Initialization of one-bit array (two methods)
array type array name[]={value 1, value 2, value 3...value n};
array type array name[]=new data Type [constant value] //This method will assign the same default value to all array elements. For numerical types, the default value is also 0
1. Array traversal
Except for the for loop, it is relatively simple Is a for-each statement; Format: for (type Variable name: array) Type: any data type; Array: defined array name {statement}
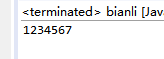
public class bianli {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int a[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
for( int i:a){
System.out.print(i);
}
}
}Ps : Direct traversal method
 Arrays.asList(a)//a is the target array to be traversed
Arrays.asList(a)//a is the target array to be traversed
import java.util.*;
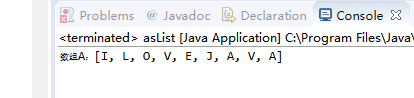
public class asList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String[] A={"I","L","O","V","E","J","A","V","A"};
System.out.println("数组A:"+Arrays.asList(A));
}
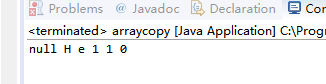
}public class arraycopy {
public static void main(String[] args){
String A[]={"H","e","1","1","0"};
String B[]=new String[6];
System.arraycopy(A, 0, B, 1, B.length-1);
for(int i=0;i<B.length;i++){
System.out.print(B[i]+" ");
}
}
} The result after running3: Filling Arrays.Fill(a,b) // a: target array name b: value to be filled
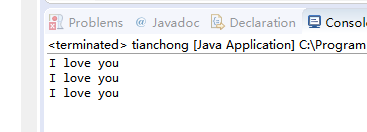
The result after running3: Filling Arrays.Fill(a,b) // a: target array name b: value to be filled import java.util.*;
public class tianchong {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String[] A=new String[3];
Arrays.fill(A, "I love you");
for(int i=0;i<A.length;i++){
System.out.println(A[i]+" ");
}
}
} After running: 4: equalArrays.equals(A,B) // Target array A and target array B
After running: 4: equalArrays.equals(A,B) // Target array A and target array Bimport java.util.Arrays;
public class xiangdeng {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String[] A={"a","b","c"};
String[] B={"A","B","C"};
String[] C={"a","b","c"};
System.out.println("数组A和B相等:"+Arrays.equals(A, B));
System.out.println("数组A和c相等:"+Arrays.equals(A, C));
}
} After running:
After running:




