostream>#defineMAX16#defineMAX_THREAD4usingnamespacestd;//placearr,keyandothervariabl
 How to find the smallest element in an array using binary search algorithm in C language?
Aug 25, 2023 pm 08:37 PM
How to find the smallest element in an array using binary search algorithm in C language?
Aug 25, 2023 pm 08:37 PM
The C programming language provides two search techniques. They are as follows: Linear Search Binary Search Binary Search This method is only suitable for ordered lists. The given list is divided into two equal parts. The given key is compared to the middle element of the list. Here, three things can happen, as follows: If the middle element matches the keyword, the search will end successfully here. If the middle element is greater than the keyword, the search will take place in the left partition. If the middle element is smaller than the keyword, the search will be performed on the right partition. Input(i/p) - unsorted list of elements, keywords. Output (o/p)-success-if failure to find the keyword-otherwise key=20mid=(low+high)/2 Program 1 The following is the use of binary search in
 How to implement binary search algorithm using java
Sep 19, 2023 pm 12:57 PM
How to implement binary search algorithm using java
Sep 19, 2023 pm 12:57 PM
How to use Java to implement binary search algorithm Binary search algorithm is an efficient search method suitable for sorted arrays. Its basic idea is to continuously narrow the search range, compare the search value with the elements in the middle of the array, and decide whether to continue searching the left half or the right half based on the comparison result until the target element is found or the search range is reduced to empty. Below we will introduce in detail how to implement the binary search algorithm in Java. Step 1: Implement the binary search method publicclassBinarySearch
 How to implement binary search algorithm using Python?
Sep 20, 2023 pm 01:24 PM
How to implement binary search algorithm using Python?
Sep 20, 2023 pm 01:24 PM
How to implement binary search algorithm using Python? The binary search algorithm, also known as the binary search algorithm, is an efficient search algorithm. It works on ordered arrays or lists, narrowing down the search by comparing the target value to elements in the middle of the array. The following will introduce how to implement the binary search algorithm in Python and provide specific code examples. Algorithm idea: Compare the target value with the element in the middle of the array; if they are equal, return the element position; if the target value is greater than the element in the middle, then on the right
 Java program to find the cube root of a number using binary search algorithm
Aug 28, 2023 pm 01:33 PM
Java program to find the cube root of a number using binary search algorithm
Aug 28, 2023 pm 01:33 PM
A cube root is an integer value that, when multiplied by itself three times in a row, results in the original value. In this article, we will write a Java program that uses binary search to find the cube root of a number. Finding the cube root of a number is an application of the binary search algorithm. In this article, we will discuss in detail how to use binary search to calculate cube roots. Input-output example Example-1:Input:64Output:4 For example, the cube root of 64 is 4, and the output is 4. Example-2:Input:216Output:6 For example, the cube root of 216 is 6, and the output is 6. Binary Search Binary search is an algorithm used to find elements (i.e. keys in a sorted array). Binary Algorithm Working
 In C program, use binary search algorithm to search rational numbers without using floating point arithmetic
Aug 27, 2023 pm 06:05 PM
In C program, use binary search algorithm to search rational numbers without using floating point arithmetic
Aug 27, 2023 pm 06:05 PM
In this problem, we are given a sorted array of rational numbers. We have to use binary search algorithm to search for a given element of this array of rational numbers without using floating point operations. Rational numbers are numbers expressed in the form p/q, where p and q are both integers. For example, ⅔, ⅕. Binary search is a search technique that finds elements by looking in the middle of an array. Used to find elements in a sorted array of rational numbers using binary search, where floating point operations are not allowed. We will compare the numerator and denominator to find out which element is greater or which element is the one to be found. Example Let's create a program for this, #include<stdio.h>structRational{ &am
 PHP algorithm analysis: How to use binary search algorithm to quickly locate elements in an ordered array?
Sep 19, 2023 pm 01:14 PM
PHP algorithm analysis: How to use binary search algorithm to quickly locate elements in an ordered array?
Sep 19, 2023 pm 01:14 PM
PHP algorithm analysis: How to use binary search algorithm to quickly locate elements in an ordered array? Overview: The binary search algorithm is an efficient search algorithm that is suitable for finding specific elements in an ordered array. This article will introduce the principle of binary search algorithm in detail and give PHP code examples. Principle: The binary search algorithm quickly locates the target element by repeatedly reducing the search range by half. The process is as follows: first, narrow the search range to the beginning and end of the array; then, calculate the index of the middle element and compare it with the target element;




