 类库下载
类库下载
 java类库
java类库
 The difference between the four access modifiers in Java and the detailed explanation of the whole process
The difference between the four access modifiers in Java and the detailed explanation of the whole process
The difference between the four access modifiers in Java and the detailed explanation of the whole process
Client programmer: A class consumer who uses data types in his application. His goal is to collect various classes for rapid application development.
Class creator: A programmer who creates a new data type with the goal of building a class.
The reasons why access control exists: a. To prevent client programmers from touching parts they should not touch; b. To allow library designers to change the internal working methods of classes without worrying about affecting client programmers
java The four keywords: public, protected, default, private (they determine who can use what is defined immediately)
Scope of application
Access rights Class Package Subclass Other packages
∨ ∨ × × × (Package access rights, that is, available in the entire package Accessed)
ulate element that cannot be accessed by anyone except the type creator and the internal method of the type]
Test class)
package com.zq.demo.test1;
/**
* 类内
* @author Administrator
*/
public class Person {
public String uname = "王五";
public void introduceMyself(){
System.out.println(uname);
}
}
package com.zq.demo.test1;
//同一个包
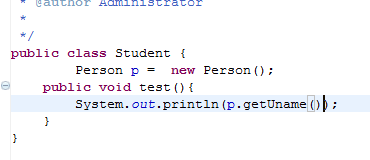
public class Student {
Person p = new Person();
public void test(){
System.out.println(p.uname);
}
}
package com.zq.demo.test1;
//子类
public class Teacher extends Person{
public int age;
Person p = new Person();
public void test1(){
System.out.println(p.uname);
}
}
package com.zq.demo.test2;
//不同包
import com.zq.demo.test1.Person;
public class Parents {
public String uname = "haha";
Person p = new Person();
public void test2(){
System.out.println(p.uname);
}
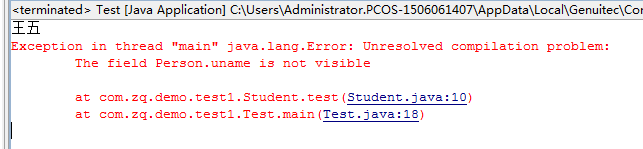
}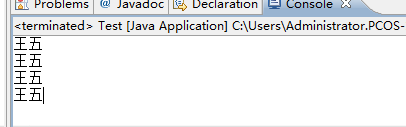 After changing the uanme in Person to protected, the class Parents reported an error The field Person .uname is not visible (indicating that it cannot be cross-packaged)
After changing the uanme in Person to protected, the class Parents reported an error The field Person .uname is not visible (indicating that it cannot be cross-packaged)
The other three have no impact
Explaining that except for cross-package, the others do not affect access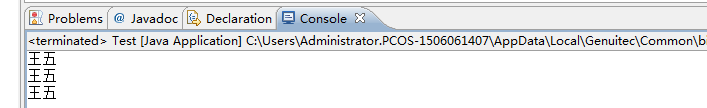 private
private


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)




